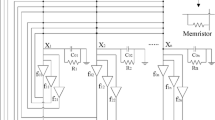
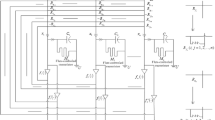
Abstract
In this paper, a generalized memristor-based recurrent neural network model with variable delays and impulse effects is considered. By using an impulsive delayed differential inequality and Lyapunov function, the exponential stability of the impulsive delayed memristor-based recurrent neural networks is investigated. Several exponential and uniform stability criteria of this impulsive delayed system are derived, which promotes the study of memristor-based recurrent neural networks. Finally, the effectiveness of obtained results is illustrated by two numerical examples.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Itoh M, Chua L (2009) Memristor cellular automata and memristor discrete-time cellular neural networks. Int J Bifurcat Chaos 19(11):3605–3656
Li H, Liao X, Lei X, Huang T, Zhu W (2013) Second-order consensus seeking in multi-agent systems with nonlinear dynamics over random switching directed networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 60(6):1595–1607
Li H, Liao X, Huang T (2013) Second-order locally dynamic consensus of multiagent systems with arbitrarily fast switching directed topologies. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 43(6):1343–1353
He X, Li C, Huang T, Li C, Huang J (2014) A recurrent neural network for solving bilevel linear programming problem. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25:824–830
Hu J, Wang J (2010) Global uniform asymptotic stability of memristorbased recurrent neural networks with time delays. In: Proceedings of IEEE international joint conference neural network Barcelona, Spain, pp 2127–2134
Guo Z, Wang J, Yan Z (2014) Attractivity analysis of memristor-based cellular neural networks with time-varying delays. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25(4):704–717
Wen S, Zeng Z, Huang T, Chen Y, Li P (2015) Circuit design and exponential stabilization of memristive neural networks. Neural Netw 63:48–56
Li H, Liao X, Huang T, Zhu W, Liu Y (2015) Second-order globally consensus in multiagent networks with random directional link failure. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 26(3):565–575
Li H, Liao X, Huang T, Zhu W (2015) Event-triggering sampling based leader-following consensus in second-order multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 60(7):1998–2003
Liu Z, Guan Z, Shen X, Feng G (2012) Consensus of multi-agent networks with aperiodic sampled communication via impulsive algorithm using position-only measurements. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 57(10):2639–2643
Guan Z, Liu Z, Feng G, Wang Y (2010) Synchronization of complex dynamical networks with time-varying delays via impulsive distributed control. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I 57(8):2182–2195
Li C, Gao D, Liu C, Chen G (2014) Impulsive control for synchronizing delayed discrete complex networks with switching topology. Neural Comput Appl 24(1):59–68
Li C, Yu W, Huang T (2014) Impulsive synchronization schemes of stochastic complex networks with switching topology: Average time approach. Neural Netw 54:85–94
Yang Z, Xu D (2005) Stability analysis of delay neural networks with impulsive effects. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II 52(8):517–521
Yang Z, Xu D (2007) Stability analysis and design of impulsive control systems with time delay. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 52(8):1448–1454
Huang T, Li C, Duan S, Starzyk J (2012) Robust exponential stability of uncertain delayed neural networks with stochastic perturbation and impulse effects. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 23(6):866–875
Chen W, Zheng W (2009) Global exponential stability of impulsive neural networks with variable: an LMI approach. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I 56(6):1248–1259
Li C, Li C, Liao X, Huang T (2011) Impulsive effects on stability of high-order BAM neural networks with time delays. Neurocomputing 74(10):1541–1550
Li H, Liao X, Chen G, Hill D, Dong Z, Huang T (2015) Event-triggered asynchronous intermittent communication strategy for synchronization in complex networks. Neural Netw 66:1–10
Strukov D, Snider G, Stewart D, Williams R (2008) The missing memristor found. Nature 453:80–83
Chua L (1971) Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans Circuit Theory 18(5):507–519
Corinto F, Ascoli A, Gilli M (2011) Nonlinear dynamics of memristor oscillators. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Reg Pap 58(6):1323–1336
Wen S, Zeng Z, Huang T, Yu X (2014) Noise cancellation of memristive neural networks. Neural Netw 60:74–83
Pershin Y, Ventra M (2012) Experimental demonstration of associative memory with memristive neural networks. Neural Netw 23:881–886
Wen S, Zeng Z, Huang T, Zhang Y (2014) Exponential lag adaptive synchronization of memristive neural networks and applications in Pseudo-random generators. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 22(6):1704–1713
Wu A, Zeng Z (2012) Exponential stabilization of memristive neural networks with time delays. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 23(12):1919–1929
Wen S, Zeng Z, Huang T (2013) Dynamic behaviors of memristor-based delayed recurrent networks. Neural Comput Appl 23(3–4):815–821
Zhang G, Shen Y, Quan Y, Sun J (2012) Global exponential stability of a class of memristor-based recurrent neural networks with time-varying delays. Neurocomputing 97:149–154
Zhang G, Shen Y (2013) New algebraic criteria for synchronization stability of chaotic memristive neural networks with time-varying delays. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24(10):1919–1929
Qi J, Li C, Huang T (2014) Stability of delayed memristive neural networks with time-varying impulses. Cogn Neurodyn 8:429–436
Wen S, Zeng Z, Huang T, Li C (2015) Passivity and passification of stochastic impulsive memristor-based piecewise linear system with mixed delays. Int J Robust Nonlinear Contr 25(4):610–624
Filippov A (1988) Differential equations with discontinuous right-hand sides. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (Grant No. [2013]47), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61372139, 61374078, 61503175, 61571372, 61101233, 60972155), Spring Sunshine Plan Research Project of Ministry of Education of China (Grant No. z2011148), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. XDJK2014A009, XDJK2016A001), Program for Excellent Talents in scientific and technological activities for Overseas Scholars, Ministry of Personnel in China (Grant No. 2012-186), University Excellent Talents Supporting Foundations in of Chongqing (Grant No. 2011-65), University Key Teacher Supporting Foundations of Chongqing (Grant No. 2011-65). High School Key Scientific Research Project of Henan Province (Grant No. 15A120013), NPRP grant ♯ NPRP 4-1162-1-181, from the Qatar National Research Fund (a member of Qatar Foundation).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Duan, S., Li, C. et al. Exponential stability analysis of delayed memristor-based recurrent neural networks with impulse effects. Neural Comput & Applic 28, 669–678 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-2094-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-2094-6