Abstract
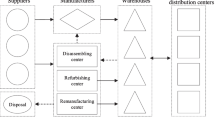
Supply chain design is one of the important and strategic decisions influencing competitive advantages and economic growth. The increasing importance of using waste products has led many companies to move toward the design of a closed-loop supply chain network. The current research considers a multilayered closed-loop supply chain for disposable appliances recycling network. Since many parameters, especially demand and costs, are uncertain, discrete random scenarios are used to describe the parameters. The network modeling aimed at maximizing the value of returning products in the reverse network and products manufactured by the forward network. Optimization of the disposable appliance supply chain network is handled by the combined genetic algorithm and robust optimization. Finally, the computational analysis shows that the proposed model obtains effective solutions for the closed-loop network of disposable appliances. Also, the analysis shows that the genetic algorithm has a good convergence. Comparison of different scenarios shows that the objective function is highly sensitive to uncertain parameters. Hence, network modeling based on different scenarios can be a good approach for deciding under uncertainty of parameters.









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Farahani RZ, Rezapour S, Drezner T et al (2014) Competitive supply chain network design: an overview of classifications, models, solution techniques and applications. Omega 45:92–118
Fathollahi Fard AM, Gholian-Jouybari F, Paydar MM et al (2017) A Bi-objective stochastic closed-loop supply chain network design problem considering downside risk. Ind Eng Manag Syst 16(3):342–362
Srivastava SK (2008) Network design for reverse logistics. Omega 36(4):535–548
Govindan K, Soleimani H, Kannan D (2015) Reverse logistics and closed-loop supply chain: a comprehensive review to explore the future. Eur J Oper Res 240(3):603–626
Chen CL, Yuan TW, Lee WC (2007) Multi-criteria fuzzy optimization for locating warehouses and distribution centers in a supply chain network. J Chin Inst Chem Eng 38(5):393–407
Petrovic D, Xie Y, Burnham K, Petrovic R (2008) Coordinated control of distribution supply chains in the presence of fuzzy customer demand. Eur J Oper Res 185(1):146–158
Qin Z, Ji X (2010) Logistics network design for product recovery in fuzzy environment. Eur J Oper Res 202(2):479–490
Efendigil T, Önüt S, Kahraman C (2009) A decision support system for demand forecasting with artificial neural networks and neuro-fuzzy models: a comparative analysis. Expert Syst Appl 36(3):6697–6707
Pishvaee MS, Torabi SA, Razmi J (2012) Credibility-based fuzzy mathematical programming model for green logistics design under uncertainty. Comput Ind Eng 62(2):624–632
El-Sayed M, Afia N, El-Kharbotly A (2010) A stochastic model for forward–reverse logistics network design under risk. Comput Ind Eng 58(3):423–431
Pishvaee MS, Farahani RZ, Dullaert W (2010) A memetic algorithm for bi-objective integrated forward/reverse logistics network design. Comput Oper Res 37(6):1100–1112
Pishvaee MS, Razmi J, Torabi SA (2012) Robust possibilistic programming for socially responsible supply chain network design: a new approach. Fuzzy Sets Syst 206:1–20
Kannan D, Diabat A, Alrefaei M, Govindan K, Yong G (2012) A carbon footprint based reverse logistics network design model. Resour Conserv Recycl 67:75–79
Soleimani H, Kannan G (2015) A hybrid particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithm for closed-loop supply chain network design in large-scale networks. Appl Math Model 39(14):3990–4012
Ramezani M, Bashiri M, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2013) A new multi-objective stochastic model for a forward/reverse logistic network design with responsiveness and quality level. Appl Math Model 37(1):328–344
Özkır V, Başlıgil H (2013) Multi-objective optimization of closed-loop supply chains in uncertain environment. J Clean Prod 41:114–125
Diabat A, Deskoores R (2016) A hybrid genetic algorithm based heuristic for an integrated supply chain problem. J Manuf Syst 38:172–180
Al-Salem M, Diabat A, Dalalah D, Alrefaei M (2016) A closed-loop supply chain management problem: reformulation and piecewise linearization. J Manuf Syst 40:1–8
Alshamsi A, Diabat A (2017) A genetic algorithm for reverse logistics network design: a case study from the GCC. J Clean Prod 151:652–669
Diabat A (2016) A capacitated facility location and inventory management problem with single sourcing. Optim Lett 10(7):1577–1592
Hiassat A, Diabat A, Rahwan I (2017) A genetic algorithm approach for locationinventory- routing problem with perishable products. J Manuf Syst 42:93–103
Shiina T, Birge JR (2004) Stochastic unit commitment problem. Int Trans Oper Res 11(1):19–32
Pishvaee MS, Naderi MJ (2017) A stochastic programming approach to integrated water supply and wastewater collection network design problem. Comput Chem Eng 104:107–127
Niknam T, Azizipanah-Abarghooee R, Narimani MR (2012) An efficient scenario-based stochastic programming framework for multi-objective optimal micro-grid operation. Appl Energy 99:455–470
Mohammadi S, Mohammadi A (2014) Stochastic scenario-based model and investigating size of battery energy storage and thermal energy storage for micro-grid. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 61:531–546
Bashiri M, Moslemi A (2012) A robust scenario based approach in an uncertain condition applied to location-allocation distribution centers problem. Int J Manag Bus Res 1:199–210
Mercier S, Uysal I (2018) Neural network models for predicting perishable food temperatures along the supply chain. Biosyst Eng 171:91–100
Silva N, Ferreiraa LMD, Silvaa C, Magalhãesa V, Netoa P (2017) Improving supply chain visibility with artificial neural networks. Procedia Manuf 11:2083–2090
Yoo JS, Hong SR, Kim CO (2009) Service level management of nonstationary supply chain using direct neural network controller. Expert Syst Appl 36(2):3574–3586
Ciupan E (2014) A study regarding the possibility of optimizing the supply batch using artificial neural networks. Procedia Eng 69:141–149
Pereira MM, Machado RL, Pires SRI, Dantas MJP, Zaluski PR, Frazzon EM (2018) Forecasting scrap tires returns in closed-loop supply chains in Brazil. J Clean Prod 188:741–750
Islam MT, Huda N (2018) Reverse logistics and closed-loop supply chain of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE)/E-waste: a comprehensive literature review. Resour Conserv Recycl 137:48–75
Wang HF, Hsu HW (2010) A closed-loop logistic model with a spanning-tree based genetic algorithm. Comput Oper Res 37(2):376–389
Kannan G, Sasikumar P, Devika K (2010) A genetic algorithm approach for solving a closed loop supply chain model: a case of battery recycling. Appl Math Model 34(3):655–670
Wang W, Zhang Y, Zhang K, Bai T, Shang J (2015) Reward-penalty mechanism for closed-loop supply chains under responsibility-sharing and different power structures. Int J Prod Econ 170:178–190
Soleimani H, Kannan G (2015) A hybrid particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithm for closed-loop supply chain network design in largescale networks. Appl Math Model 39(14):3990–4012
Kannan G, Noorul Haq A, Devika M (2009) Analysis of closed loop supply chain using genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimisation. Int J Prod Res 47(5):1175–1200
Pishvaee MS, Zanjirani Farahani R, Dullaert W (2010) A memetic algorithm for bi-objective integrated forward/reverse logistics network design. Comput Oper Res 37(6):1100–1112
Lee D, Dong M (2008) A heuristic approach to logistics network design for end-of lease computer products recovery. Transp Res Part E 44:455–474
Lee JE, Gen M, Rhee K-G (2009) Network model and optimization of reverse logistics by hybrid genetic algorithm. Comput Ind Eng 56(3):951–964
Zhou X, Zhao Z, Zhou K (2012) Remanufacturing closed-loop supply chain network design based on genetic particle swarm optimization algorithm. J Cent South Univ Technol 19:482–487
Zeballos LJ, Méndez CA, Barbosa-Povoa AP, Novais AQ (2014) Multi-period design and planning of closed-loop supply chains with uncertain supply and demand. Comput Chem Eng 66:151–164
Akbari AA, Karimi B (2015) A new robust optimization approach for integrated multi-echelon, multi-product, multi-period supply chain network design under process uncertainty. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79:229–244
Torabi SA, Namdar J, Hatefi SM, Jolai F (2015) An enhanced possibilistic programming approach for reliable closed-loop supply chain network design. Int J Prod Res 54:1–30
Govindan K, Fattahi M (2015) Investigating risk and robustness measures for supply chain network design under demand uncertainty: a case study of glass supply chain. Int J Prod Econ 183:680–699
Vahdani B, Mohammadi M (2015) A bi-objective interval-stochastic robust optimization model for designing closed loop supply chain network with multi-priority queuing system. Int J Prod Econ 170(Part A):67–87
Babazadeh R, Razmi J, Pishvaee MS, Rabbani M (2016) A sustainable second-generation biodiesel supply chain network design problem under risk. Omega 66:258–277
Keyvanshokooh E, Ryan SM, Kabir E (2016) Hybrid robust and stochastic 816 optimization for closed-loop supply chain network design using accelerated Benders decomposition. Eur J Oper Res 249:76–92
Farrokh M et al (2017) A novel robust fuzzy stochastic programming for closed loop supply chain network design under hybrid uncertainty. Fuzzy Sets Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2017.03.019
Kadambala DK, Subramanian N, Tiwari MK, Abdulrahman M, Liu C (2017) Closed loop supply chain networks: designs for energy and time value efficiency. Int J Prod Econ 183:382–393
Glover F, Woolsey E (1974) Technical note—converting the 0–1 polynomial programming problem to a 0–1 linear program. Oper Res 22:180–182
Mulvey JM, Vanderbei RJ, Zenios SA (1995) Robust optimization of large scale systems. Oper Res Lett 43(2):264–281
Mulvey JM, Ruszczynski A (1995) A new scenario decomposition method for large scale stochastic optimization. Oper Res 43:477–490
Yu C-S, Li H-L (2000) A robust optimization model for stochastic logistic problems. Int J Prod Econ 64(1):385–397
Kannan G, Sasikumar P, Devika K (2010) A genetic algorithm approach for solving a closed loop supply chain model: a case of battery recycling. Appl Math Model 34(3):655–670
Diabat A, Al-Salem M (2015) An integrated supply chain problem with environmental considerations. Int J Prod Econ 164:330–338
Taguchi G (1986) Introduction to quality engineering: designing quality into products and processes. Asian Productivity Organization, Tokyo
Naderi B, Ghomi SMTF, Aminnayeri M, Zandieh M (2011) Scheduling open shops with parallel machines to minimize total completion time. J Comput Appl Math 235:1275–1287
Phadke MS (1995) Quality engineering using robust design. Prentice Hall PTR, Upper Saddle River
Naderi B, Zandieh M, Balagh AKG, Roshanaei V (2009) An improved simulated annealing for hybrid flowshops with sequence-dependent setup and transportation times to minimize total completion time and total tardiness. Expert Syst Appl 36:9625–9633
Shah NA, Animasaun IL, Ibraheem RO, Babatunde HA, Sandeep N, Pop I (2018) Scrutinization of the effects of Grash of number on the flow of different fluids driven by convection over various surfaces. J Mol Liq 249:980–990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict in interest
The materials and the authors of the paper do not conflict in interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gholizadeh, H., Tajdin, A. & Javadian, N. A closed-loop supply chain robust optimization for disposable appliances. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 3967–3985 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3847-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3847-9