Abstract
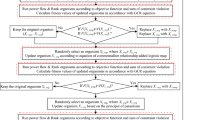
This paper proposes an improved social spider optimization (ISSO) for achieving different objectives of optimal reactive power dispatch (ORPD). The proposed ISSO method is developed by applying two modifications on new solution generation process. The proposed method uses only one modified equation for producing the first new solution generation and the second new solution generation while the standard SSO uses two equations for each process. The improvement in the proposed method is confirmed by solving benchmark optimization functions, IEEE 30-bus system and IEEE 118-bus system. Obtained results from ISSO are compared to those from other existing methods available in other studies together with other popular and state-of-the-art methods, which are implemented in the work. As compared to standard SSO for application to ORPD problem, ISSO can reduce the number of computation steps and one control parameter, and shorten simulation time. About the result comparisons with SSO and other remaining methods, ISSO can find more favorable solutions with higher quality and ISSO can stabilize solution search function with approximately all trial runs finding lower value of fitness. Furthermore, the strong search ability of ISSO is also indicated because it uses less value for control parameters. As a result, the proposed ISSO method can be a very effective optimization tool for dealing with the ORPD problem.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Abbreviations
- HI:
-
The highest iteration
- N bus :
-
Number of buses in the considered power system
- N c :
-
Number of VAR compensator buses
- Nfs, Nms :
-
Number of females and males, respectively
- N G :
-
Number of generator buses
- N line :
-
Number of transmission lines
- N load :
-
Number of load buses in the considered power system
- N pop :
-
Population size or the sum of males and females
- N t :
-
Number of buses with transformer
- Pdi, Qdi :
-
Real and reactive power required by load of bus i
- P m :
-
Movement probability of female spiders
- Q ci :
-
Reactive power generation of VAR compensator of bus i
- Qci,min, Qci,max :
-
Lower and upper limitations of reactive power generation of VAR compensator at bus i
- QGi,min, QGi,max :
-
Lower and upper limitations of reactive power generation of generator at bus i, respectively
- RNf :
-
Random number within 0 and 1 for female spider f
- S l,max :
-
Maximum apparent power flow of line l
- Ti,min, Ti,max :
-
Lower and upper limitations of tap changer of transformer at bus i
- VGi,min, VGi,max :
-
Lower and upper limitations of voltage magnitude of generator at bus i, respectively
- Vi, Vj :
-
Voltage magnitude of buses i and j
- Vloadi,min, Vloadi,max :
-
Lower and upper limitations of voltage magnitude of the load at bus i, respectively
- X fs,f :
-
Position of female spider f corresponding to a solution
- X Gbest :
-
Position of the best spider corresponding to the best solution
- X ms,m :
-
Position of male spider m corresponding to a solution
- ABCA:
-
Artificial bee colony algorithm
- ACO:
-
Ant colony optimization
- AGA:
-
Adaptive genetic algorithm
- ALO:
-
Ant lion optimizer
- ASCSA:
-
Adaptive selective cuckoo search algorithm
- BA:
-
Bat algorithm
- BB–BCA:
-
Big bang–big crunch algorithm
- BBDE:
-
Bare-bones differential evolution
- BBPSO:
-
Bare-bones particle swarm optimization
- BOFs:
-
Benchmark optimization functions
- BRCFA:
-
Binary real-coded firefly algorithm
- BTSA:
-
Backtracking search algorithm
- CABC-DE:
-
Hybrid chaotic artificial bee colony differential evolution
- CKHA:
-
Chaotic krill herd algorithm
- CLPSO:
-
Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimization
- COA:
-
Coyote optimization algorithm
- CSA:
-
Cuckoo search algorithm
- CSSA:
-
Charged system search algorithm
- DE:
-
Differential evolution
- DE–AS:
-
Differential evolution and ant system
- DPM:
-
Dynamic programming method
- DSA:
-
Differential search algorithm
- EMA:
-
Exchange market algorithm
- EP:
-
Evolution programming
- FA:
-
Firefly algorithm
- FPA:
-
Flower pollination algorithm
- GBBWCA:
-
Gaussian bare-bones water cycle algorithm
- GBTLBO:
-
Gaussian bare-bones teaching learning-based optimization
- GSA:
-
Gravitational search algorithm
- GSA-CSS:
-
Gravitational search algorithm with original selection
- GSA-NHCM:
-
Gravitational search algorithm with new constraint handling method
- GWO:
-
Gray wolf optimizer
- GWPSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization with inertia weight
- HFA-NMS:
-
Hybrid Nelder–Mead simplex-based firefly algorithm
- HFVNS:
-
Hybrid stochastic fractal search and variable neighborhood search
- HICTS:
-
Hybrid imperialist competitive algorithm and tabu search
- HISGA:
-
Hybrid interior search algorithm and genetic algorithm
- HKAGA:
-
Hybrid Keshtel algorithm and genetic algorithm
- HKASA:
-
Hybrid Keshtel algorithm and simulated annealing
- HLGA:
-
Hybrid loop genetic algorithm
- HMA:
-
Hybrid metaheuristic algorithm
- HMPSO:
-
Hybrid multi-agent particle swarm optimization
- HPSO–ICA:
-
Hybrid particle swarm optimization and imperialist competitive technique method
- HPSO–TS:
-
Hybrid particle swarm optimization and tabu search
- HRDSA:
-
Hybrid red deer algorithm and simulated annealing
- HSA:
-
Harmony search algorithm
- HSFSA:
-
Hybrid stochastic fractal search and simulated annealing
- HSSSA:
-
Hybrid salp swarm algorithm and simulated annealing
- HWPSO:
-
Hybrid whale optimization algorithm and particle swarm optimization
- HWWGA:
-
Hybrid water wave optimizer and genetic algorithm
- ICBO:
-
Improved colliding bodies optimization
- IDA:
-
Improved deterministic algorithm
- IMA:
-
Improved metaheuristic algorithm
- IPG-PSO:
-
Improved pseudo-gradient search-particle swarm optimization
- IPM:
-
Interior point method
- IQP:
-
Improved quadratic programming
- ISA:
-
Interior search algorithm
- ISSO:
-
Improved social spider optimization
- JA:
-
Jaya algorithm
- KA:
-
Keshtel algorithm
- LCA:
-
League championship algorithm
- LDGWPSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization with linearly decreasing inertia weight
- LPM:
-
Linear programming approach
- MDE:
-
Modified differential evolution
- MFO:
-
Moth flame optimization
- MLPM:
-
Mixed-integer linear programming
- MNM:
-
Modified Newton method
- MORDA:
-
Multi-objective red deer algorithm
- MPSO:
-
Modified particle swarm optimization
- MSSA:
-
Modified salp swarm algorithm
- MSSO:
-
Modified social spider optimization
- MTLT–DDE:
-
Modified teaching learning technique and double differential evolution algorithm
- NMSFLA:
-
Shuffled frog leaping algorithm and Nelder–Mead
- ORCSA:
-
One rank cuckoo search algorithm
- PG-PSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization with pseudo-gradient search
- PGSWT-PSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization with stochastic weight trade-off and pseudo-gradient search
- PSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization
- PSO-ALC:
-
Particle swarm optimization with an aging leader and challengers
- PSO-CF:
-
Particle swarm optimization with constriction factor
- PSO-GT:
-
Particle swarm optimization with graph theory
- PSO-TVAC:
-
Particle swarm optimization with time-varying acceleration coefficients
- PSO-TVIW:
-
Particle swarm optimization with time-varying inertia weight
- QODE:
-
Quasi-oppositional differential evolution
- QOTLBO:
-
Quasi-oppositional teaching learning-based optimization
- RCGA:
-
Real-coded genetic algorithm
- RDA:
-
Red deer algorithm
- RSGA:
-
Genetic algorithm with rank selection technique
- SARCGA:
-
Self-adaptive real-coded genetic algorithm
- SEO:
-
Social engineering optimizer
- SFOA:
-
Sunflower optimization algorithm
- SFS:
-
Stochastic fractal search
- SGA:
-
Specialized genetic algorithm
- SPSO-TVAC:
-
Particle swarm optimization with time-varying acceleration coefficients
- SPSO-TVAC:
-
Particle swarm optimization with self-organization and time-varying acceleration coefficients
- SSA:
-
Salp swarm algorithm
- SSO:
-
Social spider optimization
- SWT-PSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization with stochastic weight trade-off
- TVAC:
-
Time-varying acceleration coefficients
- WOA:
-
Whale optimization algorithm
- WWO:
-
Water wave optimizer
References
Haroon SS, Hassan S, Amin S, Sajjad IA, Waqar A, Aamir M, Alam I (2018) Multiple fuel machines power economic dispatch using stud differential evolution. Energies 11(6):1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061393
Nguyen TT, Vo DN, Vu QN, Van DL (2018) Modified Cuckoo search algorithm: a novel method to minimize the fuel cost. Energies 11(6):1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061328
Chintam JR, Daniel M (2018) Real-power rescheduling of generators for congestion management using a novel satin bowerbird optimization algorithm. Energies 11(1):183. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010183
Chen G, Lu Z, Zhang Z (2018) Improved krill herd algorithm with novel constraint handling method for solving optimal power flow problems. Energies 11(1):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010076
Da Costa GRM (2002) Modified Newton method for reactive dispatching. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 24(10):815–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-0615(02)00013-3
Deeb NI, Shahidehpour SM (1988) An efficient technique for reactive power dispatch using a revised linear programming approach. Electr Power Syst Res 15(2):121–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-7796(88)90016-8
Aoki K, Fan M, Nishikori A (1988) Optimal VAR planning by approximation method for recursive mixed-integer linear programming. IEEE Trans Power Syst 3(4):1741–1747. https://doi.org/10.1109/59.192990
Granville S (1994) Optimal reactive dispatch through interior point methods. IEEE Trans Power Syst 9(1):136–146. https://doi.org/10.1109/59.317548
Rezania E, Shahidehpour SM (2001) Real power loss minimization using interior point method. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 23(1):45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-0615(00)00028-4
Lu FC, Hsu YY (1995) Reactive power/voltage control in a distribution substation using dynamic programming. IEE Proc Gener Transm Distrib 142(6):639–645. https://doi.org/10.1049/ip-gtd:19952210
Grudinin N (1998) Reactive power optimization using successive quadratic programming method. IEEE Trans Power Syst 13(4):1219–1225. https://doi.org/10.1109/59.736232
Shunmugalatha A, Slochanal SMR (2008) Application of hybrid multiagent-based particle swarm optimization to optimal reactive power dispatch. Electr Power Compon Syst 36(8):788–800. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325000801911385
Mahadevan K, Kannan PS (2010) Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimization for reactive power dispatch. Appl Soft Comput 10(2):641–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2009.08.038
Sahli Z, Hamouda A, Bekrar A, Trentesaux D (2018) Reactive power dispatch optimization with voltage profile improvement using an efficient hybrid algorithm. Energies 11(8):2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11082134
Singh RP, Mukherjee V, Ghoshal SP (2015) Optimal reactive power dispatch by particle swarm optimization with an aging leader and challengers. Appl Soft Comput 29:298–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.01.006
Reddy PL, Yesuratnam G (2015) PSO based optimal reactive power dispatch for voltage profile improvement. In: Power, communication and information technology conference (PCITC), 2015 IEEE, pp 361–366. https://doi.org/10.1109/PCITC.2015.7438192
Polprasert J, Ongsakul W, Dieu VN (2016) Optimal reactive power dispatch using improved pseudo-gradient search particle swarm optimization. Electr Power Compon Syst 44(5):518–532. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325008.2015.1112449
Medani KBO, Sayah S (2016) Optimal reactive power dispatch using particle swarm optimization with time varying acceleration coefficients. In: Modelling, identification and control (ICMIC), 2016 8th international conference on IEEE, pp 780–785. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMIC.2016.7804219
Mehdinejad M, Mohammadi-Ivatloo B, Dadashzadeh-Bonab R, Zare K (2016) Solution of optimal reactive power dispatch of power systems using hybrid particle swarm optimization and imperialist competitive algorithms. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 83:104–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2016.03.039
Rayudu K, Yesuratnam G, Ali M, Jayalaxmi A (2016) Optimal reactive power dispatch based on particle swarm optimization and LP technique. In: Emerging technological trends (ICETT), international conference on IEEE, pp 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICETT.2016.7873777
Kaur D, Lie TT, Nair NK, Valles B (2016) An optimal reactive power dispatch (ORPD) for voltage security using particle swarm optimization (PSO) in graph theory. In Sustainable energy technologies (ICSET), 2016 IEEE international conference on IEEE, pp 25–30. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSET.2016.7811751
El Ela AA, Abido MA, Spea SR (2011) Differential evolution algorithm for optimal reactive power dispatch. Electr Power Syst Res 81(2):458–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2010.10.005
Huang CM, Huang YC (2012) Combined differential evolution algorithm and ant system for optimal reactive power dispatch. Energy Proc 14:1238–1243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2011.12.1082
Ghasemi M, Ghanbarian MM, Ghavidel S, Rahmani S, Moghaddam EM (2014) Modified teaching learning algorithm and double differential evolution algorithm for optimal reactive power dispatch problem: a comparative study. Inf Sci 278:231–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.03.050
Basu M (2016) Quasi-oppositional differential evolution for optimal reactive power dispatch. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 78:29–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2015.11.067
Li Y, Li X, Li Z (2017) Reactive power optimization using hybrid CABC-DE algorithm. Electr Power Compon Syst 45(9):980–989. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325008.2017.1311387
Cao YJ, Wu QH (1997) Optimal reactive power dispatch using an adaptive genetic algorithm. In: Genetic algorithms in engineering systems: innovations and applications. GALESIA 97. Second international conference on IET, pp 117–122. https://doi.org/10.1049/cp:19971166
Subbaraj P, Rajnarayanan PN (2009) Optimal reactive power dispatch using self-adaptive real coded genetic algorithm. Electr Power Syst Res 79(2):374–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2008.07.008
Alam MS, De M (2016) Optimal reactive power dispatch using hybrid loop-genetic based algorithm. In: Power systems conference (NPSC) IEEE, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/NPSC.2016.7858901
Villa-Acevedo W, López-Lezama J, Valencia-Velásquez J (2018) A novel constraint handling approach for the optimal reactive power dispatch problem. Energies 11(9):2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092352
Văduva AM, Bulac C (2016) New evolutionary algorithm method for solving optimal reactive power dispatch problem. In: Applied and theoretical electricity (ICATE), 2016 international conference on IEEE, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICATE.2016.7754626
Duman S, Sönmez Y, Güvenç U, Yörükeren N (2012) Optimal reactive power dispatch using a gravitational search algorithm. IET Gener Transm Distrib 6(6):563–576. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-gtd.2011.0681
Roy PK, Mandal B, Bhattacharya K (2012) Gravitational search algorithm based optimal reactive power dispatch for voltage stability enhancement. Electr Power Compon Syst 40(9):956–976. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325008.2012.675405
Babu MR, Lakshmi M (2016) Gravitational search algorithm based approach for optimal reactive power dispatch. In: Science technology engineering and management (ICONSTEM), Second international conference on IEEE, pp 360–366. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICONSTEM.2016.7560977
Chen G, Liu L, Zhang Z, Huang S (2017) Optimal reactive power dispatch by improved GSA-based algorithm with the novel strategies to handle constraints. Appl Soft Comput 50:58–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.11.008
El-Ela AA, Kinawy AM, El-Sehiemy RA, Mouwafi MT (2011) Optimal reactive power dispatch using ant colony optimization algorithm. Electr Eng 93(2):103–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-011-0196-4
Rayudu K, Yesuratnam G, Jayalaxmi A (2017) Ant colony optimization algorithm based optimal reactive power dispatch to improve voltage stability. In: Circuit, power and computing technologies (ICCPCT), 2017 international conference on IEEE, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCPCT.2017.8074391
Mandal B, Roy PK (2013) Optimal reactive power dispatch using quasi-oppositional teaching learning based optimization. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 53:123–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2013.04.011
Ghasemi M, Taghizadeh M, Ghavidel S, Aghaei J, Abbasian A (2015) Solving optimal reactive power dispatch problem using a novel teaching–learning-based optimization algorithm. Eng Appl Artif Intell 39:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2014.12.001
Sulaiman MH, Mustaffa Z (2017) Cuckoo search algorithm as an optimizer for optimal reactive power dispatch problems. In: Control, automation and robotics (ICCAR), 2017 3rd international conference on IEEE, pp 735–739. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCAR.2017.7942794
An NHT, Dieu VN, Nguyen TT, Kien VT (2015) One rank cuckoo search algorithm for optimal reactive power dispatch. GMSARN Int J 9:73–82
Khazali AH, Kalantar M (2011) Optimal reactive power dispatch based on harmony search algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 33(3):684–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2010.11.018
Khorsandi A, Alimardani A, Vahidi B, Hosseinian SH (2011) Hybrid shuffled frog leaping algorithm and Nelder–Mead simplex search for optimal reactive power dispatch. IET Gener Transm Distrib 5(2):249–256. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-gtd.2010.0256
Mukherjee A, Mukherjee V (2015) Solution of optimal reactive power dispatch by chaotic krill herd algorithm. IET Gener Transm Distrib 9(15):2351–2362. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-gtd.2015.0077
Rajan A, Malakar T (2015) Optimal reactive power dispatch using hybrid Nelder–Mead simplex based firefly algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 66:9–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2014.10.041
Sulaiman MH, Mustaffa Z, Mohamed MR, Aliman O (2015) Using the gray wolf optimizer for solving optimal reactive power dispatch problem. Appl Soft Comput 32:286–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.03.041
Rayudu K, Yesuratnam G, Jayalaxmi A (2016) Artificial bee colony algorithm for optimal reactive power dispatch to improve voltage stability. In: Circuit, power and computing technologies (ICCPCT), 2016 international conference on IEEE, pp 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCPCT.2016.7530203
Rajan A, Malakar T (2016) Exchange market algorithm based optimum reactive power dispatch. Appl Soft Comput 43:320–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.02.041
Abaci K, Yamaçli V (2017) Optimal reactive-power dispatch using differential search algorithm. Electr Eng 99(1):213–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-016-0410-5
Mouassa S, Bouktir T, Salhi A (2017) Ant lion optimizer for solving optimal reactive power dispatch problem in power systems. Eng Sci Technol Int J 3(20):885–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2017.03.006
Shaheen AM, El-Sehiemy RA, Farrag SM (2016) Optimal reactive power dispatch using backtracking search algorithm. Aust J Electr Electron Eng 13(3):200–210. https://doi.org/10.1080/1448837X.2017.1325134
Anbarasan P, Jayabarathi T (2017) Optimal reactive power dispatch problem solved by an improved colliding bodies optimization algorithm. In: Environment and electrical engineering and 2017 IEEE industrial and commercial power systems Europe (EEEIC/I&CPS Europe), 2017 IEEE international conference on IEEE, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/EEEIC.2017.7977592
Heidari AA, Abbaspour RA, Jordehi AR (2017) Gaussian bare-bones water cycle algorithm for optimal reactive power dispatch in electrical power systems. Appl Soft Comput 57:657–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.04.048
Mandal S, Mandal KK, Kumar S (2017) A new optimization technique for optimal reactive power scheduling using Jaya algorithm. In: Power and advanced computing technologies (i-PACT), 2017 innovations in IEEE, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/IPACT.2017.8244961
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimizer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on neural networks, pp 1942–1945. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
Yang XS. (2010). A new metaheuristic bat-inspired algorithm. In: Nature inspired cooperative strategies for optimization NICSO 2010. Springer, Berlin, pp 65–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12538-6_6
Yang XS (2014) Nature-inspired optimization algorithms. Elsevier, pp 111–127
Yang XS, Deb S (2009) Cuckoo search via Levy lights. In: World congress on nature and biologically inspired computing, NaBIC, pp 210–214. https://doi.org/10.1109/NABIC.2009.5393690
Yang XS (2012) Flower pollination algorithm for global optimization. In International conference on unconventional computing and natural computation. Springer, Berlin, pp 240–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32894-7_27
Cuevas E, Cienfuegos M, Zaldívar D, Pérez-Cisneros M (2013) A swarm optimization algorithm inspired in the behavior of the social-spider. Expert Syst Appl 40:6374–6384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.05.041
Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Aminnayeri M (2013) Keshtel Algorithm (KA); a new Optimizer algorithm inspired by Keshtels’ feeding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on industrial engineering management system, pp 2249–2253
Gandomi AH (2014) Interior search algorithm (ISA): a novel approach for global optimizer. ISA Trans 53:1168–1183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2014.03.018
Zheng YJ (2015) Water wave optimization: a new nature-inspired metaheuristic. Comput Oper Res 55:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2014.10.008
Salimi H (2015) Stochastic fractal search: a powerful metaheuristic algorithm. Knowl-Based Syst 75:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.07.025
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2016) The whale optimizer algorithm. Adv Eng Softw 95:51–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008
Fathollahi-Fard AM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M (2016) Red deer algorithm (RDA) a new optimization algorithm inspired by red deer’s mating. In: Proceedings of international conference on industrial engineering, IEEE pp 33–34
Elsayed WT, Hegazy YG, Bendary FM, El-bages MS (2016) Modified social spider algorithm for solving the economic dispatch problem. Eng Sci Technol Int J 4(19):1672–1681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2016.09.002
Sun SC, Qi H, Ren YT, Yu XY, Ruan LM (2017) Improved social spider optimization algorithms for solving inverse radiation and coupled radiation-conduction heat transfer problems. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer 87:132–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2017.07.010
El Aziz MA, Hassanien AE (2017) An improved social spider optimization algorithm based on rough sets for solving minimum number attribute reduction problem. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2804-8
Pierezan J, Coelho LDS (2018) Coyote optimization algorithm: a new metaheuristic for global optimization problems. In: 2018 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (CEC), IEEE, pp 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2018.8477769
Gomes GF, da Cunha SS, Ancelotti AC (2018) A sunflower optimization (SFO) algorithm applied to damage identification on laminated composite plates. Engineering with Computers. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-018-0620-8
Fathollahi-Fard AM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2018) The social engineering optimizer (SEO). Eng Appl Artif Intell 72:267–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2018.04.009
Fathollahi-Fard AM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M (2018) A bi-objective partial interdiction problem considering different defensive systems with capacity expansion of facilities under imminent attacks. Appl Soft Comput 68:343–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.04.011
Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Fathollahi-Fard AM (2018) A set of efficient heuristics and metaheuristics to solve a two-stage stochastic bi-level decision-making model for the distribution network problem. Comput Ind Eng 123:378–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2018.07.009
Samadi A, Mehranfar N, Fathollahi-Fard AM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M (2018) Heuristic-based metaheuristics to address a sustainable supply chain network design problem. J Ind Prod Eng 35(2):102–117. https://doi.org/10.1080/21681015.2017.1422039
Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Fathollahi-Fard AM (2018) Sustainable closed-loop supply chain network design with discount supposition. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3369-5
Fathollahi-Fard AM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Mirjalili S (2018) Hybrid optimizers to solve a tri-level programming model for a tire closed-loop supply chain network design problem. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.06.021
Mirjalili S, Gandomi AH, Mirjalili SZ, Saremi S, Faris H, Mirjalili SM (2017) Salp swarm algorithm: a bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv Eng Softw. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2017.07.00
Fathollahi-Fard AM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2018) A bi-objective green home health care routing problem. J Clean Prod 200:423–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.258
Nguyen TT, Dieu VN, Dinh BH (2018) An effectively adaptive selective cuckoo search algorithm for solving three complicated short-term hydrothermal scheduling problems. Energy 155:930–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.05.037
Kang T, Yao J, Jin M, Yang S, Duong T (2018) A novel improved cuckoo search algorithm for parameter estimation of photovoltaic (PV) models. Energies 11(5):1–31. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051060
Fayaz M, Kim D (2018) Energy consumption optimization and user comfort management in residential buildings using a bat algorithm and fuzzy logic. Energies 11(1):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11010161
Vo DN, Schegner P (2013) An improved particle swarm optimization for optimal power flow. In: Vasant PM (ed) Meta-heuristics optimization algorithms in engineering, business, economics, and finance. Pennsylvania, IGI Global, pp 1–40. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-4666-2086-5.ch001
Xiong G, Shi D (2018) Orthogonal learning competitive swarm optimizer for economic dispatch problems. Appl Soft Comput 66:134–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.02.019
MATPOWER 4.1 IEEE 30-bus and 118-bus test system. http://www.pserc.cornell.edu/matpower. Accessed 1 Jan 2018
Mernik M, Liu SH, Karaboga D, Crepinšek M (2015) On clarifying misconceptions when comparing variants of the artificial bee colony algorithm by offering a new implementation. Inf Sci 29:115–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.08.040
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, T.T., Vo, D.N. Improved social spider optimization algorithm for optimal reactive power dispatch problem with different objectives. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 5919–5950 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04073-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04073-4