Abstract
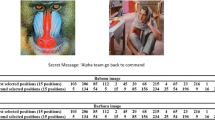
In our modern life, persons and institutions alike are rapidly embracing the shift toward communication via the Internet. As these entities adopt a faster and efficient communication protocol, information security techniques such as steganography and cryptography become powerful and necessary tools for conducting secure and secrecy communications. Currently, several steganography techniques have been developed, and the least significant bit (LSB) is one of these techniques which is a popular type of steganographic algorithms in the spatial domain. Indeed, as any other existing techniques, the selection of positions for data embedding within a cover signal mainly depends on a pseudorandom number generator without considering the relationship between the LSBs of the cover signal and the embedded data. In this paper and for best pixels’ positions adjustment, in which the visual distortion of the stego-image, as well as the embedding changes, becomes optimum, we propose two new position selection scenarios of LSBs-based steganography. Our new works are to improve the embedding efficiency, that is to say, select the suitable cover image pixels’ values that optimize the expected number of modifications per pixel and the visual distortion.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Ray PP (2015) Towards an internet of things based architectural framework for defence. In: Proceedings IEEE international conference on control instrumentation communication and computational technology, pp 411–416
Chambers J, Yan W, Garhwal A et al (2015) Currency security and forensics: a survey. Multimed Tools Appl 74(11):4013–4043
Chang CC, Lin CY, Wang YZ (2006) New image steganographic methods using run length approach. Inf Sci 176:3393–3408
Zhang X, Wang S (2004) Vulnerability of pixel-value differencing steganography to histogram analysis and modification for enhanced security. Pattern Recognit Signal Process Lett 25:331–339
Zujovic J, Pappas TN, Neuhoff DL (2013) Structural texture similarity metrics for image analysis and retrieval. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(7):2545–2558
Lee D, Plataniotis K (2015) Towards a full-reference quality assessment for color images using directional statistics. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(11):3950–3965
Ker AD , Bohme R (2008) Revisiting weighted stego-image steganalysis. In: Electronic imaging, security, forensics, steganography, and watermarking of multimedia contents X, San Jose, CA. Proceedings SPIE, January 2731, vol 6819, pp 5:1–5:17
Li X, Yang B, Cheng D, Zeng T (2009) A generalization of LSB matching. Signal Process Lett IEEE 16:69–72
Yang CH, Weng CY, Wang SJ, Sun HM (2008) Adaptive data hiding in edge areas of images with spatial LSB domain systems. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 3(3):488–497
Luo W, Huang F, Huang J (2010) Edge adaptive image steganography based on LSB matching revisited. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 5(2):201–214
Volkhonskiy D, Borisenko B, Evgeny B (2016) Generative adversarial networks for image steganography. In: ICLR 2016, open review
Shi H, Dong J, Wang W, Qian Y, Zhang XX (2018) Secure steganography based on generative adversarial networks. In: Advances in multimedia information processing PCM 2017. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 10735. Springer, Berlin
Baluja S (2017) Hiding images in plain sight: deep steganography. In: Proceedings of advances in neural information processing systems 30 (NIPS), pp 2069–2079
Zhang N, Ding S, Zhang J, Xue Y (2017) Research on point-wise gated deep networks. Appl Soft Comput 52:1210–12221
Zhang N, Ding S (2017) Unsupervised and semi-supervised extreme learning machine with wavelet kernel for high dimension data. Memet Comput 9(2):129–139
Zhang N, Ding S, Zhang J, Xue Y (2018) An overview on restricted Boltzmann machines. Neurocomputing 275:1186–1199
Bohme R, Grossklags J (2011) The security cost of cheap user interaction. In: Proceedings of the new security paradigms workshop. ACM, New York, pp 67–82
Khalil-Hani M, Marsono MN, Bakhteri R (2013) Biometric encryption based on a fuzzy vault scheme with a fast chaff generation algorithm. Future Gener Comput Syst 29:800–810
Verma AK, Patvardhan C, Lakshmi CV (2015) Robust adaptive watermarking based on image contents using wavelet technique. J Image Graph Signal Process 2:48–55
Cheddad A, Condell J, Curran K, McKevitt P (2010) Digital image steganography: survey and analysis of current methods. Sig Process 90:727–752
Malina L, Popelova L, Dzurenda P, Hajny J, Martinasek Z (2018) On feasibility of post-quantum cryptography on small devices. In: IFAC-papers on line, vol 51, no 6, pp 462–467
Abdul Manaf A, Bouroujerdizade A, Mojtaba S (2016) Collusion-resistant digital video watermarking for copyright protection application. Int J Appl Eng Res 11:3484–3495
Pradhan A, Sekhar KR, Swain G (2016) Digital image steganography based on seven way pixel value differencing. Indian J Sci Technol 9(37):1–11
Lee YP, Lee JC, Chen WK, Chang KC, Su IJ, Chang CP (2012) High-payload image hiding with quality recovery using tri-way pixel-value differencing. Inf Sci 191:214–225
Al-Shatanawi OM, El-Emam NN (2015) A new image steganography algorithm based on MLSB method with random pixels selection. Int J Net Secur Appl 7(2):37–53
Ker AD (2005) A general framework for the structural steganalysis of LSB replacement. In: Barni M, Herrera-Joancomart J, Katzenbeisser S, Prez-Gonzlez F (eds) Lecture notes in computer science: 7th international workshop on information hiding, Barcelona. Springer, Berlin, pp 296–311
Liu Z, Xi L (2007) Image information hiding encryption using chaotic sequence. In: Proceedings of the 11th international conference on knowledge-based intelligent information and engineering systems, pp 202–208
Zhang Y, Zuo F, Zhai Z, Xiaobin C (2008) A new image encryption algorithm based on multiple chaos system. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on electronic-commerce and security (ISECS’08), pp 347–350
Munir R, Riyanto B, Sutikno S, Agung WP (2007) Secure spread spectrum watermarking algorithm based on chaotic map for still images. In: Proceedings of the international conference on electrical engineering and informatics
Dawei Z, Guanrong C, Wenbo L (2004) A chaos-based robust wavelet-domain watermarking algorithm. Chaos Solut Fractals 22(1):47–54
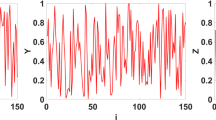
Chergui O, Bendjenna H, Meraoumia A, Patnaik S (2018) Can a chaos system provide secure communication over insecure networks? Online automatic teller machine services as a case study. J Electron Imaging 27(3):033045
Ye G, Wong KW (2012) An efficient chaotic image encryption algorithm based on a generalized Arnold map. Nonlinear Dyn 69(4):2079–2087
Komarasamy G, Wahi A (2012) An optimized K-means clustering technique using Bat algorithm. Eur J Sci Res 84(2):263–273
Yang XS (2010) A new metaheuristic bat-inspired algorithm. In: Gonzalez JR et al (eds) Nature inspired cooperative strategies for optimization (NISCO 2010), vol 284. Springer, Berlin, pp 65–74
Holland JH (1992) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. MIT Press, Cambridge
Wu Y-T, Shih FY (2006) Genetic algorithm based methodology for breaking the steganalytic systems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B 36(1):24–31
Shao-Hui L, Tian-Hang C, Hong-Xun Y, Wen G (2004) A variable depth LSB data hiding technique in images. In: Proceedings of 2004 international conference on machine learning and cybernetics, vol 7, pp 3990–3994
Fridrich J, Lisonek P, Soukal D (2007) On steganographic embedding efficiency. In: Camenisch J, Collberg C, Johnson N, Sallee P (eds) Information hiding. Springer, Berlin, pp 282–296
Westfeld A, Pfitzmann A (2001) High capacity despite better steganalysis (F5-a steganographic algorithm). In: Information hiding, 4th international workshop, pp 289–302
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the anonymous referees for their valuable and helpful comments. This research has been carried out within the PRFU project (Grant: A01L08UN120120180001) of the Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Larbi Tebessi, Tebessa. The authors thank the staff of LAMIS laboratory for helpful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laimeche, L., Meraoumia, A. & Bendjenna, H. Enhancing LSB embedding schemes using chaotic maps systems. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 16605–16623 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04523-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04523-z