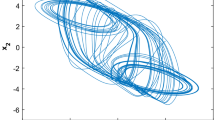
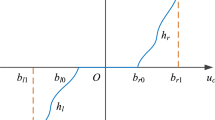
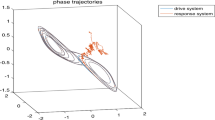
Abstract
In this paper, a prescribed performance adaptive neural network synchronization is investigated for a class of unknown chaotic systems in the presence of input saturation and external unknown disturbances. A prescribed performance function is employed to transform the constraint problem of chaotic synchronization control error into the problem of guaranteeing the boundedness of the transformed error. By introducing the Gaussian error function, the input saturation is handled. A neural network-based synchronization control scheme is then developed. Under the developed synchronization control scheme, the synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems is achieved with different initial conditions. Numerical simulation results further demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed synchronization control scheme for unknown chaotic systems subject to external unknown disturbances and input saturation.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Sun M, Tian LX, Fu Y (2007) An energy resources demand-supply system and its dynamical analysis. Chaos Solitons Fractals 32:168–180
Hu JQ, Cao JD, Hayat T (2014) Stability and Hopf bifurcation analysis for an energy resource system. Nonlinear Dyn 78:219–234
Ma JH, Chen YS (2001) Study for the bifurcation topological structure and the global complicated character of a kind of nonlinear finance system (I). Appl Math Mech 22:1240–1251
Chen WC (2008) Nonlinear dynamics and chaos in a fractional-order financial system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 36:1305–1314
Chen AM (2011) Modeling a synthetic biological chaotic system: relaxation oscillators coupled by quorum sensing. Nonlinear Dyn 63:711–718
Strogatz SH (1994) Nonlinear dynamics and chaos with applications to physics, biology, chemistry, and engineering. Perseus Books Publishing, L. L. C., New York
Mosekilde E, Maistrenko Y, Postnov D (2002) Chaotic synchronization: applications to living systems. World Scientific, Singapore
Shao SY, Min FH, Ma ML, Wang ER (2013) Non-inductive modular circuit of dislocated synchronization of fractional-order Chua’s system and its application. Acta Phys Sin 62:130504
Volos CK, Kyprianidis IM, Stouboulos IN (2013) Image encryption process based on chaotic synchronization phenomena. Signal Process 93:1328–1340
Pecora L, Carroll T (1990) Synchronization in chaotic systems. Phys Rev Lett 64:821–824
Pan L, Zhou W, Zhou L, Sun K (2011) Chaos synchronization between two different fractional-order hyperchaotic systems. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 16:2628–2640
Pan Y, Er MJ, Sun T (2012) Composite adaptive fuzzy control for synchronizing generalized Lorenz systems. Chaos Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 22:023144
Du HY, Zeng QS, Wang CH (2009) Modified function projective synchronization of chaotic system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 42:2399–2404
Mohammad PA, Khanmohammadi S, Alizadeh G (2011) Finite-time synchronization of two different chaotic systems with unknown parameters via sliding mode technique. Appl Math Model 35:3080–3091
Wan XJ, Sun JT (2011) Adaptive–impulsive synchronization of chaotic systems. Math Comput Simul 81:1609–1617
Wang M (2015) Impulsive synchronization of hyperchaotic Lü systems with two methods. Int J Mod Nonlinear Theory Appl 4:1–9
Al-sawalha MM, Noorani MSM (2009) Anti-synchronization of chaotic systems with uncertain parameters via adaptive control. Phys Lett A 373:2852–2857
Lin CM, Lin MH, Yeh RG (2013) Synchronization of unified chaotic system via adaptive wavelet cerebellar model articulation controller. Neural Comput Appl 23:965–973
Liu M, Chen H, Zhang S, Fan Z (2014) Exponential synchronization of two totally different chaotic systems based on a unified model. Neural Comput Appl 25:1801–1808
Tu JJ, He HL, Xiong P (2014) Adaptive backstepping synchronization between chaotic systems with unknown Lipschitz constant. Appl Math Comput 236:10–18
Koronovskii AA, Moskalenko OI, Hramov AE (2009) On the use of chaotic synchronization for secure communication. Phys Uspekhi 52:1213–1238
Zhu FL (2009) Observer-based synchronization of uncertain chaotic system and its application to secure communications. Chaos Solitons Fractals 40:2384–2391
Kwon OM, Park JH, Lee SM (2011) Secure communication based on chaotic synchronization via interval time-varying delay feedback control. Nonlinear Dyn 63:239–252
Meng D (2015) Neural networks adaptive synchronization for four-dimension energy resource system with unknown dead zones. Neurocomputing 151:1495–1499
Zhang XX, Liu XP, Zhu QD (2014) Adaptive chatter free sliding mode control for a class of uncertain chaotic systems. Appl Math Comput 232:431–435
Yu YG, Li HX (2010) Adaptive generalized function projective synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 11:2456–2464
Chen M, Zhou Y, Guo WW (2014) Robust tracking control for uncertain MIMO nonlinear systems with input saturation using RWNNDO. Neurocomputing 144:436–447
Mei R, Chen M, Guo WW (2015) Robust adaptive control scheme for optical tracking telescopes with unknown disturbances. Optik Int J Light Electron Opt 126:1185–1190
Pan Y, Liu Y, Yu H (2015) Simplified adaptive neural control of strict-feedback nonlinear systems. Neurocomputing 159:251–256
Pan Y, Er MJ, Huang D, Wang Q (2011) Adaptive fuzzy control with guaranteed convergence of optimal approximation error. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 19:807–818
Pan Y, Er MJ (2013) Enhanced adaptive fuzzy control with optimal approximation error convergence. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 21:1123–1132
Pan Y, Zhou Y, Sun T, Er MJ (2013) Composite adaptive fuzzy \({H^\infty }\) tracking control of uncertain nonlinear systems. Neurocomputing 99:15–24
Na J, Ren X, Herrmann G, Qiao Z (2011) Adaptive neural dynamic surface control for servo systems with unknown dead-zone. Control Eng Pract 19:1328–1343
Na J, Ren X, Shang C, Guo Y (2012) Adaptive neural network predictive control for nonlinear pure feedback systems with input delay. J Process Control 22:194–206
Na J, Herrmann G, Ren XM (2010) Neural network control of nonlinear time-delay system with unknown dead-zone and its application to a robotic servo system. Trends Intell Robot 103:338–345
Na J, Ren XM, Zheng D (2013) Adaptive control for nonlinear pure-feedback systems with high-order sliding mode observer. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24:370–382
Li YM, Tong SC, Li TS, Jing XJ (2014) Adaptive fuzzy control of uncertain stochastic nonlinear systems with unknown dead zone using small-gain approach. Fuzzy Sets Syst 235:1–24
Li YM, Tong SC, Li TS (2014) Adaptive fuzzy output-feedback control for output constrained nonlinear systems in the presence of input saturation. Fuzzy Sets Syst 248:138–155
Li YM, Tong SC, Li TS (2013) Direct adaptive fuzzy backstepping control of uncertain nonlinear systems in the presence of input saturation. Neural Comput Appl 23:1207–1216
Li YM, Tong SC, Li TS (2013) Adaptive fuzzy output feedback control of nonlinear uncertain systems with unknown backlash-like hysteresis based on modular design. Neural Comput Appl 23:261–270
Liu YJ, Chen CLP, Wen GX, Tong SC (2011) Adaptive neural output feedback tracking control for a class of uncertain discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22:1162–1167
Liu YJ, Tong SC, Wang D, Li TS, Chen CLP (2011) Adaptive neural output feedback controller design with reduced-order observer for a class of uncertain nonlinear SISO systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22:1328–1334
Wang HQ, Chen B, Liu K, Liu XP, Lin C (2014) Adaptive neural tracking control for a class of nonstrict-feedback stochastic nonlinear systems with unknown backlash-like hysteresis. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25:947–958
Wang HQ, Chen B, Lin C (2013) Adaptive neural tracking control for a class of perturbed pure-feedback nonlinear systems. Nonlinear Dyn 72:207–220
Li TS, Wang D, Feng G, Tong SC (2010) A DSC approach to robust adaptive NN tracking control for strict-feedback nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 40:915–927
Li ZJ, Ge SS, Ming A (2007) Adaptive robust motion/force control of holonomic-constrained nonholonomic mobile manipulators. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 37:607–616
Li ZJ, Ge SS, Adams M, Wijesoma WS (2008) Robust adaptive control of uncertain force/motion constrained nonholonomic mobile manipulators. Automatica 44:776–784
Chen M, Ge SS, Ren BB (2011) Adaptive tracking control of uncertain MIMO nonlinear systems with input constraints. Automatica 47:452–465
Ge SS, Li GY, Zhang J, Lee TH (2004) Direct adaptive control for a class of MIMO nonlinear systems using neural networks. IEEE Trans Autom Control 49:2001–2006
Chen M, Ge SS, How BVE (2010) Robust adaptive neural network control for a class of uncertain MIMO nonlinear systems with input nonlinearities. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 21:796–812
Chen M, Tao G, Jiang B (2014) Dynamic surface control using neural networks for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems with input saturation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 26:2086–2097
Yu JP, Shi P, Dong WJ, Chen B, Lin C (2015) Neural network-based adaptive dynamic surface control for permanent magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 26:640–645
Bechlioulis CP, Rovithakis GA (2008) Prescribed performance adaptive control of SISO feedback linearizable systems with disturbances. In: 16th mediterranean conference on control and automation pp 1035–1040
Bechlioulis CP, Rovithakis GA (2008) Robust adaptive control of feedback linearizable MIMO nonlinear systems with prescribed performance. IEEE Trans Autom Control 53:2090–2099
Kostarigka AK, Rovithakis GA (2011) Prescribed performance output feedback/observer-free robust adaptive control of uncertain systems using neural networks. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 41:1483–1494
Kostarigka AK, Rovithakis GA (2012) Adaptive dynamic output feedback neural network control of uncertain MIMO nonlinear systems with prescribed performance. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 23:138–149
Meng WC, Yang QM, Ying Y, Sun Y, Yang ZY, Sun YX (2013) Adaptive power capture control of variable-speed wind energy conversion systems with guaranteed transient and steady-state performance. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 28:716–725
Na J, Chen Q, Ren X, Guo Y (2014) Adaptive prescribed performance motion control of servo mechanisms with friction compensation. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 61:486–494
Lü JH, Chen GR (2002) A new chaotic attractor coined. Int J Bifurc Chaos 12:659–661
Ma J, Zheng Z, Li P (2015) Adaptive dynamic surface control of a class of nonlinear systems with unknown direction control gains and input saturation. IEEE Trans Cybern 45:728–741
Ma J, Ge SS, Zheng Z, Hu D (2015) Adaptive NN control of a class of nonlinear systems with asymmetric saturation actuators. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 26:1532–1538
Andrews LC (1998) Special functions of mathematics for engineers, 2nd edn. SPIE, Bellingham
Apostol TM (1963) Mathematical analysis. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Ge SS, Hang CC, Lee TH, Zhang T (2001) Stable adaptive neural network control. Kluwer, Norwell
Tee KP, Ge SS (2006) Control of fully actuated ocean surface vessels using a class of feedforward approximators. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 14:750–756
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 61573184), 333 Talents Project in Jiangsu Province (No. BRA2015359), the Six Talents Peak Project of Jiangsu Province (No. 2012-XXRJ-010), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. NE2016101) and Jiangsu Innovation Program for Graduate Education (No. KYLX16_0375).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, S., Chen, M. & Yan, X. Prescribed performance synchronization for uncertain chaotic systems with input saturation based on neural networks. Neural Comput & Applic 29, 1349–1361 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2629-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2629-5