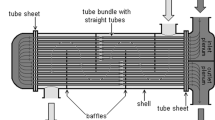
Abstract
Heat exchangers play a key role in wide industrial applications. Due to their complex design and high manufacturing cost, their efficient operation and optimum design are quite important for overall cost minimization. There have been several optimization algorithms developed so far for the optimum design of the shell-and-tube heat exchanger (STHE). In this paper, the ability to emerge AI-based optimization method referred to as cohort intelligence (CI) is demonstrated by solving the design and economic optimization of the STHEs. Three cases were solved. These three cases include fluids, which are different at both the shell side and tube side with different inlet and outlet temperatures at the shell side and tube side. The associated key variables such as tube outside diameter, baffle spacing, pitch size, shell inside diameter and number of tube passes that decide the total cost of the heat exchanger were optimized. The performance of the CI method is compared with existing algorithms. The quality and robustness of the CI solution at reasonable computational cost highlighted its applicability by solving real-world problems from mechanical engineering domain.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- b :
-
Baffle spacing (\({\text{m}}\))
- C p :
-
Specific heat (\({\text{kJ}}/{\text{kg}}\,{\text{K}}\))
- C inv :
-
Capital investment \((\EUR)\)
- C E :
-
Energy cost (\(\EUR/{\text{kW}}\,{\text{h}}\))
- C annual :
-
Annual operating cost \((\EUR/{\text{year}})\)
- \(C_{{{\text{total}}\_{\text{disc}}}}\) :
-
Total discounted operating cost \((\EUR)\)
- \(C_{\text{total}}\) :
-
Total annual cost \((\EUR)\)
- \(d\) :
-
Tube diameter (m)
- \(D\) :
-
Shell diameter (m)
- \(f\) :
-
Friction factor
- \(F\) :
-
Correction factor
- \(h\) :
-
Heat transfer coefficient (\({\text{W}}/{\text{m}}^{2} {\text{K}}\))
- \(A\) :
-
Annual operating time (\({\text{h}}/{\text{year}}\))
- \(I\) :
-
Annual discount rate \(\left( \% \right)\)
- \(k\) :
-
Thermal conductivity (\({\text{W}}/{\text{m K}}\))
- \(L\) :
-
Tube length (m)
- \(m\) :
-
Mass flow rate (\({\text{kg}}/{\text{s}}\))
- \(n_{\text{t}}\) :
-
Number of tube passes
- \(n_{\text{y}}\) :
-
Equipment life (year)
- \(N_{\text{t}}\) :
-
Number of tubes
- \(G\) :
-
Pumping power (W)
- \(Pr\) :
-
Prandtl number
- \(P_{\text{t}}\) :
-
Tube pitch (m)
- \(Q\) :
-
Heat transfer rate (W)
- \({Re}\) :
-
Reynolds number
- \(R_{\text{l}}\) :
-
Fouling resistance (\({\text{m}}^{2} {\text{K/W}}\))
- \(S\) :
-
Heat transfer surface area (m2)
- \(T\) :
-
Temperature (K)
- \(H\) :
-
Overall heat transfer coefficient (\({\text{W}}/{\text{m}}^{2} {\text{K}}\))
- \(v\) :
-
Fluid velocity (m/s)
- \(\Delta P\) :
-
Pressure drop (Pa)
- \(\Delta T_{\text{LM}}\) :
-
Logarithmic mean temperature difference (°C)
- \(\mu\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity (Pas)
- \(\vartheta\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity (m2/s)
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density (kg/m3)
- \(\eta\) :
-
Overall pumping efficiency
- i:
-
Inlet
- o:
-
Outlet
- s:
-
Belonging to shell
- t:
-
Belonging to the tube
- e:
-
Equivalent
- w:
-
Tube wall
References
Babu BV, Munawar SA (2007) Differential evolution strategies for the optimal design of shell and tube heat exchangers. Chem Eng Sci 62(14):3720–3739
Beyer HG, Schwefel HP (2002) Evolution strategies—a comprehensive introduction. Nat Comput 1(1):3–52
Caputo AC, Pelagagge PM, Salini P (2008) Heat exchanger design based on economic optimization. Appl Therm Eng 28(10):1151–1159
Chaudhari PD, Diwekar UM, Logsdon JS (1997) An automated approach for the optimal design of heat exchangers. Ind Eng Chem Res 36(9):3685–3693
Cheng MY, Prayogo D (2014) Symbiotic organisms search: a new metaheuristic optimization algorithm. Comput Struct 139:98–112
Costa ALH, Queiroz EM (2008) Design optimization of shell and tube heat exchanger. Appl Therm Eng 28(14–15):1798–1805
Deshpande AM, Phatnani GM, Kulkarni AJ (2013) Constraint handling in firefly algorithm. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on cybernetics, Lausanne, Switzerland, 13–15 June 2013, pp 186–190
Dorigo M (1992) Optimization, learning and natural algorithms. Ph.D. Thesis, Polytechnic University of Milan, Italy
Eberhart RC, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: Proceedings of the sixth international symposium on micro machine and human science, vol 1, pp 39–43
Farmer JD, Packard NH, Perelson AS (1986) The immune system, adaptation, and machine learning. Physica D 22(1):187–204
Fraas AP (1989) Heat exchanger design, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Geem ZW, Kim JH, Loganathan GV (2001) A new heuristic optimization algorithm: harmony search. Simulation 76(2):60–68
Glover F (1977) Heuristics for integer programming using surrogate constraints. Decis Sci 8(1):156–166
Glover F (1986) Future paths for integer programming and links to artificial intelligence. Comput Oper Res 13(5):533–549
Goldberg DE, Holland JH (1988) Genetic algorithms and machine learning. Mach Learn 3(2):95–99
Hadidi A, Nazari A (2013) A new design approach for shell-and-tube heat exchangers using imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA) from economic point of view. Energy Convers Manag 67:66–74
Hadidi A, Nazari A (2013) Design and economic optimization of shell-and-tube heat exchangers using biogeography-based (BBO) algorithm. Appl Therm Eng 51(1–2):1263–1272
Hewitt GF (1998) Heat exchanger design handbook. Begell House, New York
Hilbery R, Janiga G, Baron R, Thevenin D (2006) Multi-objective shape optimization of a heat exchanger using parallel genetic algorithm. Int J Heat Mass Transf 49(15):2567–2577
Holland JH, Booker LB, Colombetti M, Dorigo M, Goldberg DE, Forrest S, Wilson SW (2000) What is a learning classifier system? In learning classifier systems, (3–32). Springer, Berlin
Jegede FO, Polley GT (1992) Optimum heat exchanger design: process design. Chem Eng Res Des 70(A2):133–141
Kara YA, Güraras Ö (2004) A computer program for designing of shell-and-tube heat exchangers. Appl Therm Eng 24(13):1797–1805
Karaboga D (2005) An idea based on honey bee swarm for numerical optimization, vol 200. Technical report-tr06, Erciyes University, Engineering Faculty, Computer Engineering Department
Kazemzadeh Azad S, Hasançebi O (2014) An elitist self-adaptive step-size search for structural design optimization. Appl Soft Comput 19:226–235
Kazemzadeh Azad S, Hasançebi O, Kazemzadeh Azad S (2013) Upper bound strategy for metaheuristic based design optimization of steel frames. Adv Eng Softw 57:19–32
Kazemzadeh Azad S, Hasançebi O, Saka MP (2014) Guided stochastic search technique for discrete sizing optimization of steel trusses: a design-driven heuristic approach. Comput Struct 134:62–74
Kern DQ (1950) Process Heat Transfer, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Kirkpatrick S, Vecchi MP (1983) Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 220(4598):671–680
Krishnanand KN, Ghose D (2005) Detection of multiple source locations using a glowworm metaphor with applications to collective robotics. In: Proceedings 2005 IEEE swarm intelligence symposium, SIS 2005, IEEE, pp 84–91
Krishnasamy G, Kulkarni AJ, Paramesram R (2014) A hybrid approach for data clustering based on modified cohort intelligence and K-means. Expert Syst Appl 41(13):6009–6016
Kulkarni AJ, Baki MF, Chaouch BA (2016) Application of the cohort-intelligence optimization method to three selected combinatorial optimization problems. Eur J Oper Res 250(2):427–447
Kulkarni AJ, Durugkar IP, Kumar M (2013) Cohort intelligence: a self-supervised learning behavior. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics (SMC), pp 1396–1400
Kulkarni AJ, Krishnasamy G, Abraham A (2017) Cohort Intelligence: a socio-inspired optimization method, Intelligent Systems Reference Library, 114. Springer, Berlin. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-44254-9, ISBN: 978-3-319-44254-9
Kulkarni AJ, Shabir H (2016) Solving 0–1 knapsack problem using cohort intelligence algorithm. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 7:1–15
Kulkarni AJ, Kale IR, Tai K (2016) Probability collectives for solving discrete and mixed variable problems. Int J Comput Aided Eng Technol 8(4):325–361
Kulkarni O, Kulkarni N, Kulkarni AJ, Kakandikar G (2016) Constrained cohort intelligence using static and dynamic penalty function approach for mechanical components design. Int J Parallel Emerg Distrib Syst. doi: 10.1080/17445760.2016.1242728
Laumanns M, Rudolph G, Schwefel HP (1998) A spatial predator–prey approach to multi-objective optimization: a preliminary study. In: Parallel problem solving from nature—PPSN V. Springer, Berlin, pp 241–249
Liu Y, Passino KM (2002) Biomimicry of social foraging bacteria for distributed optimization: models, principles, and emergent behaviors. J Optim Theory Appl 115(3):603–628
Mariani VC, Duck ARK, Guerra FA, Coelho LDS, Rao RV (2012) A chaotic quantum-behaved particle swarm approach applied to optimization of the heat exchanger. Appl Therm Eng 42:119–128
Matyas J (1965) Random optimization. Autom Remote Control 26(2):246–253
Mizutani FT, Pessoa FLP, Queiroz EM, Hauan S, Grossmann IE (2003) Mathematical programming model for heat-exchanger network synthesis including detailed heat-exchanger designs. Shell-and-tube heat exchanger design. Ind Eng Chem Res 42:4009–4018
Moscato P (1989) On evolution, search, optimization, genetic algorithms and martial arts: Towards memetic algorithms. Caltech concurrent computation program, C3P Report, 826
Muralikrishna K, Shenoy UV (2000) Heat exchanger targets for minimum area and cost. Chem Eng Res Des 78(2):161–167
Ohadi MM (2000) The engineering handbook, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Patel VK, Rao RV (2010) Design optimization of shell-and-tube heat exchanger using particle swarm optimization technique. Appl Therm Eng 30(11–12):1417–1425
Patterson JH, Talbot FB, Slowinski R, Wegłarz J (1990) Computational experience with a backtracking algorithm for solving a general class of precedence and resource-constrained scheduling problems. Eur J Oper Res 49(1):68–79
Peters MS, Timmerhaus KD (1991) Plant design and economics for chemical engineers, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Poddar TK, Polley GT (1996) Heat exchanger design through parameter plotting. Chem Eng Res Des 74(8):849–852
Ponce-Ortega JM, Serna-González M, Jiménez-Gutiérrez A (2009) Use of genetic algorithms for the optimal design of shell-and-tube heat exchangers. Appl Therm Eng 29(2):203–209
Rabanal P, Rodríguez I, Rubio F (2007) Using river formation dynamics to design heuristic algorithms. In: Unconventional computation. Springer, Berlin, pp 163–177
Rastrigin LA (1963) The convergence of the random search method in the extremal control of a many parameter systems. Autom Remote Control 24(10):1337–1342
Rashedi E, Nezamabadi-pour H, Saryazdi S (2009) GSA: a gravitational search algorithm. Inf Sci 179(13):2232–2248
Ravagnani MASS, Da Silva AP, Andrade AL (2003) Detailed equipment in heat exchanger networks synthesis and optimization. Appl Therm Eng 23:141–151
Reppish M, Zagermann S (1995) A new design method for segmentally baffled heat exchangers. Comput Chem Eng 19:137–142
Rosenhow WM, Polley PJ (1973) Handbook of heat transfer, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Sahin AS, Kilic B, Kilic U (2011) Design and economic optimization of shell-and-tube heat exchangers using artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. Energy Convers Manag 52(11):1417–1425
Selbas R, Kizilkan O, Reppich M (2006) A new design approach for shell-and-tube heat exchangers using genetic algorithm from economic point of view. Chem Eng Process 45(4):268–275
Serth RW (2007) Process heat transfer, 1st edn. Principles and applications. Elsevier Science and Technology Books, Amsterdam
Shah RK, Bell KJ (2000) Handbook of thermal engineering. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Shastri AS, Jadhav PS, Kulkarni AJ, Abraham A (2015) Solution to constrained test problems using cohort intelligence algorithm, advances in intelligent and soft computing 424. In: Snacel V, Abraham A, Kromer P, Pant M, Muda AK (eds) Innovations in bio-inspired computing and applications. Springer, Berlin, pp 427–435
Simon D (2008) Biogeography-based optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 12(6):702–713
Sinnot RK (2005) Coulson and Richardson’s chemical engineering: chemical engineering design. 4th edn. vol 6. Elsevier, Oxford, MA
Storn R, Price K (1997) Differential evolution—a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J Global Optim 11(4):341–359
Sun S, Lu Y, Yan C (1993) Optimization in calculation of shell and tube heat exchanger. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer 20(5):675–685
Taal M, Bulatov I, Klemes J, Stehlik P (2003) Cost estimation and energy price forecast for economic evaluation of retrofit projects. Appl Therm Eng 23(14):1819–1835
Turgut OE, Turgut MS, Coban MT (2014) Design and economic investigation of shell and tube heat exchangers using improved intelligent tuned harmony search algorithm. Ain Shams Eng J 5(4):1215–1231
Wald RM (1993) Black hole entropy is the Noether charge. Phys Rev D 48(8):R3427
Wildi-Tremblay P, Gosselin L (2007) Minimizing shell and tube heat exchanger cost with genetic algorithms and considering maintenance. Int J Energy Res 31(9):867–885
Yang XS (2009) Firefly algorithms for multimodal optimization. In: Stochastic algorithms: foundations and applications. Springer, Berlin, pp 169–178)
Yang XS, Deb S (2009) Cuckoo search via Lévy flights. In: World congress on nature and biologically inspired computing, NaBIC 2009. IEEE, pp 210–214
Yang XS (2010) A new metaheuristic bat-inspired algorithm. In Nature inspired cooperative strategies for optimization (NICSO 2010). Springer, Berlin, pp 65–74
Zaslavskii GM (1978) The simplest case of a strange attractor. Phys Lett A 69(3):145–147
Zhang L, Wang F, Sun T, Xu B (2016) A constrained optimization method based on BP neural network. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-016-2455-9
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their comments which certainly helped to enrich the quality of the work presented in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhavle, S.V., Kulkarni, A.J., Shastri, A. et al. Design and economic optimization of shell-and-tube heat exchanger using cohort intelligence algorithm. Neural Comput & Applic 30, 111–125 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2683-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2683-z