Abstract
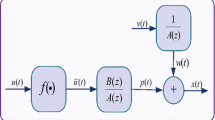
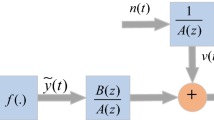
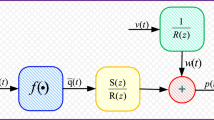
Aim of this research is to explore the strength of evolutionary and swarm intelligence techniques for parameter identification of control autoregressive moving average (CARMA) systems. The fitness function for CARMA system identification problem is formulated through error function created in mean square sense, and learning of unknown parameters of the system model is carried out with an effective global search techniques based on genetic algorithms and particle swarm optimization algorithm. Comparative study of the design methodology is conducted from actual parameters of the systems for different values of noise variance and degree of freedom in CARMA identification model. The correctness of the proposed scheme is validated through the results of various performance measures based on mean absolute error, mean weight deviation, variance account for and Theil’s inequality coefficient, and their global variants for sufficiently large number of independent runs.













Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Li H, Xu L, Zhang Z (2017) Parameter estimation of maneuvering target using maximum likelihood estimation for MIMO radar with colocated antennas. J Comput Commun 5(03):69
Ding F (2014) State filtering and parameter estimation for state space systems with scarce measurements. Signal Process 104:369–380
Ugalde HMR, Carmona JC, Reyes-Reyes J, Alvarado VM, Corbier C (2015) Balanced simplicity–accuracy neural network model families for system identification. Neural Comput Appl 26(1):171–186
Wang Y, Ding F (2016) Recursive parameter estimation algorithms and convergence for a class of nonlinear systems with colored noise. Circuits Syst Signal Process 35(10):3461–3481
Shen Q, Ding F (2016) Least squares identification for Hammerstein multi-input multi-output systems based on the key-term separation technique. Circuits Syst Signal Process 35(10):3745–3758
Ding F, Liu PX, Liu G (2010) Gradient based and least-squares based iterative identification methods for OE and OEMA systems. Digit Signal Process 20(3):664–677
Wang C, Tang T (2014) Several gradient-based iterative estimation algorithms for a class of nonlinear systems using the filtering technique. Nonlinear Dyn 77(3):769–780
Wang X, Ding F, Alsaadi FE, Hayat T (2016) Convergence analysis of the hierarchical least squares algorithm for bilinear-in-parameter systems. Circuits Syst Signal Process 35(12):4307–4330
Shen Q, Ding F (2016) Hierarchical multi-innovation extended stochastic gradient algorithms for input nonlinear multivariable OEMA systems by the key-term separation principle. Nonlinear Dyn 85(1):499–507
Wang X, Ding F (2015) Recursive parameter and state estimation for an input nonlinear state space system using the hierarchical identification principle. Signal Process 117:208–218
Chen H, Ding F (2015) Hierarchical least squares identification for Hammerstein nonlinear controlled autoregressive systems. Circuits Syst Signal Process 34(1):61–75
Mao Y, Ding F (2015) Multi-innovation stochastic gradient identification for Hammerstein controlled autoregressive autoregressive systems based on the filtering technique. Nonlinear Dyn 79(3):1745–1755
Chaudhary NI, Raja MAZ, Aslam MS, Ahmed N (2016) Novel generalization of Volterra LMS algorithm to fractional order with application to system identification. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2548-5
Raja MAZ, Chaudhary NI (2014) Adaptive strategies for parameter estimation of Box-Jenkins systems. IET Signal Process 8(9):968–980
Chaudhary NI, Raja MAZ (2015) Design of fractional adaptive strategy for input nonlinear Box-Jenkins systems. Signal Process 116:141–151
Chaudhary NI, Raja MAZ (2015) Identification of Hammerstein nonlinear ARMAX systems using nonlinear adaptive algorithms. Nonlinear Dyn 79(2):1385–1397
Chaudhary NI, Raja MAZ, Khan AUR (2015) Design of modified fractional adaptive strategies for Hammerstein nonlinear control autoregressive systems. Nonlinear Dyn 82(4):1811–1830
Bao B, Xu Y, Sheng J, Ding R (2011) Least squares based iterative parameter estimation algorithm for multivariable controlled ARMA system modelling with finite measurement data. Math Comput Model 53(9):1664–1669
Yao G, Ding R (2012) Two-stage least squares based iterative identification algorithm for controlled autoregressive moving average (CARMA) systems. Comput Math Appl 63(5):975–984
Li J, Ding F (2015) Filtering-based recursive least-squares identification algorithm for controlled autoregressive moving average systems using the maximum likelihood principle. J Vib Control 21(15):3098–3106
Raja MAZ, Chaudhary NI (2015) Two-stage fractional least mean square identification algorithm for parameter estimation of CARMA systems. Signal Process 107:327–339
Raja MAZ, Khan MAR, Mahmood T, Farooq U, Chaudhary NI (2016) Design of bio-inspired computing technique for nanofluidics based on nonlinear Jeffery–Hamel flow equations. Can J Phys 94(5):474–489
Chiroma H, Khan A, Abubakar AI, Saadi Y, Hamza MF, Shuib L, Gital AY, Herawan T (2016) A new approach for forecasting OPEC petroleum consumption based on neural network train by using flower pollination algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 48:50–58
Abubakar AI, Khan A, Nawi NM, Rehman MZ, Wah TY, Chiroma H, Herawan T (2016) Studying the effect of training levenberg marquardt neural network by using hybrid meta-heuristic algorithms. J Comput Theor Nanosci 13(1):450–460
Mall S, Chakraverty S (2015) Numerical solution of nonlinear singular initial value problems of Emden–Fowler type using Chebyshev Neural Network method. Neurocomputing 149:975–982
Draa A, Benayad Z, Djenna FZ (2015) An opposition-based firefly algorithm for medical image contrast enhancement. Int J Inf Commun Technol 7(4–5):385–405
Raja MAZ, Khan JA, Chaudhary NI, Shivanian E (2016) Reliable numerical treatment of nonlinear singular Flierl–Petviashivili equations for unbounded domain using ANN, GAs, and SQP. Appl Soft Comput 38:617–636
Draa A, Bouaziz A (2014) An artificial bee colony algorithm for image contrast enhancement. Swarm Evol Comput 16:69–84
Raja MAZ, Samar R, Haroon T, Shah SM (2015) Unsupervised neural network model optimized with evolutionary computations for solving variants of nonlinear MHD Jeffery–Hamel problem. Appl Math Mech 36(12):1611–1638
Dahi ZAEM, Mezioud C, Draa A (2016) On the efficiency of the binary flower pollination algorithm: application on the antenna positioning problem. Appl Soft Comput 47:395–414
Raja MAZ, Samar R, Alaidarous ES, Shivanian E (2016) Bio-inspired computing platform for reliable solution of Bratu-type equations arising in the modeling of electrically conducting solids. Appl Math Model 40(11):5964–5977
Abubakar AI, Shuib L, Chiroma H (2015) Optimization of neural network using cuckoo search for the classification of diabetes. J Comput Theor Nanosci 12(12):5755–5758
Baymani M, Effati S, Niazmand H, Kerayechian A (2015) Artificial neural network method for solving the Navier–Stokes equations. Neural Comput Appl 26(4):765–773
Draa A, Bouzoubia S, Boukhalfa I (2015) A sinusoidal differential evolution algorithm for numerical optimisation. Appl Soft Comput 27:99–126
Effati S, Mansoori A, Eshaghnezhad M (2015) An efficient projection neural network for solving bilinear programming problems. Neurocomputing 168:1188–1197
Raja MAZ (2014) Stochastic numerical treatment for solving Troesch’s problem. Inf Sci 279:860–873
Raja MAZ, Shah FH, Alaidarous ES, Syam MI (2017) Design of bio-inspired heuristic technique integrated with interior-point algorithm to analyze the dynamics of heartbeat model. Appl Soft Comput 52:605–629
Raja MAZ, Shah FH, Syam MI (2017) Intelligent computing approach to solve the nonlinear Van der Pol system for heartbeat model. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-2949-0
Raja MAZ, Asma K, Aslam MS (2018) Bio-inspired computational heuristics to study models of hiv infection of CD4+ T-cell. Int J Biomath. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793524518500195
Ahmad I, Raja MAZ, Bilal M, Ashraf F (2016) Bio-inspired computational heuristics to study Lane–Emden systems arising in astrophysics model. SpringerPlus 5(1):1866
Raja MAZ, Abbas S, Syam MI, Wazwaz AM (2018) Design of neuro-evolutionary model for solving nonlinear singularly perturbed boundary value problems. Appl Soft Comput 62:373–394
Raja MAZ, Manzar MA, Shah FH, Shah FH (2018) Intelligent computing for Mathieu’s systems for parameter excitation, vertically driven pendulum and dusty plasma models. Appl Soft Comput 62:359–372
Raja MAZ, Aslam MS, Chaudhary NI, Nawaz M, Shah SM (2017) Design of hybrid nature-inspired heuristics with application to active noise control systems. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3214-2
Akbar S, Raja MAZ, Zaman F, Mehmood T, Khan MAR (2017) Design of bio-inspired heuristic techniques hybridized with sequential quadratic programming for joint parameters estimation of electromagnetic plane waves. Wirel Pers Commun 96(1):1475–1494
Raja MAZ, Azad S, Shah SM (2017) Bio-inspired computational heuristics to study the boundary layer flow of the Falkner–Scan system with mass transfer and wall stretching. Appl Soft Comput 57:293–314
Lodhi S, Manzar MA, Raja MAZ (2017) Fractional neural network models for nonlinear Riccati systems. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-2991-y
Raja MAZ, Samar R, Manzar MA, Shah SM (2017) Design of unsupervised fractional neural network model optimized with interior point algorithm for solving Bagley-Torvik equation. Math Comput Simul 132:139–158
Sabouri J, Effati S, Pakdaman M (2017) A neural network approach for solving a class of fractional optimal control problems. Neural Process Lett 45(1):59–74
Pasolli E, Melgani F (2015) Genetic algorithm-based method for mitigating label noise issue in ECG signal classification. Biomed Signal Process Control 19:130–136
Raja MAZ, Mehmood A, Niazi SA, Shah SM (2016) Computational intelligence methodology for the analysis of RC circuit modelled with nonlinear differential order system. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2806-6
Valarmathi K, Devaraj D, Radhakrishnan TK (2009) Real-coded genetic algorithm for system identification and controller tuning. Appl Math Model 33(8):3392–3401
Boudjelaba K, Ros F, Chikouche D (2014) Potential of particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithms for FIR filter design. Circuits Syst Signal Process 33(10):3195–3222
Arabali A, Ghofrani M, Etezadi-Amoli M, Fadali MS, Baghzouz Y (2013) Genetic-algorithm-based optimization approach for energy management. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 28(1):162–170
Nikolos IK, Valavanis KP, Tsourveloudis NC, Kostaras AN (2003) Evolutionary algorithm based offline/online path planner for UAV navigation. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B (Cybern) 33(6):898–912
Dahi ZAEM, Mezioud C, Draa A (2016) A quantum-inspired genetic algorithm for solving the antenna positioning problem. Swarm Evol Comput 31:24–63
Raja MAZ, Shah AA, Mehmood A, Chaudhary NI, Aslam MS (2016) Bio-inspired computational heuristics for parameter estimation of nonlinear Hammerstein controlled autoregressive system. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2677-x
Raja MAZ, Sabir Z, Mehmood N, Al-Aidarous ES, Khan JA (2015) Design of stochastic solvers based on genetic algorithms for solving nonlinear equations. Neural Comput Appl 26(1):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1676-z
Raja MAZ, Kiani AK, Shehzad A, Zameer A (2016) Memetic computing through bio-inspired heuristics integration with sequential quadratic programming for nonlinear systems arising in different physical models. SpringerPlus 5(1):2063. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3750-8
Raja MAZ, Niazi SA, Butt SA (2017) An intelligent computing technique to analyze the vibrational dynamics of rotating electrical machine. Neurocomputing 219:280–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.09.032
Masood Z, Majeed K, Samar R, Raja MAZ (2017) Design of Mexican Hat Wavelet neural networks for solving Bratu type nonlinear systems. Neurocomputing 221:1–14
Raja MAZ, Zameer A, Khan AU, Wazwaz AM (2016) A new numerical approach to solve Thomas-Fermi model of an atom using bio-inspired heuristics integrated with sequential quadratic programming. SpringerPlus 5(1):1400
Raja MAZ, Farooq U, Chaudhary NI, Wazwaz AM (2016) Stochastic numerical solver for nanofluidic problems containing multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl Soft Comput 38:561–586
Özmen A, Weber GW (2014) RMARS: robustification of multivariate adaptive regression spline under polyhedral uncertainty. J Comput Appl Math 259:914–924
Özmen A, Kropat E, Weber GW (2017) Robust optimization in spline regression models for multi-model regulatory networks under polyhedral uncertainty. Optimization 66(12):2135–2155
Özmen A (2016) Robust optimization of spline models and complex regulatory networks: theory methods and applications. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-30800-5
Kara G, Özmen A, Weber GW (2017) Stability advances in robust portfolio optimization under parallelepiped uncertainty. Cent Eur J Oper Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10100-017-0508-5
Taylan P, Weber GW, Yerlikaya F (2008) May. Continuous optimization applied in MARS for modern applications in finance, science and technology. In: ISI Proceedings of 20th mini-EURO conference continuous optimization and knowledge-based technologies, pp 317–322
Weber GW, Batmaz İ, Köksal G, Taylan P, Yerlikaya-Özkurt F (2012) CMARS: a new contribution to nonparametric regression with multivariate adaptive regression splines supported by continuous optimization. Inverse Probl Sci Eng 20(3):371–400
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors of the manuscript declared that there are no potential conflicts of interest.
Human and animal rights statements
All the authors of the manuscript declared that there is no research involving human participants and/or animal.
Informed consent
All the authors of the manuscript declared that there is no material that required informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehmood, A., Zameer, A., Raja, M.A.Z. et al. Nature-inspired heuristic paradigms for parameter estimation of control autoregressive moving average systems. Neural Comput & Applic 31, 5819–5842 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3406-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3406-4