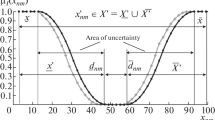
Abstract
The present paper covers the issue of training of an artificial neural network in an intelligent diagnostic system whose purpose is to evaluate repairable technical objects. The structure of the diagnostic system was characterized, and the measurement and diagnostic subsystems were described. An artificial neural network is an important element in an intelligent diagnostic subsystem. The structure, the algorithm, the organization of a neural network and the basic relations that describe its work were presented. The information presented in the form of the vectors of diagnostic signals, and their standard vectors constitute the primary information base used in “DIAG” computer program. Training of an artificial neural network is an important aspect that is presented in the paper. The issue concerning these problems is not presented in the literature. Training of a network was presented on the grounds of teaching vectors, which are determined in a diagnostic system in the process of a simulation of a specific state in the object examined. An example of training of a network was presented in a diagnostic system which evaluates a control system of the operation of a car engine. Appropriate connections were presented for the purpose of a qualitative assessment of the training process of a neural network.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Barlow RE, Proschan F (1995) Mathematical theory of reliability. Wiley, New York, p 335
Białko M (2000) Podstawowe właściwości sieci neuronowych i hybrydowych systemów ekspertowych. Wyd. Politechniki Koszalińskiej, Koszalin (in Polish)
Birolini A (1999) Reliability engineering theory and practice. Springer, New York 221
Duer S (2009) Artificial neural network-based technique for operation process control of a technical object. Def Sci J DESIDOC 59(3):305–313
Duer S (2010) Expert knowledge base to support the maintenance of a radar system. Def Sci J 60(5):531–540. http://publications.drdo.gov.in/ojs/index.php/dsj
Duer S, Duer R (2010) Diagnostic system with an artificial neural network which determines a diagnostic information for the servicing of a reparable technical object. Neural Comput Appl 19(5):755–766
Duer S (2010) Investigation of the operation process of a repairable technical object in an expert servicing system with an artificial neural network. Neural Comput Appl 19(5):767–774
Dhillon BS (2006) Applied reliability and quality, fundamentals, methods and procedures. Springer, London, p 186
Hojjat A, Shih Lh (1995) Machine learning, neural networks, genetic algorithms and fuzzy systems. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, p 398
Ito K, Nakagawa T (2000) Optimal inspection policies for a storage system with degradation at periodic tests. Math Comput Model 31:191–195
Gupta MadanM, Jin Liang, Homma Noriyasu (2003) Static and dynamic neural networks, from fundamentals to advanced theory. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, p 718
Mathirajan M, Chandru V, Sivakumar AI (2007) Heuristic algorithms for scheduling heat-treatment furnaces of steel casting industries. Sadahana 32(5):111–119
Nakagawa T (2005) Maintenance theory of reliability. Springer, London, p 264
Nakagawa T, Ito K (2000) Optimal inspection policies for a storage system with degradation at periodic tests. Math Comput Model 31:191–195
Nakagawa T (2002) Two-unit redundant models. In: Osaki S (ed) Stochastic models in reliability and maintenance. Springer, New York, pp 165–185
Tang L, Liu J, Rong A, Yang Z (2002) Modeling and genetic algorithm solution for the slab stack shuffling problem when implementing steel rolling schedules. Int J Prod Res 40(7):272–276
Teramoto T, Nakagawa T, Motoori M (1990) Optimal inspection policy for a parallel redundant system. Microelectron Reliab 30:151–155
Ushakov IA (1994) Handbook of reliability engineering. Wiley, New York
Wiliams JM, Zipser D (1989) A learning algorithm for continually running fully recurrent neural networks. Neural Comput 1:270–280
Zurada IM (1992) Introduction to artificial neural systems. West Publishing Company, St. Paul, MN, p 324
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duer, S., Zajkowski, K., Płocha, I. et al. Training of an artificial neural network in the diagnostic system of a technical object. Neural Comput & Applic 22, 1581–1590 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-012-1052-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-012-1052-9