Abstract
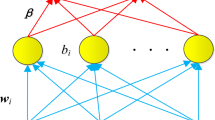
By incorporating prior knowledge in the form of implications into extreme learning machine (ELM), a novel knowledge-based extreme learning machine (KBELM) formulation is proposed in this work. In this approach, the nonlinear prior knowledge implications are converted into linear inequalities and are then included as linear equality constraints in the ELM formulation. The proposed KBELM formulation has the advantage that it leads to solving a system of linear equations. Effectiveness of the proposed approach is demonstrated on three synthetic and the publicly available Wisconsin Prognostic Breast Cancer datasets by comparing their results with ELM and optimally pruned ELM using additive and radial basis function hidden nodes.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Balasundaram S, Gupta D, Kapil (2014) 1-Norm extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification using Newton method. Neurocomputing 128:4–14
Balasundaram S, Kapil (2011) Application of error minimized extreme learning machine for simultaneous learning of a function and its derivatives, Neurocomputing 74:2511–2519
Chen Z, Zhu H, Wang Y (2013) A modified extreme learning machine with sigmoidal activation functions. Neural Comput Appl 22:541–550
Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J (2000) An Introduction to support vector machines and other kernel based learning methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Feng G, Huang G-B, Lin Q, Gay R (2009) Error minimized extreme learning machine with growth of hidden nodes and incremental learning. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 20:1352–1357
Fung G, Mangasarian OL (2001) Proximal support vector machine classifiers. In: Proceedings of the international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, San Francisco, CA, pp 77–86
Fung G, Mangasarian OL, Shavlik J (2002) Knowledge-based support vector machine classifiers. In: Becker Suzanna, Thrun Sebastian, Obermayer Klaus (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems, vol 15. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 521–528
Fung G, Mangasarian OL, Shavlik J (2002) Knowledge-based nonlinear kernel classifiers. In: Warmuth M, Scholkopf LB (eds) Conference on learning theory (COLT 03) and workshop on kernel machines. Springer, Berlin, pp 102–113
Huang G-B, Chen L (2007) Convex incremental extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 70:3056–3062
Huang G-B, Chen L (2008) Enhanced random search based incremental extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 71:3460–3468
Huang G-B, Chen L, Siew C-K (2006) Universal approximation using incremental constructive feedforward networks with random hidden nodes. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17:879–892
Huang G-B, Wang DH, Lan Y (2011) Extreme learning machines: a survey. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 2:107–122
Huang G-B, Zhou H, Ding X, Zhang R (2012) Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man and Cybern Part B Cybern 42:513–528
Huang G-B, Zhu Q-Y, Siew C-K (2006) Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70:489–501
Khemchandani R, Jayadeva, Chandra S (2009) Knowledge based proximal support vector machines. Eur J Oper Res 195:914–923
Lan Y, Soh C, Huang G-B (2010) Two-stage extreme learning machine for regression. Neurocomputing 73:3028–3038
Mangasarian OL (2004) Knowledge-based kernel approximation. J Mach Learn Res 5:1127–1141
Mangasarian OL, Wild EW (2007) Nonlinear knowledge in kernel approximation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 18:300–306
Mangasarian OL, Wild EW (2008) Nonlinear knowledge in kernel machines. In: CRM proceedings and lecture notes, vol 45, pp 181–198
Mangasarian OL, Wild EW, Fung GM (2009) Proximal knowledge based classification. Stat Anal Data Min 1(4):215–222
Miche Y, Sorjamaa A, Bas P, Simula O, Jutten C, Lendasse A (2010) OP-ELM: optimally pruned extreme learning machine. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 21:158–162
Miche Y, Heeswijk M, Bas P, Simula O, Lendasse A (2011) TROP-ELM: a double-regularized ELM using LARS and Tikhonov regularization. Neurocomputing 74:2413–2421
Rao CR, Mitra SK (1971) Generalized inverse of matrices and its applications. Wiley, NewYork
Suykens JAK, Vandewalle J (1999) Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process Lett 9(3):293–300
Yuan Y, Wang Y, Cao F (2011) Optimization approximation solution for regression problem based on extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 74:2475–2482
Zhang D, Tian Y, Shi Y (2011) A group of knowledge-incorporated multiple criteria linear programming classifiers. J Comput Appl Math 235:3705–3717
Zhang H, Yin Y, Zhang S, Sun C (2014) An improved ELM algorithm based on PCA technique. In: Cao J et al. (eds) Proceedings in adaptation, learning and optimization, vol 4, pp 95–104
Zhang H, Zhang S, Yin Y (2013) An improved ELM algorithm based on EM-ELM and ridge regression. In: Sun C et al (eds) LNCS 8261, pp 756–763
Zhu Q-Y, Qin AK, Suganthan PN, Huang G-B (2005) Evolutionary extreme learning machine. Pattern recognit 38:1759–1763
Acknowledgments
The authors are extremely thankful to the learned referees for their very helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balasundaram, S., Gupta, D. Knowledge-based extreme learning machines. Neural Comput & Applic 27, 1629–1641 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1961-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1961-5