Abstract
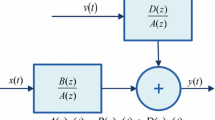
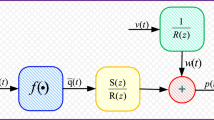
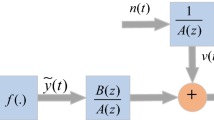
In this study, strength of evolutionary computational intelligence based on genetic algorithms (GAs) is exploited for parameter identification of nonlinear Hammerstein controlled autoregressive (NHCAR) systems. The fitness function is constructed for the NHCAR system by defining an error function in the mean square sense. Unknown adjustable weights of the system are optimized with GAs, used as an effective tool for effective global search. Comparative analysis of the proposed scheme is made from true parameters of the systems for a number of scenarios based on different levels of signal-to-noise ratios. The validation of the performance is made through statistics based on sufficiently large number of runs using indices of mean absolute error, variance account for, and Thiel’s inequality coefficient as well as their global versions.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Corbier C, El Badaoui M, Ugalde HMR (2015) Huberian approach for reduced order ARMA modeling of neurodegenerative disorder signal. Signal Process 113:273–284
Ding F, Wang Y, Ding J (2015) Recursive least squares parameter identification algorithms for systems with colored noise using the filtering technique and the auxilary model. Digit Signal Process 37:100–108
Raja MAZ, Chaudhary NI (2014) Adaptive strategies for parameter estimation of Box–Jenkins systems. IET Signal Process 8(9):968–980
Zhang T, Qian W, Zhang G, Ye F, Gao C, Zhao H (2016) Parameter estimation of MC-CDMA signals based on modified cyclic autocorrelation. Digit Signal Process 54:46–53
Chaudhary NI, Raja MAZ, Aslam MS, Ahmed N (2016) Novel generalization of Volterra LMS algorithm to fractional order with application to system identification. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-016-2548-5
Raja MAZ, Chaudhary NI (2015) Two-stage fractional least mean square identification algorithm for parameter estimation of CARMA systems. Signal Process 107:327–339
Wang Z, Ruimin H, Shao Z, Hou Z (2014) Parameter estimation in sparse representation based face hallucination. Digit Signal Process 31:28–34
Mao Y, Ding F (2015) Multi-innovation stochastic gradient identification for Hammerstein controlled autoregressive autoregressive systems based on the filtering technique. Nonlinear Dyn 79(3):1745–1755
Ding F, Liu XP, Liu G (2011) Identification methods for Hammerstein nonlinear systems. Digit Signal Process 21(2):215–238
Chen H, Ding F, Xiao Y (2015) Decomposition-based least squares parameter estimation algorithm for input nonlinear systems using the key term separation technique. Nonlinear Dyn 79(3):2027–2035
Chen J, Ding F (2010) Modified stochastic gradient identification algorithms with fast convergence rates. J Vib Control 17(9):1281–1286. doi:10.1177/1077546310376989
Mao Y, Ding F (2015) A novel data filtering based multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for Hammerstein nonlinear systems. Digit Signal Process 46:215–225
Chaudhary NI, Raja MAZ (2015) Identification of Hammerstein nonlinear ARMAX systems using nonlinear adaptive algorithms. Nonlinear Dyn 79(2):1385–1397
Chaudhary NI, Raja MAZ (2015) Design of fractional adaptive strategy for input nonlinear Box–Jenkins systems. Signal Process 116:141–151
Shen Q, Ding F (2016) Hierarchical multi-innovation extended stochastic gradient algorithms for input nonlinear multivariable OEMA systems by the key-term separation principle. Nonlinear Dyn 85(1):499–507
Ding F, Shi Y, Chen T (2007) Auxiliary model-based least-squares identification methods for Hammerstein output-error systems. Syst Control Lett 56(5):373–380
Hu H, Ding R (2014) Least squares based iterative identification algorithms for input nonlinear controlled autoregressive systems based on the auxiliary model. Nonlinear Dyn 76(1):777–784
Li G et al (2011) Identification of a class of nonlinear autoregressive models with exogenous inputs based on kernel machines. IEEE Trans Signal Process 59(5):2146–2159
Xiong W, Fan W, Ding R (2012) Least-squares parameter estimation algorithm for a class of input nonlinear systems. J Appl Math 2012, Article ID 684074. doi:10.1155/2012/684074
Chen H, Ding F (2015) Hierarchical least squares identification for Hammerstein nonlinear controlled autoregressive systems. Circuits Syst Signal Process 34(1):61–75
Chen H, Ding F (2013) Decomposition based recursive least squares parameter estimation for Hammerstein nonlinear controlled autoregressive systems. In: IEEE American control conference (ACC)
Xiao Y, Song G, Liao Y, Ding R (2012) Multi-innovation stochastic gradient parameter estimation for input nonlinear controlled autoregressive models. Int J Control Autom Syst 10(3):639–643
Chaudhary NI, Raja MAZ, Khan JA, Aslam MS (2013) Identification of input nonlinear control autoregressive systems using fractional signal processing approach. Sci World J 2013, Article ID 467276. doi:10.1155/2013/467276
Chaudhary NI, Raja MAZ, Khan AUR (2015) Design of modified fractional adaptive strategies for Hammerstein nonlinear control autoregressive systems. Nonlinear Dyn 82(4):1811–1830
Raja MAZ, Farooq U, Chaudhary NI, Wazwaz AM (2016) Stochastic numerical solver for nanofluidic problems containing multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl Soft Comput 38:561–586. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2015.10.015 (in press)
Chiroma H, Abdulkareem S, Herawan T (2015) Evolutionary neural network model for West Texas Intermediate crude oil price prediction. Appl Energy 142:266–273
Onan A, Bulut H, Korukoglu S (2016) An improved ant algorithm with LDA-based representation for text document clustering. J Inf Sci. doi:10.1177/0165551516638784
Raja MAZ (2014) Solution of the one-dimensional Bratu equation arising in the fuel ignition model using ANN optimised with PSO and SQP. Connect Sci 26(3):195–214. doi:10.1080/09540091.2014.907555
Onan A, Korukoğlu S, Bulut H (2016) A multiobjective weighted voting ensemble classifier based on differential evolution algorithm for text sentiment classification. Expert Syst Appl 62:1–16. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2016.06.005
Raja MAZ, Khan JA, Chaudhary NI, Shivanian E (2016) Reliable numerical treatment of nonlinear singular Flierl–Petviashivili equations for unbounded domain using ANN, GAs, and SQP. Appl Soft Comput 38:617–636
Kahourzade S, Mahmoudi A, Mokhlis HB (2015) A comparative study of multi-objective optimal power flow based on particle swarm, evolutionary programming, and genetic algorithm. Electr Eng 97(1):1–12
Ugalde HMR, Carmona JC, Reyes-Reyes J, Alvarado VM, Mantilla J (2015) Computational cost improvement of neural network models in black box nonlinear system identification. Neurocomputing 166:96–108
Gotmare A, Patidar R, George NV (2015) Nonlinear system identification using a cuckoo search optimized adaptive Hammerstein model. Expert Syst Appl 42(5):2538–2546
Ugalde HMR, Carmona JC, Reyes-Reyes J, Alvarado VM, Corbier C (2015) Balanced simplicity–accuracy neural network model families for system identification. Neural Comput Appl 26(1):171–186
Raja MAZ, Samar R, Alaidarous ES, Shivanian E (2016) Bio-inspired computing platform for reliable solution of Bratu-type equations arising in the modeling of electrically conducting solids. Appl Math Model 40(11):5964–5977. doi:10.1016/j.apm.2016.01.034
Aledo JA, Gámez JA, Molina D (2016) Using metaheuristic algorithms for parameter estimation in generalized Mallows models. Appl Soft Comput 38:308–320
Da Ros S et al (2013) A comparison among stochastic optimization algorithms for parameter estimation of biochemical kinetic models. Appl Soft Comput 13(5):2205–2214
Mall S, Chakraverty S (2013) Comparison of artificial neural network architecture in solving ordinary differential equations. Adv Artif Neural Syst 2013:12
Jaddi NS, Abdullah S, Hamdan AR (2015) Optimization of neural network model using modified bat-inspired algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 37:71–86
Raja MAZ, Manzar MA, Samar R (2015) An efficient computational intelligence approach for solving fractional order Riccati equations using ANN and SQP. Appl Math Model 39:3075–3093. doi:10.1016/j.apm.2014.11.024
Raja MAZ, Shah FH, Ahad A, Khan NA (2016) Design of bio-inspired computational intelligence technique for solving steady thin film flow of Johnson–Segalman fluid on vertical cylinder for drainage problem. J Tiawan Inst Chem Eng. doi:10.1016/j.jtice.2015.10.020
Gozde H (2015) Comparative analysis of swarm optimization-based control method for direct matrix converter. Electr Eng 97(3):181–193
Raja MAZ (2014) Stochastic numerical techniques for solving Troesch’s problem. Inf Sci 279:860–873. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2014.04.036
Raja MAZ, Khan JA, Behloul D, Haroon T, Siddiqui AM, Samar R (2015) Exactly satisfying initial conditions neural network models for numerical treatment of first Painlevé equation. Appl Soft Comput 26:244–256. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2014.10.009
Agrawal RK, Bawane NG (2015) Multiobjective PSO based adaption of neural network topology for pixel classification in satellite imagery. Appl Soft Comput 28:217–225
Khan JA, Raja MAZ, Syam MI, Tanoli SAK, Awan SE (2015) Design and application of nature inspired computing approach for nonlinear stiff oscillatory problems. Neural Comput Appl 26(7):1763–1780
Holland JH (1975) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. University of Michigan press, Ann arbor
Zhu Z, Aslam MW, Nandi AK (2014) Genetic algorithm optimized distribution sampling test for M-QAM modulation classification. Signal Process 94:264–277
Alirezazadeh P, Fathi A, Abdali-Mohammadi F (2015) A genetic algorithm-based feature selection for kinship verification. IEEE Signal Process Lett 22(12):2459–2463
Yao L, Sethares WA (1994) Nonlinear parameter estimation via the genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans Signal Process 42(4):927–935
Pasolli E, Melgani F (2015) Genetic algorithm-based method for mitigating label noise issue in ECG signal classification. Biomed Signal Process Control 19:130–136
Arabali A et al (2013) Genetic-algorithm-based optimization approach for energy management. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 28(1):162–170
Stanković L, Popović-Bugarin V, Radenović F (2013) Genetic algorithm for rigid body reconstruction after micro-Doppler removal in the radar imaging analysis. Signal Process 93(7):1921–1932
Couceiro MS, Rocha RP, Fonseca Ferreira NM, Tenreiro Machado JA (2012) Introducing the fractional-order Darwinian PSO. Signal Image Video Process 6(3):343–350
Couceiro M, Ghamisi P (2016) Fractional order Darwinian particle swarm optimization. Springer International Publishing, Berlin, pp 11–20
Pires EJS, Tenreiro Machado JA, de Moura Oliveira PB, Boaventura Cunha J, Mendes L (2010) Particle swarm optimization with fractional-order velocity. Nonlinear Dyn 61(1-2):295–301
Couceiro MS, Martins FML, Rocha RP, Ferreira NMF, Sivasundaram S (2012) Introducing the fractional order robotic Darwinian PSO. In: AIP conference proceedings-American Institute of Physics, vol 1493, no 1, p 242
Ghamisi P, Couceiro MS, Martins FML, Benediktsson JA (2014) Multilevel image segmentation based on fractional-order Darwinian particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 52(5):2382–2394
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors of the manuscript declared that there are no potential conflicts of interest.
Human and animal rights
All the authors of the manuscript declared that there is no research involving human participants and/or animal.
Informed consent
All the authors of the manuscript declared that there is no material that required informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raja, M.A.Z., Shah, A.A., Mehmood, A. et al. Bio-inspired computational heuristics for parameter estimation of nonlinear Hammerstein controlled autoregressive system. Neural Comput & Applic 29, 1455–1474 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2677-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2677-x