Abstract
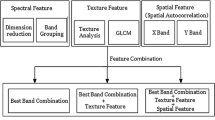
Most studies have been based on the original computation mode of semivariogram and discrete semivariance values. In this paper, a set of texture features are described to improve the accuracy of object-oriented classification in remotely sensed images. So, we proposed a classification method support vector machine (SVM) with spectral information and texture features (ST-SVM), which incorporates texture features in remotely sensed images into SVM. Using kernel methods, the spectral information and texture features are jointly used for the classification by a SVM formulation. Then, the texture features were calculated based on segmented block matrix image objects using the panchromatic band. A comparison of classification results on real-world data sets demonstrates that the texture features in this paper are useful supplement information for the spectral object-oriented classification, and proposed ST-SVM classification accuracy than the traditional SVM method with only spectral information.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Murray H, Lucieer A, Williams R (2010) Texture-based classification of sub-antarctic vegetation communities on Heard Island. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 12:138–187
Yan H, Anzhi Y, Su W, Daoliang L, Ming L, Yijun J, Chao Z (2008) Texture feature extraction for land-cover classification of remote sensing data in land consolidation district using semi-variogram analysis. WSEAS Trans Comput 7:857–923
Farrokhnia F, Jain AK (1991) A multi-channel filtering approach to texture segmentation. In: Proceedings of IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE Computer Society Press, Maui, pp 364–434
Fogel I, Sagi D (1989) Gabor filters as texture discriminator. Biol Cybern 61:103–116
Manjunath BS, Ma WY (1996) Texture features for browsing and retrieval of image data. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 18:837–879
Tuceryan M, Jain AK (1998) Texture analysis. In: Chen CH, Pau LF, Wagn PSP (eds) Handbook of pattern recognition and computer vision. World Scientific Publishing Company, Hackensack, pp 207–255
Tuceryan M, Ahuja N (1990) Extraction of early perceptual structure in dot patterns: integrating region, boundary, and component gestalt. Comput Vis Graph Image Process 49:279–359
Cesmeli E, Wang DL (2001) Texture segmentation using Gaussian-Markov random fields and neural oscillator networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 12:394–404
Chaudhuri BB, Sarkar N (1995) Texture segmentation using fractal dimension. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 17:72–79
Maillard P (2003) Comparing texture analysis methods through classification. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 69:357–424
Su W, Zhang C, Yang J, Wu H, Deng L, Yue A, Chen M (2012) Analysis of wavelet packet and statistical textures for object oriented classification of forest-agriculture ecotones using SPOT 5 imagery. Int J Remote Sens 33:3557–3636
Atkinson PM, Lewis P (2000) Geostatistical classification for remote sensing: an introduction. Comput Geosci 26:361–432
Chica-Olmo M, Abarca-Hernandez F (2000) Computing geostatistical image texture for remotely sensed data classification. Comput Geosci 26:373–456
Miranda FP, Fonseca LEN, Carr JR (1998) Semivariogram textural classification of JERS-1 (Fuyo-1) SAR data obtained over a flooded area of the amazon rainforest. Int J Remote Sens 19:549–605
Yue A, Zhang C, Yang J, Su W, Yun W, Zhu D (2013) Texture extraction for object-oriented classification of high spatial resolution remotely sensed images using a semivariogram. Int J Remote Sens 34(11):3736–3759. doi:10.1080/01431161.2012.759298
Ohanian PP, Dubes RC (1992) Perfor mance evaluation for four classes of textural features. Pattern Recognit 25:819–852
Lloyd CD, Berberoglu S, Curran PJ, Atkinson PM (2004) A comparison of texture measures for the per-field classification of mediterranean land cover. Int J Remote Sens 25:3943–4008
Su W, Li J, Chen YH, Liu ZG, Zhang JS, Low TM, Suppiah I, Hashim SAM (2008) Textural and local spatial statistics for the object-oriented classification of urban areas using high resolution imagery. Int J Remote Sens 29:3105–3122
Cortes C, Vapnik VN (1995) Support vector networks. Mach Learn 20:273–297
Vapnik VN (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Vapnik VN (1999) An overview of statistical learning theory. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10:988–999
Varshney PK, Arora MK (2004) Advanced image processing techniques for remotely sensed hyperspectral data. Springer, Berlin
Osuna E, Freund R, Girosi F (1997) Training support vector machines: an application to face detection. In: Proceedings of computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 130–136
Deniz O, Castrillon M, Hernandez M (2003) Face recognition using independent component analysis and support vector machines. Pattern Recognit Lett 24(13):2153–2157
Chapelle O, Haffner P, Vapnik VN (1999) Support vector machines for histogram-based image classification. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10(5):1055–1064
Guo G, Li S (2003) Content-based audio classification and retrieval by support vector machines. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 14(1):209–215
Mukherjee S, Osuna E, Girosi F (1997) Nonlinear prediction of chaotic time series using support vector machines. In: Proceedings of the IEEE workshop on neural networks for signal processing, Amelia Island, pp 511–520
Zhu G, Blumberg DG (2002) Classification using ASTER data and SVM algorithms: the case study of Beer Sheva, Israel. Remote Sens Environ 80(2):233–240
Nemmour H, Chibani Y (2006) Multiple support vector machines for land cover change detection: an application for mapping urban extensions. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 61(2):125–133
Melgani F, Bruzzone L (2004) Classification of hyperspectral remote sensing images with support vector machines. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 42(8):1778–1790
Pal M, Mather PM (2005) Support vector machines for classification in remote sensing. Int J Remote Sens 26(5):1007–1011
Inglada J (2007) Automatic recognition of man-made objects in high resolution optical remote sensing images by SVM classification of geometric image features. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 62(3):236–248
Gao J, Fan L (2011) Kernel-based weighted discriminant analysis with QR decomposition and its application face recognition. WSEAS Trans Math 10(10):358–367
Gao J, Li L, Fan L, Xu L (2013) An application of weighted kernel fuzzy discriminant analysis. Adv Comput Math Appl 2(4):329–338
Gao J, Fan L, Li L, Xu L (2013) A practical application of kernel-based fuzzy discriminant analysis. Int J Appl Math Comput Sci 23(4):887–903
Camps-Valls G, Bruzzone L (2005) Kernel-based methods for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 43(6):1351–1362
Fauvel M, Chanussot J, Benediktsson JA (2012) A spatial–spectral kernel-based approach for the classification of remote-sensing images. Pattern Recognit 45(1):381–392
Fauvel M et al (2013) Advances in spectral–spatial classification of hyperspectral images. Proc IEEE 101(3):652–675
Guo B, Gunn S, Damper R, Nelson J (2008) Customizing kernel functions for SVM-based hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Image Process 17(4):622–629
Camps-Valls G, Gomez-Chova L, Munoz-Mari J, Vila-Frances J, Calpe-Maravilla J (2006) Composite kernels for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 3(1):93–97
Mercier G, Girard-Ardhuin F (2006) Partially supervised oil-slick detection by SAR imagery using kernel expansion. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 44(10):2839–2846
Gao J, Xu L, Shi A, Huang F (2014) A kernel-based block matrix decomposition approach for the classification of remotely sensed images. Appl Math Comput 228:531–545
Song B, Li J, Mura MD, Li P, Plaza A, Bioucas-Dias JM, Benediktsson JA, Chanussot J (2013) Remotely sensed image classification using sparse representations of morphological attribute profiles. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. doi:10.1109/TGRS.2013.2286953
Chen Y, Nasrabadi N, Tran T (2011) Hyperspectral image classification using dictionary-based sparse representation. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 49(10):3973–3985
Plaza A, Benediktsson JA, Boardman JW et al (2009) Recent advances in techniques for hyperspectral image processing. Remote Sens Environ 113:S110–S122
Cover TM (1965) Geometrical and statistical properties of systems of linear inequalities with application in pattern recognition. IEEE Trans Electron Comput 14(3):326–334
Schölkopf B, Smola A (2002) Learning with kernels-support vector machines, regularization, optimization and beyond. MIT Press, Cambridge
Zhang R, Ma J (2008) An improved SVM method P-SVM for classification of remotely sensed data. Int J Remote Sens 29(20):6029–6036
Ulaby FT, Kouyate F, Brisco B et al (1986) Textural infornation in SAR images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 24(2):235–245
Haralick RM, Shanmugam K, Dinstein IH (1973) Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 3(6):610–621
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2001) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machine. http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/cjlin/libsvm
IEEE, GRSS data fusion technical committee (2012). http://www.grss-ieee.org/community/technical-committees/datafusion/
Park CH, Park H (2008) A comparison of generalized linear discriminant analysis algorithms. Pattern Recognit 41:1083–1097
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to the editor and anonymous referees reviews for their valuable comments and helpful suggestions. In addition, this work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61271386), and the Graduates’ Research Innovation Program of Higher Education of Jiangsu Province of China (Grant No. CXZZ13-0239).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, J., Xu, L. & Huang, F. A spectral–textural kernel-based classification method of remotely sensed images. Neural Comput & Applic 27, 431–446 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1862-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1862-7