Abstract
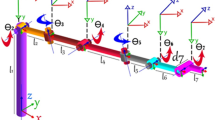
In this study, a 4-degree-of-freedom (DOF) serial robot manipulator was designed and developed for the pick-and-place operation of a flexible manufacturing system. The solution of the inverse kinematics equation, one of the most important parts of the control process of the manipulator, was obtained by using four different optimization algorithms: the genetic algorithm (GA), the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm, the quantum particle swarm optimization (QPSO) algorithm and the gravitational search algorithm (GSA). These algorithms were tested with two different scenarios for the motion of the manipulator’s end-effector. One hundred randomly selected workspace points were defined for the first scenario, while a spline trajectory, also composed of one hundred workspace points, was used for the second. The optimization algorithms were used for solving of the inverse kinematics of the manipulator in order to successfully move the end-effector to these workspace points. The four algorithms were compared according to the execution time, the end-effector position error and the required number of generations. The results showed that the QPSO could be effectively used for the inverse kinematics solution of the developed manipulator.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Koker R, Oz C, Cakar T, Ekiz H (2004) A study of neural network based inverse kinematics solution for a three-joint robot. Rob Auton Syst 49:227–234
Bingul Z, Ertunc HM, Oysu C (2005) Comparison of inverse kinematics solutions using neural network for 6R robot manipulator with offset. ICSC congress on computational intelligence methods and applications. Istanbul, Turkey, pp 1–5
Huang HC, Chen CP, Wang PR (2012) Particle swarm optimization for solving the inverse kinematics of 7-DOF robotic manipulators. IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics. Seoul, Korea, pp 3105–3110
Rubio JJ, Bravo AG, Pacheco J, Aguilar C (2014) Passivity analysis and modeling of robotic arms. IEEE Lat Am Trans 12(8):1381–1389
Kou YL, Lin TP, Wu CY (2014) Experimental and numerical study on the semi-closed loop control of a planar robot manipulator. Math Probl Eng 2014:1–9. doi:10.1155/2014/769038
Kucuk S, Bingul Z (2004) The inverse kinematics solutions of industrial robot manipulators. In: IEEE international conference on mechatronics, pp 274–279
Gan JQ, Oyama E, Rosales EM, Hu H (2005) A complete analytical solution to the inverse kinematics of the pioneer 2 robotic arm. Robotica 23:123–129
Wang P, Li D, Zhang D, Liu K, Ni X (2007) Practical algorithm for solving real time inverse kinematics of industrial 7R robot. In: IEEE international conference on automation and logistics, pp 1963–1967
Xie J, Qiang W, Liang B, Li C (2007) Inverse kinematics problem for 6‐DOF space manipulator based on the theory of screw. In: International conference on robotics and biomimetics, pp 1659–1663
Sariyildiz E, Temeltas H (2009) Solution of inverse kinematics problem for serial robot using dual quaterninons and Plucker coordinates. In: IEEE/ASME international conference on advanced intelligent mechatronics, pp 338–343
Karpinska J, Tchon K, Janiak M (2012) Approximation of Jacobian inverse kinematics algorithms: differential geometric vs. variational approach. J Intell Robot Syst 68:211–224
Rubio JJ, Aquino V, Figueroa M (2013) Inverse kinematics of a mobile robot. Neural Comput Appl 23(1):187–194
Kucuk S, Bingul Z (2014) Inverse kinematics solutions for industrial robot manipulators with offset wrists. Appl Math Model 38:1983–1999
Veslin EY, Dutra MS, Lengerke O, Carreño EA (2014) A hybrid solution for the inverse kinematic on a seven DOF robotic manipulator. IEEE Lat Am Trans 12(2):212–218
Holland JH (1992) Genetic algorithms. Sci Am 267:66–72
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: IEEE international conference on neural networks, pp 1943–1948
Storn R, Price K (1997) Differential evolution-a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J Global Optim 11:341–359
Geem ZW, Kim JH, Loganathan GV (2001) A new heuristic optimization algorithm: harmony search. Simulation 76(2):60–68
Aarts EHL, Laarhoven PJM (1989) Simulated annealing: an introduction. Stat Neerl 43:31–52
Dorigo M, Birattari M, Stutzle T (2006) Ant colony optimization. IEEE Comput Intell Mag 1:28–39
Simon D (2008) Biogeography-based optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 12:702–713
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Let a biogeography-based optimizer train your multi-layer perceptron. Inf Sci 269:188–209. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2014.01.038
Saremi S, Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2014) Biogeography-based optimisation with chaos. Neural Comput Appl 25(5):1077–1097
Saremi S, Mirjalili S (2013) Integrating chaos to biogeography-based optimization algorithm. Int J Comput Commun Eng 2:655–658
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Grey wolf optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61
Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-Pour H, Saryazdi S (2009) GSA: a gravitational search algorithm. Inf Sci 179:2232–2248
Gandomi AH, Alavi AH (2012) Krill herd: a new bio-inspired optimization algorithm. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 17:4831–4845
Guo L, Wang G-G, Gandomi AH, Alavi AH, Duan H (2014) A new improved krill herd algorithm for global numerical optimization. Neurocomputing 138:392–402
Wang G-G, Gandomi AH, Alavi AH (2013) An effective krill herd algorithm with migration operator in biogeography-based optimization. Appl Math Model 38(9–10):2454–2462
Wang G-G, Gandomi AH, Alavi AH (2014) Stud krill herd algorithm. Neurocomputing 128:363–370
Wang G-G, Guo L, Gandomi AH, Hao G-S, Wang H (2014) Chaotic krill herd algorithm. Inf Sci 274:17–34
Wang G, Guo L, Wang H, Duan H, Liu L, Li J (2014) Incorporating mutation scheme into krill herd algorithm for global numerical optimization. Neural Comput Appl 24:583–871
Saremi S, Mirjalili SM, Mirjalili S (2014) Chaotic krill herd optimization algorithm. Procedia Technol 12(2014):180–185
Chyan GS, Ponnambalam SG (2012) Obstacle avoidance control of redundant robots using variants of particle swarm optimization. Robot Cim Int Manuf 28(2):147–153
Huapeng W, Handroos H (2000) Inverse kinematics analysis of a parallel redundant manipulator by means of differential evolution. In: International conference on machine automation, pp 321–326
Zi-wu R, Zhen-hua W, Li-ning S (2012) A global harmony search algorithm and its application to inverse kinematics problem for humanoid arm. Control Theor Appl 29(7):867–876
He G, Hongming G, Zhang G, Wu L (2006) Using adaptive genetic algorithm to the placement of serial robot manipulator serial robot manipulator. In: IEEE international conference on engineering of intelligent systems, pp 1–6
Guan-Zheng T, Huan H, Aaron S (2007) Ant colony system algorithm for real-time globally optimal path planning of mobile robots. Acta Autom Sin 33(3):279–285
Mon H, Xu L (2015) Research of biogeography particle swarm optimization for robot path planning. Neurocomputing 148:91–99
Savsani P, Jhala RL, Savsani VJ (2014) Comparative study of different metaheuristics for the trajectory planning of a robotic arm. IEEE Syst J 2014:1–12. doi:10.1109/JSYST.2014.2342292
Jordehi AR (2015) Enhanced leader PSO (ELPSO): a new PSO variant for solving global optimisation problems. Appl Soft Comput 26:401–417
Toz M, Erdogmus P, Sahin I (2011) A new educational toolbox for solving robotic optimization problems using GA and PSO. E-J New World S Acad 6:1630–1644
Ayyildiz M, Cetinkaya K (2014) Inverse kinematics solution of a 4-DOF real serial robot manipulator using QPSO. In: The first international symposium on industrial design engineering, pp 1–5
Eberhart R, Kennedy J (1999) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: The sixth international symposium on micro machine and human science, pp 39–43
Craig JJ (2005) Introduction to robotics mechanics and control, 3rd edn. Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning. Addison-Wesley, USA
Jang JSR (1997) Neuro-fuzzy and soft computing: a computational approach to learning and machine intelligence. Chapter 7: derivative-free optimization. Prentice-Hall, USA
Jamalipour M, Gharib M, Sayareh R, Khoshahval F (2013) PWR power distribution flattening using Quantum Particle Swarm intelligence. Ann Nucl Energy 56:143–150
Sun J, Xu W, Feng B (2005) Adaptive parameter control for quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization on individual level. In: IEEE international conference on systems, man and cybernetics, pp 1–6
Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-pour H, Saryazdi S (2009) GSA: a gravitational search algorithm. Inf Sci 179:2232–2248
Kazak N (2011) Developed gravitational search algorithm, Bilecik University institute of science and technology, Master’s thesis
Rubio JJ (2014) Stable and optimal controls of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Int J Control 87(11):2338–2347
Shen H, Park JH, Zang L, Wu Z (2014) Robust extended dissipative control for sampled-data Markov jump systems. Int J Control 87(8):1549–1564
Wilcoxon F (1945) Individual comparisons by ranking methods. Biom Bull 1:80–83
Derrac J, García S, Molina D, Herrera F (2011) A practical tutorial on the use of nonparametric statistical tests as a methodology for comparing evolutionary and swarm intelligence algorithms. Swarm Evol Comput 1(1):3–18
García S, Molina D, Lozano M, Herrera F (2009) A study on the use of non-parametric tests for analyzing the evolutionary algorithms’ behaviour: a case study on the CEC’2005 special session on real parameter optimization. J Heuristics 15:617–644
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2013) S-shaped versus V-shaped transfer functions for binary particle swarm optimization. Swarm Evol Comput 9:1–14
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Karabük University Research Project Directorate, Project No.KBÜ-BAP-11-2-DR-001, for their financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayyıldız, M., Çetinkaya, K. Comparison of four different heuristic optimization algorithms for the inverse kinematics solution of a real 4-DOF serial robot manipulator. Neural Comput & Applic 27, 825–836 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1898-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1898-8