Abstract
The fuzzy decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory (fuzzy DEMATEL) has been used to solve various multi-criteria group decision-making problems where triangular type-1 fuzzy sets are utilized in defining decision makers’ linguistic evaluation. Most of the fuzzy DEMATEL modifications are built from linguistic variables based on type-1 fuzzy sets (T1FS). Previous literature suggests that interval type-2 fuzzy sets (IT2FS) can offer an alternative that can handle vagueness and uncertainty. This paper proposes a modification fuzzy DEMATEL characterized by IT2FS for linguistic variables. Differently from the typical fuzzy DEMATEL which directly utilizes triangular type-1 fuzzy numbers, this modification introduces trapezoidal IT2 fuzzy numbers to enhance evaluation in the group decision-making environment. This new modification includes linguistic variables expressed by IT2FS and an expected value method for normalizing upper and lower memberships of IT2FS to crisp numbers. The proposed modification is applied to a case of knowledge management (KM) where eleven criteria are considered. Three experts in KM were invited to provide linguistic judgments with respect to the criteria, and the eight-step computational procedure of the proposed modification was implemented without losing the originality of the DEMATEL method. The results unveiled that ‘trust’ is the most influential criteria in KM. Therefore, trust is a phenomenon that impacts on the success of KM. Comparable results are also presented to check the feasibility of the proposed method. It is shown that the criteria weight and the causal relationship of criteria using the proposed method are consistent with the other two methods.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Abdullah L, Najib L (2014) A new type-2 fuzzy set of linguistic variables for the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. Expert Syst Appl 41:3297–3305
Abdullah L, Sunadia J, Imran T (2009) A new analytic hierarchy process in multi-attribute group decision making. Int J Soft Comput 4(5):208–2014
Asan U, Erhan BC, Polat S (2004) A fuzzy approach to qualitative cross impact analysis. Omega 32(6):443–458
Baas SM, Kwakernaak H (1977) Rating and ranking of multiple aspect alternative using fuzzy sets. Automatica 13:47–58
Bixler C (2002) Knowledge management and the learning organization converge. KM World 11(4):21–22
Bortolan G, Degani R (1985) A review of some methods for ranking fuzzy subsets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 15:1–19
Chang B, Chang CW, Wu CH (2011) Fuzzy DEMATEL method for developing supplier selection criteria. Expert Syst Appl 38:1850–1858
Chen SM, Lee LW (2010) Fuzzy multiple attributes group decision-making based on ranking values and the arithmetic operations of interval type-2 fuzzy sets. Experts Syst Appl 37:824–833
Chiu YJ, Chen HC, Tzeng GH, Shyu JZ (2006) Marketing strategy based on customer behaviour for the LCD-TV. Int J Manag Decis Mak 7:143–165
Dalalah D, Hayajneh M, Batieha F (2011) A fuzzy multi-criteria decision making model for supplier selection. Expert Syst Appl 38:8384–8391
Gabus A, Fontela E (1972) World problems, an invitation to further thought within the framework of DEMATEL. Battelle Geneva Research Centre, Geneva
Gabus A, Fontela E (1973) Perceptions of the world problematique: communication procedure, communicating with those bearing collective responsibility (DEMATEL report no. 1). Battelle Geneva Research Centre, Geneva
Hagras H, Doctor F, Callaghan V, Lopez A (2007) An incremental adaptive lifelong learning approach for type-2 fuzzy embedded agents in ambient intelligent environments. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 15(1):41–55
Hosseini MB, Tarokh MJ (2013) Type-2 fuzzy set extension of DEMATEL method combined with perceptual computing for decision making. J Ind Eng Int 9:1–10
Hu J, Zhang Y, Chen X, Liu Y (2013) Multi-criteria decision making method based on possibility degree of interval type-2 fuzzy number. Knowl Based Syst 43:21–29
Huang CY, Shyu JZ, Tzeng GH (2007) Reconfiguring the innovation policy portfolios for Taiwan’s SIP Mall industry. Technovation 27(12):744–765
Jammeh EA, Fleury M, Wagner C, Hagras H, Ghanbari M (2009) Interval type-2 fuzzy logic congestion control for video streaming across IP networks. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 17(5):1123–1142
Jassbi J, Mohamadnejad F, Nasrollahzadeh H (2011) A fuzzy DEMATEL framework for modeling cause and effect relationships of strategy map. Expert Syst Appl 38(5):5967–5973
Jeng DJF, Tzeng GH (2012) Social influence on the use of clinical decision support systems: revisiting the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology by the fuzzy DEMATEL technique. Comput Ind Eng 62(3):819–828
Kilic M, Kaya I (2015) Investment project evaluation by a decision making methodology based on type-2 fuzzy sets. Appl Soft Comput 27:399–410
Kundu P, Kar S, Maiti M (2015) Multi-item solid transportation problem with type-2 fuzzy parameters. Appl Soft Comput 31:61–80
Lee ES, Li RL (1988) Comparison of fuzzy numbers based on the probability measure of fuzzy events. Comput Math Appl 15:887–896
Lin RJ (2013) Using fuzzy DEMATEL to evaluate the green supply chain management practices. J Clean Prod 40:32–39
Liou JH, Chuang YC, Tzeng GH (2014) A fuzzy integral-based model for supplier evaluation and improvement. Inf Sci 266:199–217
Liu P, Yang L, Wang L, Li S (2014) A solid transportation problem with type-2 fuzzy variables. Appl Soft Comput 24:543–558
Mangla SK, Kumar P, Barua MK (2016) A fuzzy DEMATEL-based approach for evaluation of risks in green initiatives in supply chain. Int J Logist Syst Manag 24(2):226–243
Martensson M (2000) A critical review of knowledge management as a management tool. J Knowl Manag 4(3):204–216
Mendel JM (2001) Uncertain rule-based fuzzy logic systems: Introduction and new directions. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River
Mendel JM (2007) Computing with words and its relationships with fuzzistics. Inf Sci 177(4):988–1006
Mendel JM, John RI, Liu FL (2006) Interval type-2 fuzzy logical systems made simple. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 14(6):808–821
Mendel JM, Wu DR (2010) Perceptual computing: aiding people in making subjective judgments. Wiley, New York
Mendel JM, Zadeh LA, Trillas E, Yager RR, Lawry J, Hagras H, Guadarrama S (2010) What computing with words means to me. IEEE Comput Intell Mag 5(1):20–26
Ozen T, Garibaldi JA (2004) Effect of type-2 fuzzy membership function shape on modelling variation in human decision making. IEEE Int Conf Fuzzy Syst 1–3:971–976
Paliszkiewicz J (2010) Organizational trust—a critical review of the empirical research. In: Proceedings of 2010 international conference on technology innovation and industrial management, 16–18 June 2010 Pattaya, Thailand
Politis JD (2003) The connection between trust and knowledge management: what are its implications for team performance. J Knowl Manag 7(5):55–66
Sangaiah AK, Subramaniam PR, Zheng X (2015) A combined fuzzy DEMATEL and fuzzy TOPSIS approach for evaluating GSD project outcome factors. Neural Comput Appl 26(5):1025–1040
Tamura M, Nagata H, Akazawa K (2002) Extraction and systems analysis of factors that prevent safety and security by structural models. In 41st SICE annual conference, Osaka, Japan
Trksen IB (2002) Type 2 representation and reasoning for CWW. Fuzzy Sets Syst 127(1):17–36
Tsai WH, Yang CC, Leu JD, Lee YF, Yang CH (2013) An integrated group decision making support model for corporate financing decisions. Group Decis Negot 22(6):1103–1127
Tzeng GH, Huang CY (2012) Combined DEMATEL technique with hybrid MCDM methods for creating the aspired intelligent global manufacturing & logistics systems. Ann Oper Res 197(1):159–190
Uygun Ö, Dede A (2016) Performance evaluation of green supply chain management using integrated fuzzy multi-criteria decision making techniques. Comput Ind Eng 102:502–511
Von Altrock C (1996) Fuzzy logic and neuro fuzzy applications in business and finance. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey
Wu DR, Mendel JM (2008) Corrections to aggregation using the linguistic weighted average and interval type-2 fuzzy sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 16(6):1664–1666
Wu DR, Mendel JM (2011) On the continuity of type-1 and interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 19(1):179–192
Yang YPO, Shieh HM, Tzeng GH (2013) A VIKOR technique based on DEMATEL and ANP for information security risk control assessment. Inf Sci 232(20):482–500
Zadeh LA (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning—I. Inf Sci 8(3):199–249
Zhang Z, Zhang S (2013) A novel approach to multi attribute group decision making based on trapezoidal interval type-2 fuzzy soft sets. Appl Math Model 37:4948–4971
Acknowledgements
The present work is part of the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme, Project Number 59389. We acknowledge financial support from the Malaysian Ministry of Higher Education and Universiti Malaysia Terengganu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Appendices
Appendix 1
1.1 Trapezoidal fuzzy numbers
A trapezoidal fuzzy number can be defined as \( \tilde{m} = \left( {a,b,c,d} \right) \) where the membership functions \( \mu_{{\tilde{m}}} \) of \( \tilde{m} \) is given by:
where b and c are called a mode interval of \( \tilde{m} \), a and d are called lower and upper limits of \( \tilde{m} \), respectively [35].
Let \( \tilde{A} \) and \( \tilde{B} \) be two positive trapezoidal fuzzy numbers parameterized by \( \left( {a_{1} ,a_{2} ,a_{3} ,a_{4} } \right) \) and \( \left( {b_{1} ,b_{2} ,b_{3} ,b_{4} } \right) \), then the arithmetic operations of these two trapezoidal fuzzy numbers are given as follows [6].
1.2 Type-1 fuzzy set
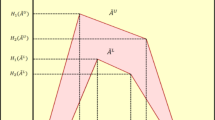
Let \( \tilde{A} \) be a type-1 trapezoidal fuzzy set, \( \tilde{A} = \left( {a_{1} ,a_{2} ,a_{3} ,a_{4} ;H_{1} \left( A \right),H_{2} \left( A \right)} \right) \). Figure 2 shows the \( \tilde{A} \) where \( H_{1} \left( {\tilde{A}} \right) \) denotes the membership value of the element \( a_{2} ,H_{2} \left( {\tilde{A}} \right) \) denotes the membership value of the element \( a_{3} ,0 \le H_{1} \left( A \right) \le 1 \) and \( 0 \le H_{2} \left( A \right) \le 1 \). If \( a_{2} = a_{3} \), then the type-1 fuzzy set \( \tilde{A} \) becomes a triangular T1FS.
1.3 Interval type-2 fuzzy set
We briefly present some definitions of T2FS and IT2 FS. Mendel et al. [30] proposed the following definitions of T2FS.
Definition 1.1
A type-2 fuzzy set \( \tilde{\tilde{A}} \) in the universe of discourse X can be represented by a type-2 membership function \( {\mu_{{\tilde{\tilde{A}}}}} \) shown as follows:
where Jx denotes an interval in [0, 1].
The type-2 fuzzy set \( \tilde{\tilde{A}} \) also can be written as follows.
Definition 1.2
A type-2 fuzzy set \( \tilde{\tilde{A}} \) in the universe of discourse X can be represented by a type-2 membership function \( \mu_{{\tilde{\tilde{A}}}} \).
where \( J_{x} \subseteq \left[ {0,1} \right] \) and \( \int {\int {} } \) denotes the union over all admissible x and u.
For simplicity, the T2FS \( \tilde{\tilde{A}} \) may be written as interval membership.
Definition 1.3
Let \( \tilde{\tilde{A}} \) be a T2FS in the universe of discourse X represented by the type-2 membership function \( \mu_{{\tilde{\tilde{A}}}} \). If all \( \mu_{{\tilde{\tilde{A}}}} \left( {x,u} \right) = 1 \), then \( \tilde{\tilde{A}} \) is called IT2 FS. An IT2 FS \( \tilde{\tilde{A}} \) can be regarded as a special case of T2FS, shown as follows:
where \( J_{x} \subseteq \left[ {0,1} \right] \).
The property of interval in defining the T2FS paves a way to introduce boundary membership of upper and lower. The upper and lower memberships are defined as follows.
Definition 1.4
The upper membership function (UMF) and lower membership function (LMF) of \( \mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{ \approx } \) are two type-1 membership functions.
The heights of the UMF and LMF of IT2 FS are also defined to characterize IT2 FS. Figure 3 shows trapezoidal IT2 FS where upper and lower fuzzy numbers are drawn as reference points.
Figure 2 shows the upper trapezoidal membership function \( \tilde{A}_{i}^{U} \) and the lower trapezoidal membership function \( \tilde{A}_{i}^{L} \) of IT2 FS \( \tilde{A}_{i} \).
1.4 Arithmetic operations of trapezoidal interval type-2 fuzzy sets
Arithmetic operations of trapezoidal IT2FSs are described by [42]. It is recalled as follows.
Definition 1.5
The addition operation between the trapezoidal IT2FS
and
is defined as follows:
Definition 1.6
The subtraction operation between the trapezoidal IT2FS
and
is defined as follows:
Definition 1.7
The multiplication operation between the trapezoidal IT2FS
and
is defined as follows:
The above definitions and arithmetic operations are prevalently employed in the proposed IT2 fuzzy DEMATEL.
Appendix 2
2.1 Appendix 2.1
Evaluation of C1 by DM1
DM1 | C1 |
|---|---|
C1 | 0 |
C2 | ((0.8,0.9,0.9,1.0;1,1), (0.85,0.9,0.9,0.95;0.9,0.9)) |
C3 | ((0.4,0.5,0.5,0.6;1,1), (0.45,0.5,0.5,0.55;0.9,0.9)) |
C4 | ((0.4,0.5,0.5,0.6;1,1), (0.45,0.5,0.5,0.55;0.9,0.9)) |
C5 | ((0.6,0.7,0.7,0.8;1,1), (0.65,0.7,0.7,0.75;0.9,0.9)) |
C6 | ((0.6,0.7,0.7,0.8;1,1), (0.65,0.7,0.7,0.75;0.9,0.9)) |
C7 | ((0.8,0.9,0.9,1.0;1,1), (0.85,0.9,0.9,0.95;0.9,0.9)) |
C8 | ((0.8,0.9,0.9,1.0;1,1), (0.85,0.9,0.9,0.95;0.9,0.9)) |
C9 | ((0.8,0.9,0.9,1.0;1,1), (0.85,0.9,0.9,0.95;0.9,0.9)) |
C10 | ((0.6,0.7,0.7,0.8;1,1), (0.65,0.7,0.7,0.75;0.9,0.9)) |
C11 | ((0.6,0.7,0.7,0.8;1,1), (0.65,0.7,0.7,0.75;0.9,0.9)) |
2.2 Appendix 2.2
Evaluation of C1 by DM2
DM2 | C1 |
|---|---|
C1 | 0 |
C2 | ((0.6,0.7,0.7,0.8;1,1), (0.65,0.7,0.7,0.75;0.9,0.9)) |
C3 | ((0.2,0.3,0.3,0.4;1,1), (0.25,0.3,0.3,0.35;0.9,0.9)) |
C4 | ((0.4,0.5,0.5,0.6;1,1), (0.45,0.5,0.5,0.55;0.9,0.9)) |
C5 | ((0.8,0.9,0.9,1.0;1,1), (0.85,0.9,0.9,0.95;0.9,0.9)) |
C6 | ((0.4,0.5,0.5,0.6;1,1), (0.45,0.5,0.5,0.55;0.9,0.9)) |
C7 | ((0.8,0.9,0.9,1.0;1,1), (0.85,0.9,0.9,0.95;0.9,0.9)) |
C8 | ((0.6,0.7,0.7,0.8;1,1), (0.65,0.7,0.7,0.75;0.9,0.9)) |
C9 | ((0.6,0.7,0.7,0.8;1,1), (0.65,0.7,0.7,0.75;0.9,0.9)) |
C10 | ((0.2,0.3,0.3,0.4;1,1), (0.25,0.3,0.3,0.35;0.9,0.9)) |
C11 | ((0.4,0.5,0.5,0.6;1,1), (0.45,0.5,0.5,0.55;0.9,0.9)) |
2.3 Appendix 2.3
Evaluation of C1 by DM3
DM3 | C1 |
|---|---|
C1 | 0 |
C2 | ((0.6,0.7,0.7,0.8;1,1), (0.65,0.7,0.7,0.75;0.9,0.9)) |
C3 | ((0.4,0.5,0.5,0.6;1,1), (0.45,0.5,0.5,0.55;0.9,0.9)) |
C4 | ((0.6,0.7,0.7,0.8;1,1), (0.65,0.7,0.7,0.75;0.9,0.9)) |
C5 | ((0.6,0.7,0.7,0.8;1,1), (0.65,0.7,0.7,0.75;0.9,0.9)) |
C6 | ((0.6,0.7,0.7,0.8;1,1), (0.65,0.7,0.7,0.75;0.9,0.9)) |
C7 | ((0.8,0.9,0.9,1.0;1,1), (0.85,0.9,0.9,0.95;0.9,0.9)) |
C8 | ((0.6,0.7,0.7,0.8;1,1), (0.65,0.7,0.7,0.75;0.9,0.9)) |
C9 | ((0.8,0.9,0.9,1.0;1,1), (0.85,0.9,0.9,0.95;0.9,0.9)) |
C10 | ((0.4,0.5,0.5,0.6;1,1), (0.45,0.5,0.5,0.55;0.9,0.9)) |
C11 | ((0.4,0.5,0.5,0.6;1,1), (0.45,0.5,0.5,0.55;0.9,0.9)) |
Appendix 3
Initial direct-relation matrix, A
C1 | C2 | C3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
C1 | ((0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) |
C2 | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) | ((0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) | ((0.6 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.8) | (0.65 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.75)) |
C3 | ((0.33 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.53) | (0.38 | 0.433 | 0.433 | 0.48)) | ((0.6 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.8) | (0.65 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.75)) | ((0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) |
C4 | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.517 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) |
C5 | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) | ((0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6) | (0.45 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.55)) |
C6 | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.53) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) | ((0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6) | (0.45 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.55)) |
C7 | ((0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1) | (0.85 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.95)) | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.716 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) |
C8 | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) | ((0.33 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.53) | (0.38 | 0.433 | 0.433 | 0.48)) | ((0.33 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.53) | (0.383 | 0.433 | 0.433 | 0.48)0 |
C9 | ((0.73 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.93) | (0.78 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.88)) | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) | ((0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6) | (0.45 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.55)) |
C10 | ((0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6) | (0.45 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.55)) | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.517 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) |
C11 | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.53) | (0.583 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) |
C4 | C5 | C6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
C1 | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | ((0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) |
C2 | ((0.80 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 1.00) | (0.85 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.95)) | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) | ((0.40 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.60) | ((0.45 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.55)) |
C3 | ((0.40 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.60) | (0.45 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.55)) | ((0.33 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.53) | (0.38 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.48)) | ((0.40 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.60) | ((0.45 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.55)) |
C4 | ((0`00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) | ((0.40 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.60) | (0.45 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.55)) | ((0.40 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.60) | ((0.45 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.55)) |
C5 | ((0.33 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.53) | (0.38 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.48)) | ((0`00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | ((0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) |
C6 | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) | ((0.33 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.53) | (0.38 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.48)) | ((0`00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) |
C7 | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | (0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | ((0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) |
C8 | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | (0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) | ((0.73 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.93) | (0.78 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.88)) | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | ((0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) |
C9 | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) | ((0.40 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.60) | ((0.45 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.55)) |
C10 | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) | ((0.27 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.47) | (0.32 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.42)) | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | ((0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) |
C11 | ((0.40 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.60) | (0.45 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.55)) | ((0.40 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.60) | (0.45 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.55)) | ((0.33 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.53) | ((0.38 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.48)) |
C7 | C8 | C9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
C1 | ((0.73 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.93) | (0.78 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.88)) | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) |
C2 | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | (0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) | ((0.33 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.53) | (0.38 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.48)) | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | (0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) |
C3 | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | (0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) | ((0.27 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.47) | (0.32 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.42)) | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) |
C4 | ((0.40 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.60) | (0.45 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.55)) | ((0.40 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.60) | (0.45 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.55)) | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) |
C5 | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | (0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) |
C6 | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | (0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | (0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) |
C7 | ((0`00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) | ((0.40 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.60) | (0.45 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.55)) | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | (0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) |
C8 | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) | ((0`00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | (0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) |
C9 | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) | ((0`00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) |
C10 | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | (0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) |
C11 | ((0.80 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 1.00) | (0.85 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.95)) | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) |
C10 | C11 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
C1 | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) |
C2 | ((0.33 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.53) | (0.38 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.48)) | ((0.33 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.53) | (0.38 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.48)) |
C3 | ((0.33 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.53) | (0.38 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.48)) | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) |
C4 | ((0.67 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.87) | (0.72 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.82)) | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) |
C5 | ((0.40 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.60) | (0.45 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.55)) | ((0.40 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.60) | (0.45 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.55)) |
C6 | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) |
C7 | ((0.47 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.67) | (0.52 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.62)) | ((0.80 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 1.00) | (0.85 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.95)) |
C8 | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) |
C9 | ((0.33 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.53) | (0.38 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.48)) | ((0.33 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.53) | (0.38 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.48)) |
C10 | ((0`00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) | ((0.60 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.80) | (0.65 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.75)) |
C11 | ((0.53 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.73) | (0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.68)) | ((0`00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) |
Appendix 4
Normalized initial direct-relation matrix, D
C1 | C2 | C3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
C1 | ((0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) |
C2 | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) | ((0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) |
C3 | ((0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07) | (0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06)) | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) | ((0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) |
C4 | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) |
C5 | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) |
C6 | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.07) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) |
C7 | ((0.10 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.13) | (0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.12)) | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) |
C8 | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) | ((0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07) | (0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06)) | ((0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07) | (0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06)) |
C9 | ((0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.12) | (0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11)) | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) |
C10 | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) |
C11 | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.07) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) |
C4 | C5 | C6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
C1 | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) |
C2 | ((0.10 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.13) | (0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.12)) | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) |
C3 | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) | ((0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07) | (0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06)) | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) |
C4 | ((0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) |
C5 | ((0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07) | (0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06)) | ((0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) |
C6 | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) | ((0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07) | (0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06)) | ((0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) |
C7 | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) |
C8 | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) | ((0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.12) | (0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11)) | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) |
C9 | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) |
C10 | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) | ((0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06) | (0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05)) | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) |
C11 | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) | ((0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07) | (0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06)) |
C7 | C8 | C9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
C1 | ((0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.12) | (0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11)) | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) |
C2 | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) | ((0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07) | (0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06)) | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) |
C3 | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) | ((0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06) | (0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05)) | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) |
C4 | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) |
C5 | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) |
C6 | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) |
C7 | ((0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) |
C8 | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) | ((0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) |
C9 | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) | ((0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) |
C10 | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) |
C11 | ((0.10 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.13) | (0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.12)) | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) |
C10 | C11 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
C1 | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) |
C2 | ((0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07) | (0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06)) | ((0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07) | (0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06)) |
C3 | ((0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07) | (0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06)) | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) |
C4 | ((0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11) | (0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10)) | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) |
C5 | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) | ((0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.08) | (0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07)) |
C6 | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) |
C7 | ((0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08) | (0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08)) | ((0.10 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.13) | (0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.12)) |
C8 | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) |
C9 | ((0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07) | (0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06)) | ((0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07) | (0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06)) |
C10 | ((0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) | ((0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10) | (0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09)) |
C11 | ((0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09) | (0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09)) | ((0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00) | (0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00)) |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdullah, L., Zulkifli, N. A new DEMATEL method based on interval type-2 fuzzy sets for developing causal relationship of knowledge management criteria. Neural Comput & Applic 31, 4095–4111 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3304-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3304-1