Abstract
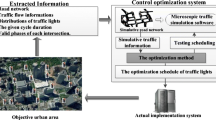
Urban traffic congestion becomes a severe problem for many cities all around the world. How to alleviate traffic congestions in real cities is a challenging problem. Benefited from concise and efficient evolution rules, the Biham, Middleton and Levine (BML) model has a great potential to provide favorable results in the dynamic and uncertain traffic flows within an urban network. In this paper, an enhanced BML model (EBML) is proposed to effectively simulate the urban traffic where the timing scheduling optimization algorithm (TSO) based on the quantum particle swarm optimization is creatively introduced to optimize the timing scheduling of traffic light. The main contributions include that: (1) The actual urban road network with different two-way multi-lane roads is firstly mapped into the theoretical lattice space of BML. And the corresponding updating rules of each lattice site are proposed to control vehicle dynamics; (2) compared with BML, a much deeper insight into the phase transition and traffic congestions is provided in EBML. And the interference among different road capacities on forming traffic congestions is elaborated; (3) based on the scheduling simulation of EBML, TSO optimizes the timing scheduling of traffic lights to alleviate traffic congestions. Extensive comparative experiments reveal that TSO can achieve excellent optimization performances in real cases.











Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Al-Deek H, Lochrane TWP, Chandra CSR, Khattak A (2012) Diversion during unexpected congestion on toll roads: the role of traffic information displayed on dynamic message signs. IET Intell Transp Syst 6(2):97–106
Sun R, Ochieng WY, Feng S (2015) An integrated solution for lane level irregular driving detection on highways. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 56:61–79
Sun R, Han K, Hu J, Wang Y, Hu M, Ochieng WY (2016) Integrated solution for anomalous driving detection based on BeiDou/GPS/IMU measurements. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 69:193–207
Finotti C, Gaio E (2014) Continuous model in dq frame of thyristor controlled reactors for stability analysis of high power electrical systems. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 63:836–845
Sazhin SS, Xie JF, Shishkova IN, Elwardany AE, Heikal MR (2013) A kinetic model of droplet heating and evaporation: effects of inelastic collisions and a non-unity evaporation coefficient. Int J Heat Mass Transf 56(1):525–537
Peng GH, Cheng RJ (2013) A new car-following model with the consideration of anticipation optimal velocity. Phys A 392(17):3563–3569
Ding ZJ, Jiang R, Gao ZY, Wang BH, Long J (2013) Effect of overpasses in the Biham–Middleton–Levine traffic flow model with random and parallel update rule. Phys Rev E 88(2):022809
Biham O, Middleton AA, Levine D (1992) Self-organization and a dynamical transition in traffic-flow models. arXiv preprint cond-mat/9206001
Hu W, Wang H, Min Z (2014) A storage allocation algorithm for outbound containers based on the outer-inner cellular automaton. Inf Sci 281:147–171
Chowdhury D, Schadschneider A (1999) Self-organization of traffic jams in cities: effects of stochastic dynamics and signal periods. Phys Rev E 59(2):R1311
Hu J, Song J, Zhang Y, Guo D, Xu Y (2005) Modelling and analysis for self-organization of urban traffic flow. In: Proceedings of intelligent transportation systems, vol 111. IEEE, pp 237–242
D’Souza R (2005) Coexisting phases and lattice dependence of a cellular automaton model for traffic flow. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 71(2):531–536
Chung et al (1995) Two-dimensional traffic flow problems with faulty traffic lights. Phys Rev E 51:772–774
Xie et al (2013) Dynamical traffic light strategy in the Biham–Middleton–Levine model. Phys Rev E 87(2):022812
Sun D, Jiang R, Wang B (2010) Timing of traffic lights and phase separation in two-dimensional traffic flow. Comput Phys Commun 181(2):301–304
Fukui et al (1996) Flow of cars crossing with unequal velocities in a two-dimensional cellular automaton model. J Phys Soc Jpn 65(8):2514–2517
Török and Kertész (1996) The green wave model of two-dimensional traffic: transitions in the flow properties and in the geometry of the traffic jam. Phys A 231(4):515–533
Horiguchi T, Sakakibara T (1998) Numerical simulations for traffic-flow models on a decorated square lattice. Phys A 252(3):388–404
Bouwmeester D, Ekert A, Zeilinger A (2010) The physics of quantum information: quantum cryptography, quantum teleportation, quantum computation, 2000 edn. Springer
Li Y, Jiao L, Shang R, Stolkin R (2015) Dynamic-context cooperative quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization based on multilevel thresholding applied to medical image segmentation. Inf Sci 294:408–422
Maerivoet S, Moor BD (2005) Cellular automata models of road traffic. Phys Rep 419(1):1–64
Li P, Lam J, Cheung KC (2014) Velocity-dependent multi-objective control of vehicle suspension with preview measurements. Mechatronics 24:464–475
Cardillo A, Scellato S, Latora V, Porta S (2006) Structural properties of planar graphs of urban street patterns. Phys Rev E 73(6):066107
Barthélemy M, Flammini A (2008) Modeling urban street patterns. Phys Rev Lett 100(13):138702
Leung JY (2004) Handbook of scheduling: algorithms, models, and performance analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Tang D, Cai Y, Zhao J, Xue Y (2014) A quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization with memetic algorithm and memory for continuous non-linear large scale problems. Inf Sci 289(24):162–189
Kachroudi S, Bhouri N (2009) A multimodal traffic responsive strategy using particle swarm optimization. Control Transport Sys 42:531–537
Liu J, Teo KL, Wang X, Wu C (2015) An exact penalty function-based differential search algorithm for constrained global optimization. Soft Comput 20(4):1305–1313
Sánchez-Medina JJ, Galán-Moreno MJ, Rubio-Royo E (2010) Traffic signal optimization in “La Almozara” district in Saragossa under congestion conditions, using genetic algorithms, traffic microsimulation, and cluster computing. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 11:132–141
Hu Z, Bao Y, Xiong T (2014) Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimization based memetic algorithm for model selection in short-term load forecasting using support vector regression. Appl Soft Comput 25:15–25
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation, China (No. 61572369), the Hubei Province Natural Science Foundation (No. 2015CFB423), and Wenbin Hu is the grant recipient of these two foundations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Wenbin Hu declares that he has no conflict of interest in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, W., Wang, H., Qiu, Z. et al. A quantum particle swarm optimization driven urban traffic light scheduling model. Neural Comput & Applic 29, 901–911 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2508-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2508-0