Abstract
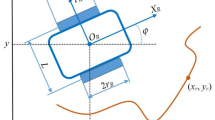
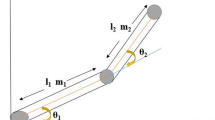
This work presents a discrete-time sliding mode neuro-adaptive control (DTSMNAC) method for robot manipulators. Due to the dynamics variations and uncertainties in the robot model, the trajectory tracking of robot manipulators has been one of the research areas for the last years. The proposed control structure is a practical design that combines a discrete-time neuro-adaptation technique with sliding mode control to compensate the dynamics variations in the robot. Using an online adaptation technique, a DTSMNAC controller is used to approximate the equivalent control in the neighborhood of the sliding surface. A sliding control is included to guarantee that the discrete-time neural sliding mode control can improve a stable closed-loop system for the trajectory tracking control of the robot with dynamics variations. The proposed technique simultaneously ensures the stability of the adaptation of the neural networks and can be obtained a suitable equivalent control when the parameters of the robot dynamics are unknown in advance. This neural adaptive system is applied to a SCARA robot manipulator and shows to be able to ensure that the output tracking error will converge to zero. Finally, experiments on a SCARA robot have been developed to show the performance of the proposed technique, including the comparison with a PID controller.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Wit CC, Siciliano B, Bastin G (1996) Theory of robot control. Springer, New York
Lewis F, Abdallah C, Dawson D (1993) Control of robot manipulators. MacMillan Publishing Co., New York
Samson C, Le Borgne M, Espinau B (1991) Robot control. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Spong M (1996) Motion control of robot manipulator. In: Levine W (ed) Handbook control. CRC Press, pp 1339–1350
Khalil W, Dombre E (2002) Modeling identification and control of robots. Hermes Penton Science, London
Jiang Z-H, Ishida T (2007) Trajectory tracking control of industrial robot manipulators using a neural network controller. In: IEEE international conference on systems, man and cybernetics, 2007. ISIC, pp 2390–2395
Khalal O, Mellit A, Rahim M, Salhi H, Guessoum A (2007) Robust control of manipulator robot by using the variable structure control with sliding mode. In: Mediterranean conference on control & automation, 2007. MED ‘07, pp 1–6
Raafat SM, Said WK, Akmeliawati R, Tariq NM (2009) Improving trajectory tracking of a three-axis SCARA robot using neural networks. In: IEEE symposium on industrial electronics & applications, 2009. ISIEA 2009, pp 283–288
Benjanarasuth T, Sowannee N, Naksuk N (2010) Two-degree-of-freedom simple servo adaptive control for SCARA robot. In: 2010 international conference on control automation and systems (ICCAS), p 480–484
Suvilath S, Khongsomboun K, Benjanarasuth T, Kominet N (2011) IMC-based PID controllers design for a two-links SCARA robot. In: TENCON 2011–2011 IEEE region 10 conference, p 1030–1034
Al-Khedher MA, Alshamasin MS (2012) SCARA robot control using neural networks. In: 2012 4th international conference on intelligent and advanced systems (ICIAS), vol 1, pp 126–130
Thanok S (2014) Design of an adaptive PD controller with dynamic friction compensation for direct-drive SCARA robot. In: Electrical engineering congress (iEECON), 2014 international. IEEE, 2014
Escobar F, Díaz S, Gutiérrez C, Ledeneva Y, Hernández C, Rodríguez D, Lemus R (2014) Simulation of control of a Scara robot actuated by pneumatic artificial muscles using RNAPM. J Appl Res Technol 12(5):939–946
Maeda Y, Fujiwara T, Ito H (2014) Robot control using high-dimensional neural networks. In: 2014 Proceedings of the SICE annual conference (SICE), p 738–743
Lin TC, Chang SW, Hsu CH (2012) Robust adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control for a class of uncertain discrete-time nonlinear systems. Int J Innov Comput Inf Control 8(1):347–359
Rossomando FG, Soria C, Carelli R (2014) Sliding mode neuro adaptive control in trajectory tracking for mobile robots. J Intell Robot Syst 74(3):931–944. ISSN: 0921-0296
Asada H, Slotine JJE (1986) Robot analysis and control. Wiley, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossomando, F.G., Soria, C.M. Discrete-time sliding mode neuro-adaptive controller for SCARA robot arm. Neural Comput & Applic 28, 3837–3850 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2242-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2242-7