Abstract
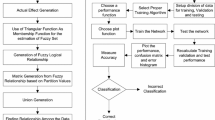
This paper presents a new method based on fuzzy cognitive map (FCM) and possibilistic fuzzy c-means (PFCM) clustering algorithm for categorizing celiac disease (CD). CD is a complex disorder whose development is affected by genetics (HLA alleles) and gluten ingestion. The celiac patients who are not treated are at a high risk of cancer, malignant lymphoma, and small bowel neoplasia. Therefore, CD diagnosis and grading are of paramount importance. The proposed FCM models human thinking for the purpose of classifying patients suffering from CD. We used the latest grading method where three grades A, B1, and B2 are used. To improve FCM efficiency and classification capability, a nonlinear Hebbian learning algorithm is applied for adjusting the FCM weights. To this end, 89 cases are studied. Three experts extracted seven main determinant characteristics of CD which were considered as FCM concepts. The mutual effects of these concepts on one another and on the final concept were expressed in the form of fuzzy rules and linguistic variables. Using the center of gravity defuzzifier, we obtained the numerical values of these weights and obtained the total weight matrix. Ultimately, combining the FCM model with PFCM algorithm, we obtained the grades A, B1, and B2 accuracies as 88, 90, and 91%, respectively. The main advantage of the proposed FCM is the good transparency and interpretability in the decision-making procedure, which make it a suitable tool for daily usage in the clinical practice.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stylios CD, Groumpos PP (2000) Fuzzy cognitive maps in modeling supervisory control systems. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 8:83–98
Amirkhani A, Shirzadeh M, Papageorgiou EI, Mosavi MR (2016) Visual-based quadrotor control by means of fuzzy cognitive maps. ISA Trans 60:128–142
Mourhir A, Rachidi T, Papageorgiou EI et al (2016) A cognitive map framework to support integrated environmental assessment. Environ Model Softw 77:81–94
Georgopoulos VC, Malandraki GA, Stylios CD (2003) A fuzzy cognitive map approach to differential diagnosis of specific language impairment. Artif Intell Med 29:261–278
Amirkhani A, Mosavi MR, Naimi A (2015) Unsupervised fuzzy cognitive map in diagnosis of breast epithelial lesions. In: IEEE 22nd Iranian conference on biomedical engineering, pp 115–119
Papageorgiou EI (2011) A new methodology for decisions in medical informatics using fuzzy cognitive maps based on fuzzy rule-extraction techniques. Appl Soft Comput 11:500–513
Song H, Miao C, Roel W et al (2010) Implementation of fuzzy cognitive maps based on fuzzy neural network and application in prediction of time series. Fuzzy Syst IEEE Trans 18:233–250
Stach W, Kurgan LA, Pedrycz W (2008) Numerical and linguistic prediction of time series with the use of fuzzy cognitive maps. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 16:61–72
Papakostas GA, Boutalis YS, Koulouriotis DE, Mertzios BG (2008) Fuzzy cognitive maps for pattern recognition applications. Int J Pattern Recogn Artif Intell 22:1461–1486
Papageorgiou EI, Stylios CD, Groumpos PP (2004) Active Hebbian learning algorithm to train fuzzy cognitive maps. Int J Approx Reason 37:219–249
Papageorgiou E, Stylios C, Groumpos P (2003) Fuzzy cognitive map learning based on nonlinear Hebbian rule. In: AI 2003 advanced artificial intelligence. Springer, pp 256–268
Papageorgiou EI, Parsopoulos KE, Stylios C et al (2005) Fuzzy cognitive maps learning using particle swarm optimization. J Intell Inf Syst 25:95–121
Stach W, Kurgan L, Pedrycz W, Reformat M (2005) Genetic learning of fuzzy cognitive maps. Fuzzy Sets Syst 153:371–401
Stach W (2010) Learning and aggregation of fuzzy cognitive maps—an evolutionary approach. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada. [Online]. Available: http://gradworks.umi.com/NR/62/NR62921.html
Papageorgiou EI (2012) Learning algorithms for fuzzy cognitive maps—a review study. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 42:150–163
Papageorgiou EI, Salmeron JL (2013) A review of fuzzy cognitive maps research during the last decade. Fuzzy Syst IEEE Trans 21:66–79
Papageorgiou EI, Stylios CD, Groumpos PP (2008) The soft computing technique of fuzzy cognitive maps for decision making in radiotherapy. In: Haas O, Burnham K (eds) Intelligent and adaptive systems in medicine, chap 5. Taylor & Francis, New York, pp 106–127
Papageorgiou EI (2012) Fuzzy cognitive map software tool for treatment management of uncomplicated urinary tract infection. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 105:233–245
Papageorgiou EI, Spyridonos PP, Stylios CD et al (2006) Advanced soft computing diagnosis method for tumour grading. Artif Intell Med 36:59–70
Amirkhani A, Mosavi MR, Mohammadizadeh F, Shokouhi SB (2014) Classification of intraductal breast lesions based on the fuzzy cognitive map. Arab J Sci Eng 39:3723–3732
Papageorgiou EI, Froelich W (2012) Application of evolutionary fuzzy cognitive maps for prediction of pulmonary infections. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 16:143–149
Ludvigsson JF, Leffler DA, Bai JC et al. (2013) The Oslo definitions for coeliac disease and related terms. Gut 62(1):43–52
Nasiriyan-Rad H, Amirkhani A, Naimi A, Mohammadi K (2016) Learning fuzzy cognitive map with PSO algorithm for grading celiac disease. In: IEEE 23rd Iranian conference on biomedical engineering
March MN (1992) Gluten, major histocompatibility complex, and the small intestine. Gastroenterology 102:330–354
Oberhuber G, Granditsch G, Vogelsang H (1999) The histopathology of coeliac disease: time for a standardized report scheme for pathologists. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 11:1185
Corazza GR, Villanacci V (2005) Coeliac disease. J Clin Pathol 58:573–574
Axelrod R (1976) Structure of decisions: the cognitive maps of political elites. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Kosko B (1986) Fuzzy cognitive maps. Int J Man Mach Stud 24:65–75
Kim J, Han M, Lee Y, Park Y (2016) Futuristic data-driven scenario building: incorporating text mining and fuzzy association rule mining into fuzzy cognitive map. Expert Syst Appl 57:311–323
Bueno S, Salmeron JL (2009) Benchmarking main activation functions in fuzzy cognitive maps. Expert Syst Appl 36:5221–5229
Hassoun MH (1995) Fundamentals of artificial neural networks. MIT Press, London
Papageorgiou EI, Stylios C, Groumpos PP (2006) Unsupervised learning techniques for fine-tuning fuzzy cognitive map causal links. Int J Hum Comput Stud 64:727–743
Kannappan A, Tamilarasi A, Papageorgiou EI (2011) Analyzing the performance of fuzzy cognitive maps with non-linear Hebbian learning algorithm in predicting autistic disorder. Expert Syst Appl 38:1282–1292
Dunn JC (1973) A fuzzy relative of the ISODATA process and its use in detecting compact well-separated clusters. Cybern Syst 3(3):32–57
Bezdek JC (1973) Fuzzy mathematics in pattern classification. Ph.D. dissertation, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY
Zhang L, Lu W, Liu X et al (2016) Fuzzy c-means clustering of incomplete data based on probabilistic information granules of missing values. Knowl-Based Syst 99:51–70
Timm H, Borgelt C, Döring C, Kruse R (2004) An extension to possibilistic fuzzy cluster analysis. Fuzzy Sets Syst 147:3–16
Zhang J-S, Leung Y-W (2004) Improved possibilistic c-means clustering algorithms. Fuzzy Syst IEEE Trans 12:209–217
Pal NR, Pal K, Keller JM, Bezdek JC (2005) A possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Fuzzy Syst IEEE Trans 13:517–530
Namkoong Y, Heo G, Woo YW (2010) An extension of possibilistic fuzzy c-means with regularization. In: 2010 IEEE international conference on fuzzy system (FUZZ). IEEE, pp 1–6
Diri B, Albayrak S (2008) Visualization and analysis of classifiers performance in multi-class medical data. Expert Syst Appl 34:628–634
Zhang D-Q, Chen S-C (2003) Clustering incomplete data using kernel-based fuzzy c-means algorithm. Neural Process Lett 18:155–162
Babuka R, Van der Veen PJ, Kaymak U (2002) Improved covariance estimation for Gustafson–Kessel clustering. In: 2002 IEEE international conference on fuzzy system (FUZZ), pp 1081–1085
Honda K, Sugiura N, Ichihashi H, Araki S (2001) Collaborative filtering using principal component analysis and fuzzy clustering. In: Web intelligence: research and development. Springer, pp 394–402
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amirkhani, A., Mosavi, M.R., Mohammadi, K. et al. A novel hybrid method based on fuzzy cognitive maps and fuzzy clustering algorithms for grading celiac disease. Neural Comput & Applic 30, 1573–1588 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2765-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2765-y