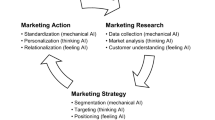
Abstract
This research proposes a radio frequency identification (RFID)-based intelligent shopping environment and its distributed reading capability to raise quality of service through improving the automation of product presentation, inventory monitor, billing procedures, manpower logistics, and customer lifetime value prediction. This research also uses RFID to successfully create a smart-shelf-enabled system as an advanced decision-making mechanism for managers. A case study based on a well-known fashion retailing company is used to demonstrate how the proposed system can significantly improve daily business operations. In addition, this research also used artificial neural network to predict the VIP member classification and customer retention rate. The experimental results figure out that the artificial intelligence approach would be outperformed the statistical and decision tree methods. Finally, a questionnaire was administered to 120 customers and investigated their degree of RFID usage willingness and purchase intention based on the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology model. The empirical results of our study present the easy-to-use and social influence factors that would be most influenced the customers’ usage willing and purchase intention with RFID technology.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
You I, Hara T (2010) Mobile and wireless networks. Mob Inf Syst 6(1):1–3
You I, Han YH, Chen YS, Chao HC (2011) Next generation mobility management. Wirel Commun Mob Comput 11:443–445
ABI Research (2009) RFID market to achieve 11% growth in 2009–2010 despite depressed economy. From http://www.abiresearch.com
IDTechEx (2010) RFID in 2010: the new dawn. Retrieved from http://www.idtechex.com/research/articles/rfid_in_2010_the_new_dawn_00002437.asp
O’Connor MC (2006) Boeing selects chipmaker for parts tags. RFID J. Retrieved from http://www.rfidjournal.com/article/articleview/2236/
Chen JV, Pfleuger P (2008) RFID in retail: a framework for examining consumers’ ethical perceptions. Int J Mobile Commun 6(1):53–66
Rekik Y, Sahin E, Dallery Y (2008) Analysis of the impact of the RFID technology on reducing product misplacement errors at retail stores. Int J Prod Econ 112:264–278
Ngai EWT, Suk FFC, Lo SYY (2008) Development of an RFID-based sushi management system: The case of a conveyor-belt sushi restaurant. Int J Prod Econ 112:630–645
Andersson P, Rosenqvist C, Ashrafi O (2007) Mobile innovations in healthcare: customer involvement and the co-creation of value. Int J Mobile Commun 5(4):371–388
Oztaysi B, Baysan S, Akpinar F (2009) Radio frequency identification (RFID) in hospitality. Technovation 29:618–624
Chen RS, Tu M (2009) Development of an agent-based system for manufacturing control and coordination with ontology and RFID technology. Expert Syst Appl 36:7581–7593
Trappey JC, Lu TH, Fu LD (2009) Development of an intelligent agent system for collaborative mold production with RFID technology. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 25:42–56
Fosso-Wamba S, Lefebvre LA, Bendavid Y, Lefebvre E (2007) Exploring the impact of RFID technology and the EPC network on mobile B2B e-Commerce. A case study in the retail industry. Int J Prod Econ 112(2):614–629
Bottani E, Rizzi A (2008) Economical assessment of the impact of RFID technology and EPC system on the fast-moving consumer goods supply chain. Int J Prod Econ 112:548–569
Ve’ronneau S, Roy J (2009) RFID benefits, costs, and possibilities: The economical analysis of RFID deployment in a cruise corporation global service supply chain. Int J Prod Econ 122:692–702
Hou JL, Chen TG (2011) An RFID-based shopping service system for retailers. Adv Eng Inform 25:103–115
Wong WK, Leung SYS, Guo ZX, Zeng XH, Mok PY (2012) Intelligent product cross-selling system with radio frequency identification technology for retailing. Int J Prod Econ 135:308–319
De Marco A, Cagliano AC, Nervo ML, Rafele C (2012) Using system dynamics to assess the impact of RFID technology on retail operations. Int J Prod Econ 135:333–344
McCarthy JF, Nguyen DH, Rashid AM, Soroczak S (2003) Proactive displays & the experience UbiComp project. Proceedings of the fifth international conference on ubiquitous computing, pp 78–81
Nogee A (2004) RFID tags and chip: changing the world for less than the price of a cup of coffee, In-Stat/MDR
Stockman H (1948) Communication by means of reflected power. Proc Inst Radio Eng 36(10):1196–1204
Asif Z, Mandviwalla M (2005) Integrating the supply chain with RFID. A technical and business analysis. Commun AIS 15(24):393–427
Becker J, Winkelmann A, Fuchs P (2009) IT in the consumer products industry. Value-add and future trends from the scientific perspective. In: Otto A, Schoppengerd FJ, Shariatmadari R (eds) Direct store delivery. Concepts, applications and instruments. Springer, Berlin, pp 161–173
Ngai EWT, Moon KKL, Riggins FJ, Yi CY (2008) RFID research: an academic literature review (1995–2005) and future research directions. Int J Prod Econ 112(2):507–515
Irani Z, Gunasekaran A, Dwivedi YK (2010) Radio frequency identification (RFID): research trends and framework. Int J Prod Res 48(9):2485–2511
Meer S, Jennings B (2004) Design principles for smart space management. Waterford institute of technology, Waterford
Vall’ee M, Ramparany F, Vercouter L (2005) Dynamic service composition in ambient intelligence environments: a multi-agent approach. In Proceeding of the first European young researcher workshop on service-oriented computing. Leicester, UK. Retrieved from http://www.cse.dmu.ac.uk/YRSOC/Programme.html
Rabbat M, Nowak R (2004) Distributed optimization in sensor networks. Proceedings of the 3rd international symposium on Information processing in sensor networks, Berkeley, pp 49–60
Chen YS, Hsu CS, Hsieh PT (2009) An efficient bow-based on-demand QoS routing protocol for MIMO ad hoc networks. Comput Commun 32(15):1613–1630
Chen YS, Lin YW, Pan CY (2011) DIR: diagonal-intersection-based routing protocol for vehicular ad hoc networks. Telecomm Syst 46(4):299–316
Ogiela MR, Ogiela U (2011) Secure information management protocol based on linguistic sharing techniques. Proceedings of the fifth international conference on innovative mobile and internet services in ubiquitous computing, pp 169–174
Temelkova S, Paunkoska N, Pavloski M, Atanasovski V, Gavrilovska L (2009) Sensors and RFID enabling smart space. 17th Telecommunications forum TELFOR 2009, Serbia, Belgrade, pp 1478–1481
Moon KL, Ngai EWT (2008) The adoption of RFID in fashion retailing: a business value-added framework. Ind Manag Data Syst 108(5):596–612
Harrop P, Das R, Holland G (2009) Apparel RFID 2009–2019. IDTechEx Ltd
Bajo J, Corchado JM, De Paz Y, De Paz JF, Rodríguez S, Martín Q, Abraham A (2009) SHOMAS: intelligent guidance and suggestions in shopping centres. Appl Soft Comput 9:851–862
Mohanty R, Ravi V, Patra MR (2010) Web-services classification using intelligent techniques. Expert Syst Appl 37(7):5484–5490
Coussement K, Benoit DF, Van den Poel D (2010) Improved marketing decision making in a customer churn prediction context using generalized additive models. Expert Syst Appl 37(3):2132–2143
Shim B, Choi K, Suh Y (2012) CRM strategies for a small-sized online shopping mall based on association rules and sequential patterns. Expert Syst Appl 39(9):7736–7742
Coussement K, Bock KW (2013) Customer churn prediction in the online gambling industry: the beneficial effect of ensemble learning. J Bus Res 66(9):1629–1636
Herbst J, Karagiannis D (2000) Integrating machine learning and workflow management to support acquisition and adaptation of workflow models. Int J Intell Syst Account Financ Manag 9:67–92
Hughes AM (1994) Strategic database marketing. Probus Publishing Company, Chicago
Davis FD (1986) A technology acceptance model for empirically testing new end-user information systems: theory and results. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Sloan School of Management, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA
Davis FD (1993) User acceptance of information technology: system characteristics, user perceptions and behavioral impacts. Int J Man Mach Stud 38:475–487
Venkatesh V, Morris MG, Davis GB, Davis FD (2003) User acceptance of information technology: toward a unified view. MIS Q 27(3):425–478
Hasan B, Ahmed MU (2007) Effects of interface style on user perceptions and behavioral intention to use computer systems. Comput Hum Behav 23(6):3025–3037
Maass W, Kowatsch T (2008) Adoption of dynamic product information: an empirical investigation of supporting purchase decisions on product bundles. Paper presented at the 16th European conference on information systems (ECIS)
Abushanab E, Pearson JM (2007) Internet banking in Jordan: the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT) perspective. J Syst Inf Technol 9(1):78–97
Eckhardt A, Laumer S, Weitzel T (2009) Who influences whom? Analyzing workplace referents’ social influence on its adoption and non-adoption. J Inf Technol 24(1):11–24
Wang YS, Wu MC, Wang HY (2009) Investigating the determinants and age and gender differences in the acceptance of mobile learning. Br J Educ Technol 40(1):92–118
Chen CC (2012) Identifying drivers for adoption intention in RFID service. Int J Mobile Commun 10(3):231–247
Acknowledgments
The author is grateful for the support of the National Scientific Council (NSC) of the Republic of China (ROC) under Grant No. NSC-100-2622-E-029-003-CC3 and NSC-100-2410-H-029-043. The author also gratefully acknowledges the Editor and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and constructive suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CC. RFID-based intelligent shopping environment: a comprehensive evaluation framework with neural computing approach. Neural Comput & Applic 25, 1685–1697 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1652-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1652-7