Abstract
Brain emotional learning-based intelligent controller (BELBIC) is a developed class of model-free learning controllers (MFC), which has been inspired from the MFC mechanism of human brain. BELBIC suffers from a major drawback that is related to the learning module. The learning module of BELBIC is not universal approximator and cannot be used for model-based applications. In this paper, a generalized BELBIC (G-BELBIC) is proposed which is inspired from a model-based learning controller (MBC) of brain. In contrast to BELBIC, proposed G-BELBIC applies a nonlinear learning module with universal approximation (UA) property and can be applicable in various MBC engineering applications. The UA proof and stability analysis of G-BELBIC are presented, and the novel controller is tested on single-link robot arm and continuous stirred tank reactor as case studies. Comparative results indicate the superiority of the approach in terms of higher control accuracy and robustness property.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Notes
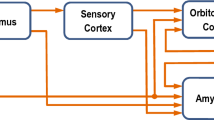
For more simplicity, the notation of Ai and Oi applied in some references is not used in this presentation.
References
Lucas Caro, Shahmirzadi Danial, Sheikholeslami Nima (2004) Introducing BELBIC: brain emotional learning based intelligent controller. Intell Autom Soft Comput 10(1):11–21
Lucas Caro, Milasi Rasoul M, Araabi Babak N (2006) Intelligent modeling and control of washing machine using locally linear neuro-fuzzy (llnf) modeling and modified brain emotional learning based intelligent controller (BELBIC). Asian J Control 8(4):393–400
Rouhani H et al (2007) Brain emotional learning based intelligent controller applied to neurofuzzy model of micro-heat exchanger. Expert Syst Appl 32(3):911–918
Mehrabian AR, Lucas C, Roshanian J (2006) Aerospace launch vehicle control: an intelligent adaptive approach. Aerosp Sci Technol 10(2):149–155
Sharbafi MA, Lucas C, Daneshvar R (2010) Motion control of omni-directional three-wheel robots by brain-emotional-learning-based intelligent controller. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern C (Appl Rev) 40(6):630–638
Farhangi R, Boroushaki M, Hosseini SH (2012) Load–frequency control of interconnected power system using emotional learning-based intelligent controller. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 36(1):76–83c
Khalghani MR et al (2010) A self-tuning load frequency control strategy for microgrids: human brain emotional learning. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 75:311–319
Rahman MA et al (2008) Implementation of emotional controller for interior permanent-magnet synchronous motor drive. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 44(5):1466–1476
Markadeh GR et al (2011) Speed and flux control of induction motors using emotional intelligent controller. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 47(3):1126–1135
Daryabeigi E et al (2015) Online MTPA control approach for synchronous reluctance motor drives based on emotional controller. IEEE Trans Power Electron 30(4):2157–2166
Khooban M-H, Javidan Reza (2016) A novel control strategy for DVR: optimal bi-objective structure emotional learning. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 83:259–269
Dehkordi BM et al (2011) Sensorless speed control of switched reluctance motor using brain emotional learning based intelligent controller. Energy Convers Manag 52(1):85–96
Daryabeigi E, Abjadi NR, Arab Markadeh GR (2014) Automatic speed control of an asymmetrical six-phase induction motor using emotional controller (BELBIC). J Intell Fuzzy Syst 26(4):1879–1892
Haith AM, Krakauer JW (2013) Model-based and model-free mechanisms of human motor learning. Progress in motor control. Springer, New York, pp 1–21
Dayan P, Berridge KC (2014) Model-based and model-free Pavlovian reward learning: revaluation, revision, and revelation. Cognit Affective Behav Neurosci 14(2):473–492
McDannald MA et al (2012) Model-based learning and the contribution of the orbitofrontal cortex to the model-free world. Eur J Neurosci 35(7):991–996
Doya K, Kimura H, Kawato M (2001) Neural mechanisms of learning and control. IEEE Control Syst 21(4):42–54
Jamali MR et al (2009) Emotion on FPGA: model driven approach. Expert Syst Appl 36(4):7369–7378
César MB, Gonçalves J, Coelho J, de Barros RC (2017) Brain emotional learning based control of a SDOF structural system with a MR samper. In: Garrido P, Soares F, Moreira A (eds) CONTROLO 2016. Lecture notes in electrical engineering, vol 402. Springer, Cham, pp 547–557. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-43671-5_46
Sharma MK, Kumar A (2015) Performance comparison of brain emotional learning-based intelligent controller (BELBIC) and PI controller for continually stirred tank heater (CSTH). In: Maharatna K, Dalapati G, Banerjee P, Mallick A, Mukherjee M (eds) Computational advancement in communication circuits and systems. Lecture notes in electrical engineering, vol 335. Springer, New Delhi, pp 293–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2274-3_32
Valipour MH, Maleki KN, Ghidary SS (2015) Optimization of emotional learning approach to control systems with unstable equilibrium. In: Lee R (ed) Software engineering, artificial intelligence, networking and parallel/distributed computing. Studies in computational intelligence. vol 569. Springer, Cham, pp 45–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10389-1_4
Vargas-Clara A, Redkar S (2015) Unmanned ground vehicle navigation using brain emotional learning based intelligent controller (BELBIC). Smart Sci 3(1):10–15
Morén J, Balkenius C (2000) A computational model of emotional learning in the AMYG. In: Meyer JA, Berthoz A, Floreano D, Roitblat HL, Wilson SW (eds) From animals to animats 6: proceedings of the 6th international conference on the simulation of adaptive behaviour. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA., USA., pp 115–124
Morén J (2002) Emotion and learning-A computational model of the AMYG. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Cognitive Science, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
Dehkordi BM et al (2011) A comparative study of various intelligent based controllers for speed control of IPMSM drives in the field-weakening region. Expert Syst Appl 38(10):12643–12653
Khalilian M, Abedi A, Zadeh AD (2012) Position control of hybrid stepper motor using brain emotional controller. Energy Proc 14:1998–2004
Qutubuddin MD, Yadaiah N (2017) Modeling and implementation of brain emotional controller for permanent magnet synchronous motor drive. Eng Appl Artif Intell 60(2017):193–203
El-Saify MH, El-Garhy AM, El-Sheikh GA (2017) Brain emotional learning based intelligent decoupler for nonlinear multi-input multi-output distillation columns. Math Prob Eng 2017:13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8760351
LeDoux JE (1992) Brain mechanisms of emotion and emotional learning. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2(2):191–197
Morris JS, Öhman A, Dolan RJ (1998) Conscious and unconscious emotional learning in the human amygdala. Nature 393(6684):467–470
Veit R et al (2002) Brain circuits involved in emotional learning in antisocial behavior and social phobia in humans. Neurosci Lett 328(3):233–236
Lotfi E, Akbarzadeh-T M-R (2014) Practical emotional neural networks. Neural Netw 59:61–72
Babaie T, Karimizandi R, Lucas C (2008) Learning based brain emotional intelligence as a new aspect for development of an alarm system. Soft Comput 12(9):857–873
Fakhrmoosavy SH, Setayeshi S, Sharifi A (2017) A modified brain emotional learning model for earthquake magnitude and fear prediction. Eng Comput, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-017-0538-6
Asad M et al (2017) Neo-fuzzy supported brain emotional learning based pattern recognizer for classification problems. IEEE Access 5:6951–6968. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2698419
Milad HS, Farooq U, El-Hawary ME, Asad MU (2017) Neo-fuzzy integrated adaptive decayed brain emotional learning network for online time series prediction. IEEE Access 5:1037–1049
Farhoudi Z, Setayeshi S, Rabiee A (2017) Using learning automata in brain emotional learning for speech emotion recognition. Int J Speech Technol 20(3):553–562
Daryabeigi E, Arab Markadeh GR, Lucas C (2010) Emotional controller (BELBIC) for electric drives—a review. In: IECON 2010-36th annual conference on IEEE industrial electronics society. IEEE
Khorashadizadeh S, Mahdian M (2016) Voltage tracking control of DC–DC boost converter using brain emotional learning. In: 2016 4th International conference on control, instrumentation, and automation (ICCIA). IEEE
Jamali MR, Dehyadegari M, Arami A et al (2010) Real-time embedded emotional controller. Neural Comput Appl 19(1):13–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-008-0227-x
El-Garhy AM, El-Shimy ME (2015) BELBIC for MRAS with highly non-linear process. Alexandria Eng J 54(1):7–16
Hsu C-F, Lee T-T (2017) Emotional fuzzy sliding-mode control for unknown nonlinear systems. Int J Fuzzy Syst 19(3):942–953
Klecker S, Plapper P (2016) BELBIC-sliding mode control of robotic manipulators with uncertainties and switching constraints. In: Proceedings of the ASME 2016 international mechanical engineering congress and exposition
Rizzi C, Johnson CG, Fabris F, Vargas PA (2017) A situation-aware fear learning (SAFEL) model for robots. Neurocomputing 221:32–47
El-Saify MH, El-Sheikh GA, El-Garhy AM (2017) Novel multi-input multi-output brain emotional learning based intelligent controller for PUMA 560 robotic arm. In: International conference on advanced intelligent systems and informatics. Springer, Cham, pp 81–93
Jafari M, Fehr R, Carrillo LRG, Xu H (2017) Brain emotional learning-based intelligent tracking control for unmanned aircraft systems with uncertain system dynamics and disturbance. In: 2017 International Conference on unmanned aircraft systems (ICUAS). IEEE, pp 1470–1475
Jafari M, Xu H (2017) A biologically-inspired distributed resilient flocking control for multi-agent system with uncertain dynamics and unknown disturbances. In: Resilience week (RWS), IEEE, Wilmington, DE, pp 71–76. https://doi.org/10.1109/RWEEK.2017.8088651
Jafari M, Xu H, Carrillo LRG (2017) Brain emotional learning-based intelligent controller for flocking of multi-agent systems. In: American control conference (ACC), 2017. IEEE, pp 1996–2001
Jafari M, Fehr R, Carrillo LRG, Quesada ESE, Xu H (2017) Implementation of brain emotional learning-based intelligent controller for flocking of multi-agent systems. IFAC-PapersOnLine 50(1):6934–6939
Klecker S, Hichri B, Plapper P (2017) Robust BELBIC-extension for trajectory tracking control. J Mech Eng Autom 7(2017):84–93. https://doi.org/10.17265/2159-5275/2017.02.005
Kim JW, Oh CY, Chung JW, Kim KH (2017) Brain emotional limbic-based intelligent controller design for control of a haptic device. Int J Autom Control 11(4):358–371
Coelho JP, Pinho TM, Boaventura-Cunha J, de Oliveira JB (2017) A new brain emotional learning Simulink® toolbox for control systems design. IFAC-PapersOnLine 50(1):16009–16014
Abshari M, Safa HH, Saghaiannejad SM (2017) Indirect torque control of SRM by intelligent controller with considering torque ripple reduction. In: 2017 8th Power electronics, drive systems & technologies conference (PEDSTC). IEEE, pp 270–275
Dashti ZAS, Gholami M, Hajimani M (2017) Brain emotional learning based intelligent controller for velocity control of an electro hydraulic servo system. IOSR J Elec Electron Eng 12(4):29–35
Koyuncu T (2017) Practical efficiency of photovoltaic panel used for solar vehicles. In: IOP conference series: earth and environmental science. IOP Publishing, vol 83(1), p 012001
Gunapriya B, Sabrigiriraj M, Karthik M, Deepa B, Devi RN (2017) Power electronic drives and control technology status: brief review. In: Proceedings of 2nd international conference on intelligent computing and applications. Springer Singapore, pp 493–512
Jokar A, Zomorodian R, Ghofrani MB, Khodaparast P (2016) Active control of surge in centrifugal compressors using a brain emotional learning-based intelligent controller. Proc Inst Mech Eng C J Mech Eng Sci 230(16):2828–2839
Balasubramaniam PM, Prabha SU (2015) Performance comparison of AI controllers for DC link voltage of SAPF system for power quality enhancements. In: Kamalakannan C, Suresh L, Dash S, Panigrahi B (eds) Power electronics and renewable energy systems. Lecture notes in electrical engineering, vol 326. Springer, New Delhi, pp 1385–1395. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2119-7_135
Sasikumar M, Senthilkumar S, Balabharathi B, Praveen M (2015) New intelligent controller for induction motor speed control. J Test Eval 44(3):1148–1160
Soreshjani MH, Markadeh GA, Daryabeigi E, Abjadi NR, Kargar A (2015) Application of brain emotional learning-based intelligent controller to power flow control with thyristor-controlled series capacitance. IET Gener Transm Distrib 9(14):1964–1976
El-Garhy MAAA, Mubarak RI, El-Bably M (2017) Improving maximum power point tracking of partially shaded photovoltaic system by using IPSO-BELBIC. J Instrum 12(08):P08012
Lotfi E, Akbarzadeh-T M-R (2016) A winner-take-all approach to emotional neural networks with universal approximation property. Inf Sci 346:369–388
Lotfi E, Khazaei O, Khazaei F (2017) Competitive brain emotional learning. Neural ProcessLett. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-017-9680-9
Chen YC, Teng CC (1995) A model reference control structure using a fuzzy neural network. Fuzzy Sets Syst 73(3):291–312
di Bernardo M, Montanaro U, Ortega R, Santini S (2016) Extended hybrid model reference adaptive control of piecewise affine systems. Nonlinear Anal Hybrid Syst 21:11–21
Åkesson BM, Toivonen HT (2006) A neural network model predictive controller. J Process Control 16(9):937–946
Haley P, Soloway D (1996) Experimental validation of generalized predictive control for active flutter suppression. In: Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE international conference on control applications, 1996, IEEE
Cooper DJ (2009) Practical process control. Electronic textbook. http://www.controlguru.com. Accessed 20 Apr 2009
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank independent reviewers for their excellent feedback on the paper. We also acknowledge the support of Azad University of Torbat-e Jam and Payam-e Noor University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lotfi, E., Rezaee, A.A. Generalized BELBIC. Neural Comput & Applic 31, 4367–4383 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3352-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3352-1