Abstract
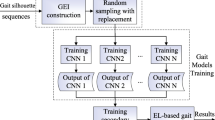
Gait has been well known as an unobtrusive promising biometric to identify a person from a distance. However, the effectiveness of silhouette-based approaches in gait recognition is diluted due to variations of view angles. In this paper, we put forward a novel and effective method of gait recognition: cross-view gait recognition based on ensemble learning. The proposed method greatly enhances the effectiveness and reduces the sensitivity of gait recognition under various view angles conditions. Furthermore, in this paper we will introduce a novel algorithm based on ensemble learning for combining several gait learners together, which utilizes a well-designed gait feature based on area average distance. Through experimental evaluations on the well-known CASIA gait database and OU-ISIR gait database, our paper demonstrates the advantages of the proposed method in comparison with others. The contribution of this research work is to resolve the multiview angles problem of gait recognition through assembling several gait learners.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Sarkar S, Phillips P, Liu Z (2005) The humanID gait challenge problem: data sets, performance, and analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(02):162–177
Wu Z, Huang Y, Wang L, Wang X, Tan T (2017) A comprehensive study on cross-view gait based human identification with deep CNNs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(02):209–226
Zhang J, Pu J, Chen C, Fleischer R (2010) Low-resolution gait recognition. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B (Cybernetics) 40(4):986–996
Guan Y, Li C, Roli F (2015) On reducing the effect of covariate factors in gait recognition: a classifier ensemble method. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(07):1521–1529
Yu S, Tan D, Tan T (2006) A framework for evaluating the effect of view angle, clothing and carrying condition on gait recognition. In: International conference on pattern recognition, pp 441–444
Iwama H, Okumura M, Makihara Y, Yagi Y (2012) The OU-ISIR gait database comprising the large population dataset and performance evaluation of gait recognition. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 7(5):1511–1521
Moustakas Konstantinos, Tzovaras Dimitrios, Stavropoulos Georgios (2010) Gait recognition using geometric features and soft biometrics. IEEE Signal Process Lett 17(04):367–370
Huang X, Boulgouris N (2012) Gait recognition with shifted energy image and structural feature extraction. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(04):2256–2268
Kusakunniran W, Wu Q, Zhang J, Li H (2012) Gait recognition across various walking speeds using higher order shape configuration based on a differential composition model. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B (Cybernetics) 42(6):1654–1668
Rida I, Jiang X, Marcialis GL (2016) Human body part selection by group lasso of motion for model-free gait recognition. IEEE Signal Process Lett 23(01):154–159
Theekhanont P, Kurutach W, Miguet S (2012) Gait recognition using GEI and pattern trace transform. In: International Symposium on Information Technologies in Medicine and Education, pp 936–940
Wang X, Wang J, Yan K (2018) Gait recognition based on Gabor wavelets and (2D)2PCA. Multimed Tools Appl 77(10):12545–12561
Zhang J, Pu J, Chen C, Fleischer R (2010) Low-resolution gait recognition. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 40(04):986–997
Lai Z, Xu Y, Jin Z, Zhang D (2014) Human gait recognition via sparse discriminant projection learning. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 24(10):1651–1662
Muramatsu D, Makihara Y, Yagi Y (2015) Cross-view gait recognition by fusion of multiple transformation consistency measures. IET Biom 4(2):62–73
Muramatsu D, Shiraishi A, Makihara Y, Uddin MZ, Yagi Y (2015) Gait-based person recognition using arbitrary view transformation model. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(1):140–154
Choudhury Sruti Das, Tjahjadi Tardi (2015) Robust view-invariant multiscale gait recognition. Pattern Recognit 48(03):798–811
Hu M, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Zhang D, Little JJ (2013) Incremental learning for video-based gait recognition with LBP flow. IEEE Trans Cybern 43(1):77–89
Connie T, Goh M, Teoh A (2017) A grassmannian approach to address view change problem in gait recognition. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(06):1395–1408
DaigoMuramatsu Makihara, Yagi Yasushi (2016) View transformation model incorporating quality measures for cross-view gait recognition. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(07):1602–1615
Zhang C, Liu W, Ma H, Fu H (2016) Siamese neural network based gait recognition for human identification. In: IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, pp 2832–2836
Boulgouris N, Huang X (2013) Gait recognition using HMMs and dual discriminative observations for sub-dynamics analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(09):3636–3647
Islam M, Islam M, Hossain M, Ferworn A, Molla M (2017) Subband entropy-based features for clothing invariant human gait recognition. Adv Robot 31(10):519–530
Aggarwal H, Vishwakarma D (2017) Covariate conscious approach for gait recognition based upon zernike moment invariants. IEEE Trans Cogn Dev Syst 1(99):1–1
Wang Liang, Ning Huazhong, Tan Tieniu, Weiming Hu (2004) Fusion of static and dynamic body biometrics for gait recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 14(2):149–158
Cuntoor N, Kale A, Chellappa R (2003) Combining multiple evidences for gait recognition. In: IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, vol 3, p III–33
Veres GV, Nixon MS, Middleton L, Carter JN (2005) Fusion of dynamic and static features for gait recognition over time. In: The 7th international conference on information fusion, vol 2, pp 7–16
Wang Liang, Tan Tieniu, Ning Huazhong, Weiming Hu (2003) Silhouette analysis-based gait recognition for human identification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 25(12):1505–1518
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521(5):436–445
Zhang H, Ji Y, Huang W, Liu L (2018) Sitcom-star-based clothing retrieval for video advertising: a deep learning framework. Neural Comput Appl 1(1):1–20
Takemura N, Makihara Y, Muramatsu D, Echigo T, Yagi Y (2018) On input/output architectures for convolutional neural network-based cross-view gait recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 28(1):316–322
Kuncheva LI, Bezdek JC, Duin RPW (2001) Decision templates for multiple classifier fusion: an experimental comparison. Pattern Recognit 34(2):299–314
Wang Xuan, Wu Qingxiang, Lin Xiaojin, Zhuo Zhigiang, Huang Liuping (2016) Pedestrian identification based on fusion of multiple features and multiple classifiers. Neurocomputing 188(SI):151–159
Nguyen Tien Thanh, Nguyen Thi Thu Thuy, Pham Xuan Cuong, Liew Alan Wee-Chung (2016) A novel combining classifier method based on variational inference. Pattern Recognit 49:198–212
Dempster AP, Laird NM, Rubin DB (1977) Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. R Stat Soc 39(1):1–22
Epaillard Elise, Bouguila Nizar (2016) Proportional data modeling with hidden Markov models based on generalized Dirichlet and Beta-Liouville mixtures applied to anomaly detection in public areas. Pattern Recognit 55:125–136
Zhang Q, Xu S (2009) Gait-based recognition of human using an embedded hidden Markov models. In: International conference on information engineering and computer science, pp 1–4
Shakhnarovich G, Darrell T (2002) On probabilistic combination of face and gait cues for identification. In: Proceedings of fifth IEEE international conference on automatic face gesture recognition, pp 176–181
Zhang H, Liu G, Chow TWS, Liu W (2011) Textual and visual content-based anti-phishing: a bayesian approach. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(10):1532–1546
McLachlan G, Krishnan T (2008) The EM algorithm and extensions. Wiley, New York
Zheng S, Zhang J, Huang K, He R, Tan T (2011) Robust view transformation model for gait recognition. In: The 18th IEEE international conference on image processing, pp 2073–2076
Acknowledgements
We thank reviewers for their constructive suggestions and valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled “Cross-View Gait Recognition Through Ensemble Learning”.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant Nos. 61303146 and 61602431 as well as a scholarship from the China Scholarship Council (CSC).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Yan, W.Q. Cross-view gait recognition through ensemble learning. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 7275–7287 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04256-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04256-z