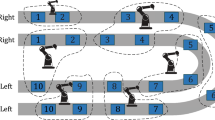
Abstract
Robots are employed in assembly lines to increase the productivity. The objective of robotic assembly line balancing (rALB) problem is to balance the assembly line, by allocating equal amount of tasks to the workstations on the line while assigning the most efficient robot to perform the assembly task at the workstation. In this paper, bio-inspired search algorithms, viz. particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm and a hybrid cuckoo search and particle swarm optimization (CS-PSO), are proposed to balance the robotic assembly line with the objective of minimizing the cycle time. The performance of the proposed PSO and hybrid CS-PSO is evaluated using the 32 benchmark problems available in the literature. The simulation results show that both PSO and hybrid CS-PSO are capable of providing solutions within the upper bound obtained by hybrid GA, the only metaheuristic reported so far for rALB in the literature and comparable to the solutions obtained by IBM CPLEX Optimization solver. It is also observed that hybrid CS-PSO is performing better than PSO in terms of cycle time.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Salveson ME (1955) The assembly line balancing problem. J Ind Eng 6(3):18–25
Kilincci O, Bayhan GM (2006) A Petri net approach for simple assembly line balancing problems. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 30(11–12):1165–1173
Baybars I (1986) A survey of exact algorithms for the simple assembly line balancing problem. Manage Sci 32(8):909–932
Rashid MFF, Hutabarat W, Tiwari A (2012) A review on assembly sequence planning and assembly line balancing optimisation using soft computing approaches. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 59(1–4):335–349
Scholl A, Scholl A (1999) Balancing and sequencing of assembly lines. Physica-Verlag, Heidelberg
Levitin G, Rubinovitz J, Shnits B (2006) A genetic algorithm for robotic assembly line balancing. Eur J Oper Res 168(3):811–825
Gao J, Sun L, Wang L, Gen M (2009) An efficient approach for type II robotic assembly line balancing problems. Comput Ind Eng 56(3):1065–1080
Graves SC, Lamar BW (1983) An integer programming procedure for assembly system design problems. Oper Res 31(3):522–545
Graves SC, Redfield CH (1988) Equipment selection and task assignment for multiproduct assembly system design. Int J Flex Manuf Syst 1(1):31–50
Gutjahr AL, Nemhauser GL (1964) An algorithm for the line balancing problem. Manage Sci 11(2):308–315
Pinto PA, Dannenbring DG, Khumawala BM (1981) Branch and bound and heuristic procedures for assembly line balancing with paralleling of stations. Int J Prod Res 19(5):565–576
Pinto PA, Dannenbring DG, Khumawala BM (1983) Assembly line balancing with processing alternatives: an application. Manage Sci 29(7):817–830
Nicosia G, Pacciarelli D, Pacifici A (2002) Optimally balancing assembly lines with different workstations. Discrete Appl Math 118(1):99–113
Rubinovitz J, Bukchin J, Lenz E (1993) RALB–A heuristic algorithm for design and balancing of robotic assembly lines. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 42(1):497–500
Bukchin J, Tzur M (2000) Design of flexible assembly line to minimize equipment cost. IIE Trans 32(7):585–598
Tsai D-M, Yao M-J (1993) A line-balance-based capacity planning procedure for series-type robotic assembly line. Int J Prod Res 31(8):1901–1920
Kim H, Park S (1995) A strong cutting plane algorithm for the robotic assembly line balancing problem. Int J Prod Res 33(8):2311–2323
Yoosefelahi A, Aminnayeri M, Mosadegh H, Ardakani HD (2012) Type II robotic assembly line balancing problem: an evolution strategies algorithm for a multi-objective model. J Manuf Syst 31(2):139–151
Daoud S, Chehade H, Yalaoui F, Amodeo L (2014) Solving a robotic assembly line balancing problem using efficient hybrid methods. J Heuristics 20(3):235–259
Scholl A, Becker C (2006) State-of-the-art exact and heuristic solution procedures for simple assembly line balancing. Eur J Oper Res 168(3):666–693
Sörensen K, Glover FW (2013) Metaheuristics. In: Gass S, Fu M (eds) Encyclopedia of operations research and management science. Springer, New York, pp 960–970
Yang X-S, Deb S (2014) Cuckoo search: recent advances and applications. Neural Comput Appl 24(1):169–174
Atasagun Y, Kara Y (2013) Bacterial foraging optimization algorithm for assembly line balancing. Neural Comput Appl 25(1):237–250
Sivasankaran P, Shahabudeen P (2014) Literature review of assembly line balancing problems. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73(9–12):1665–1694
Ghodrati A, Lotfi S (2012) A hybrid CS/PSO algorithm for global optimization. In: Pan J-S, Chen S-M, Nguyen N (eds) Intelligent information and database systems. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 89–98
Noroozi A, Mokhtari H, Kamal Abadi IN (2013) Research on computational intelligence algorithms with adaptive learning approach for scheduling problems with batch processing machines. Neurocomputing 101:190–203
Mukund Nilakantan J, Ponnambalam S (2012) An efficient PSO for type II robotic assembly line balancing problem. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on automation science and engineering (CASE), pp 600–605
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on neural networks, pp 1942–1948
Del Valle Y, Venayagamoorthy GK, Mohagheghi S, Hernandez J-C, Harley RG (2008) Particle swarm optimization: basic concepts, variants and applications in power systems. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 12(2):171–195
Hu X (2006) PSO tutorial http://www.swarmintelligence.org/tutorials.php
Huang K-W, Chen J-L, Yang C-S, Tsai C-W (2014) A memetic particle swarm optimization algorithm for solving the DNA fragment assembly problem. Neural Comput Appl 1–12. doi:10.1007/s00521-014-1659-0
Ponnambalam S, Aravindan P, Naidu GM (2000) A multi-objective genetic algorithm for solving assembly line balancing problem. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 16(5):341–352
Yang X-S, Deb S (2009) Cuckoo search via Lévy flights. Proc World Congr Nat Biol Inspired Comput NaBIC 2009:210–214
Burnwal S, Deb S (2013) Scheduling optimization of flexible manufacturing system using cuckoo search-based approach. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 64(5–8):951–959
Long W, Liang X, Huang Y, Chen Y (2014) An effective hybrid cuckoo search algorithm for constrained global optimization. Neural Comput Appl 25(3–4):911–926
Davis L (1985) Applying adaptive algorithms to epistatic domains. In: Proceedings of IJCAI, pp 162–164
Rubinovitz J, Levitin G (1995) Genetic algorithm for assembly line balancing. Int J Prod Econ 41(1):343–354
Valian E, Mohanna S, Tavakoli S (2011) Improved cuckoo search algorithm for global optimization. Int J Commun Inf Technol 1(1):31–44
Scholl A (1995) Data of assembly line balancing problems. Darmstadt Technical University, Department of Business Administration, Economics and Law, Institute for Business Studies (BWL)
Gunther RE, Johnson GD, Peterson RS (1983) Currently practiced formulations for the assembly line balance problem. J Oper Manag 3(4):209–221
Holm S (1979) A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand J Stat 6:65–70
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukund Nilakantan, J., Ponnambalam, S.G., Jawahar, N. et al. Bio-inspired search algorithms to solve robotic assembly line balancing problems. Neural Comput & Applic 26, 1379–1393 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1811-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1811-x