Abstract
This paper considers the problem of leveraging multiple sources of information or data modalities (e.g., images and text) in neural networks. We define a novel model called gated multimodal unit (GMU), designed as an internal unit in a neural network architecture whose purpose is to find an intermediate representation based on a combination of data from different modalities. The GMU learns to decide how modalities influence the activation of the unit using multiplicative gates. The GMU can be used as a building block for different kinds of neural networks and can be seen as a form of intermediate fusion. The model was evaluated on two multimodal learning tasks in conjunction with fully connected and convolutional neural networks. We compare the GMU with other early- and late-fusion methods, outperforming classification scores in two benchmark datasets: MM-IMDb and DeepScene.








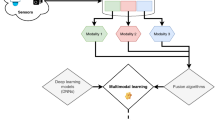
(Image taken from Valada et al. [65])



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Notes
We discarded the image with ID b275-311 from test set because it is incorrectly annotated.
References
Akata Z, Lee H, Schiele B (2014) Zero-shot learning with structured embeddings. CoRR abs/1409.8. arxiv:1409.8403
Alvear-Sandoval RF, Figueiras-Vidal AR (2018) On building ensembles of stacked denoising auto-encoding classifiers and their further improvement. Inf Fusion 39:41–52
Anand D (2014) Evaluating folksonomy information sources for genre prediction. In: Advance computing conference (IACC), 2014 IEEE international, pp 887–892. https://doi.org/10.1109/IAdCC.2014.6779440
Andrew G, Arora R, Bilmes JA, Livescu K (2013) Deep canonical correlation analysis. In: ICML (3), pp 1247–1255
Antol S, Agrawal A, Lu J, Mitchell M, Batra D, Lawrence Zitnick C, Parikh D (2015) Vqa: visual question answering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 2425–2433
Arevalo J, Solorio T, Montes-y Gómez M, González FA (2017) Gated multimodal units for information fusion. In: 5th international conference on learning representations 2017 workshop
Atrey PK, Hossain MA, El Saddik A, Kankanhalli MS (2010) Multimodal fusion for multimedia analysis: a survey. Multimed Syst 16(6):345–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-010-0182-0
Bengio Y (2012) Practical recommendations for gradient-based training of deep architectures. In: Montavon G, Orr GB, Müller KR (eds) Neural networks: tricks of the trade. Springer, Berlin, pp 437–478
Bengio Y, Ducharme R, Vincent P, Janvin C (2003) A neural probabilistic language model. J Mach Learn Res 3:1137–1155
Bergstra J, Bengio Y (2012) Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J Mach Learn Res 13(Feb):281–305
Bhatt C, Kankanhalli M (2011) Multimedia data mining: state of the art and challenges. Multimed Tools Appl 51(1):35–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-010-0645-5
Bouckaert RR, Frank E (2004) Evaluating the replicability of significance tests for comparing learning algorithms. In: Pacific-Asia conference on knowledge discovery and data mining. Springer, pp 3–12
Chen LC, Yang Y, Wang J, Xu W, Yuille AL (2016) Attention to scale: scale-aware semantic image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3640–3649
Cho K, Van Merriënboer B, Gulcehre C, Bahdanau D, Bougares F, Schwenk H, Bengio Y (2014) Learning phrase representations using rnn encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:14061078
Choromanska A, Henaff M, Mathieu M, Arous GB, LeCun Y (2015) The loss surfaces of multilayer networks. J Mach Learn Res 38:192–204
Coates A, Ng AY (2011) The importance of encoding versus training with sparse coding and vector quantization. In: Proceedings of the 28th international conference on machine learning (ICML-11), pp 921–928
Deng L (2014) A tutorial survey of architectures, algorithms, and applications for deep learning. APSIPA Trans Signal Inf Process. https://doi.org/10.1017/atsip.2013.9
Dietterich TG (1998) Approximate statistical tests for comparing supervised classification learning algorithms. Neural Comput 10(7):1895–1923
Feng F, Li R, Wang X (2013) Constructing hierarchical image-tags bimodal representations for word tags alternative choice. arXiv preprint arXiv:13071275
Fernando T, Denman S, Sridharan S, Fookes C (2018) Pedestrian trajectory prediction with structured memory hierarchies. arXiv preprint arXiv:180708381
Frome A, Corrado GS, Shlens J, Bengio S, Dean J, Ranzato MA, Mikolov T (2013) DeViSE: a deep visual-semantic embedding model. In: Burges CJC, Bottou L, Welling M, Ghahramani Z, Weinberger KQ (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems, vol 26. Curran Associates Inc., Hook, pp 2121–2129
Goodfellow I, Warde-farley D, Mirza M, Courville A, Bengio Y (2013) Maxout networks. In: Dasgupta S, Mcallester D (eds) Proceedings of the 30th international conference on machine learning (ICML-13), JMLR workshop and conference proceedings, vol 28, pp 1319–1327
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J (1997) Long short-term memory. Neural Comput 9(8):1735–1780. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
Huang EH, Socher R, Manning CD, Ng A (2012) Improving word representations via global context and multiple word prototypes. In: Proceedings of the 50th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics: long papers, vol 1. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 873–882
Huete A, Justice C, Van Leeuwen W (1999) Modis vegetation index (mod13). Algorithm Theor basis Doc 3:213
Ioffe S, Szegedy C (2015) Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: Proceedings of The 32nd international conference on machine learning, pp 448–456
Ivasic-Kos M, Pobar M, Mikec L (2014) Movie posters classification into genres based on low-level features. In: 2014 37th international convention on information and communication technology, electronics and microelectronics (MIPRO), vol i. IEEE, pp 1198–1203. https://doi.org/10.1109/MIPRO.2014.6859750
Ivasic-Kos M, Pobar M, Ipsic I (2015) Automatic movie posters classification into genres. In: Bogdanova MA, Gjorgjevikj D (eds) ICT Innovations 2014: world of data. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 319–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09879-1_32
Jacobs RA, Jordan MI, Nowlan SJ, Hinton GE (1991) Adaptive mixtures of local experts. Neural Comput 3(1):79–87
Janowczyk A, Madabhushi A (2016) Deep learning for digital pathology image analysis: a comprehensive tutorial with selected use cases. J Pathol Inform 7:1–29
Johnson J, Karpathy A, Fei-Fei L (2015) Densecap: fully convolutional localization networks for dense captioning. arXiv preprint arXiv:151107571
Kanaris I, Stamatatos E (2009) Learning to recognize webpage genres. Inf Process Manag 45(5):499–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2009.05.003
Kang Y, Kim S, Choi S (2012) Deep learning to hash with multiple representations. In: 2012 IEEE 12th international conference on data mining. IEEE, pp 930–935
Kiela D, Bottou L (2014) Learning image embeddings using convolutional neural networks for improved multi-modal semantics. In: Proceedings of the conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP-14), pp 36–45
Kiela D, Grave E, Joulin A, Mikolov T (2018) Efficient large-scale multi-modal classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:180202892
Kingma D, Ba J (2014) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:14126980
Kiros R, Salakhutdinov R, Zemel RS (2014a) Multimodal neural language models. ICML 14:595–603
Kiros R, Salakhutdinov R, Zemel RS (2014b) Unifying visual-semantic embeddings with multimodal neural language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:14112539
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Pereira F, Burges CJC, Bottou L, Weinberger KQ (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems 25. Curran Associates Inc, New york, pp 1097–1105
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521(7553):436–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Li Deng DY (2014) Deep learning: methods and applications. NOW Publishers, Boston
Liu F, Shen C, Lin G (2015) Deep convolutional neural fields for depth estimation from a single image. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5162–5170
Liu H, Wu Y, Sun F, Fang B, Guo D (2018) Weakly paired multimodal fusion for object recognition. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 15(2):784–795. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASE.2017.2692271
Logan I, Robert L, Humeau S, Singh S (2017) Multimodal attribute extraction. arXiv preprint arXiv:171111118
Lu X, Wu F, Li X, Zhang Y, Lu W, Wang D, Zhuang Y (2014) Learning multimodal neural network with ranking examples. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM international conference on multimedia. ACM, pp 985–988
Madjarov G, Kocev D, Gjorgjevikj D, Džeroski S (2012) An extensive experimental comparison of methods for multi-label learning. Pattern Recognit 45(9):3084–3104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2012.03.004
Makita E, Lenskiy A (2016) A movie genre prediction based on Multivariate Bernoulli model and genre correlations. arXiv preprint arXiv:160408608 (May), arxiv:1604.08608
Makita E, Lenskiy A (2016) A multinomial probabilistic model for movie genre predictions. arXiv preprint arXiv:160307849, http://arxiv.org/abs/1603.07849
Mandal D, Biswas S (2016) Generalized coupled dictionary learning approach with applications to cross-modal matching. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(8):3826–3837
Mao J, Xu W, Yang Y, Wang J, Yuille AL (2014) Explain images with multimodal recurrent neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:14101090
Mikolov T, Chen K, Corrado G, Dean J (2013) Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv preprint arXiv:13013781
Mikolov T, Sutskever I, Chen K, Corrado GS, Dean J (2013) Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In: Burges CJC, Bottou L, Welling M, Ghahramani Z, Weinberger KQ (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems. Curran Associates Inc, New york, pp 3111–3119
Ngiam J, Khosla A, Kim M (2011) Multimodal deep learning. In: Proceedings of the 28th international conference on machine learning (ICML-11), pp 689–696. http://ai.stanford.edu/~ang/papers/icml11-MultimodalDeepLearning.pdf. Accessed June 7 2018
Norouzi M, Mikolov T, Bengio S, Singer Y, Shlens J, Frome A, Corrado GS, Dean J (2014) Zero-shot learning by convex combination of semantic embeddings. CoRR abs/1312.5, arxiv:1312.5650
Pei D, Liu H, Liu Y, Sun F (2013) Unsupervised multimodal feature learning for semantic image segmentation. In: The 2013 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN). IEEE, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2013.6706748
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:14091556
Socher R, Ganjoo M, Manning CD, Ng A (2013) Zero-shot learning through cross-modal transfer. In: Burges CJC, Bottou L, Welling M, Ghahramani Z, Weinberger KQ (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems, vol 26. Curran Associates Inc, Hook, pp 935–943
Socher R, Karpathy A, Le QV, Manning CD, Ng AY (2014) Grounded compositional semantics for finding and describing images with sentences. Trans Assoc Comput Linguist (TACL) 2:207–218
Srivastava N, Salakhutdinov R (2012) Multimodal learning with deep Boltzmann machines. In: Pereira F, Burges C, Bottou L, Weinberger K (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems, vol 25. Curran Associates Inc, Hook, pp 2222–2230
Srivastava RK, Greff K, Schmidhuber J (2015) Highway networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:150500387
Suk HI, Shen D (2013) Deep learning-based feature representation for AD/MCI classification. In: Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics), vol 8150. LNCS, pp 583–590. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40763-5_72
Treml M, Arjona-Medina J, Unterthiner T, Durgesh R, Friedmann F, Schuberth P, Mayr A, Heusel M, Hofmarcher M, Widrich M et al (2016) Speeding up semantic segmentation for autonomous driving. NIPSW 1(7):8
Tu J, Wu Z, Dai Q, Jiang YG, Xue X (2014) Challenge Huawei challenge: fusing multimodal features with deep neural networks for mobile video annotation. In: 2014 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo workshops (ICMEW), pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMEW.2014.6890609
Valada A, Dhall A, Burgard W (2016) Convoluted mixture of deep experts for robust semantic segmentation. In: IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS) workshop, state estimation and terrain perception for all terrain mobile robots
Valada A, Oliveira G, Brox T, Burgard W (2016) Deep multispectral semantic scene understanding of forested environments using multimodal fusion. In: The 2016 international symposium on experimental robotics (ISER 2016), Tokyo, Japan. http://ais.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/publications/papers/valada16iser.pdf. Accessed June 7 2018
Van Merriënboer B, Bahdanau D, Dumoulin V, Serdyuk D, Warde-Farley D, Chorowski J, Bengio Y (2015) Blocks and fuel: frameworks for deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:150600619
Vinyals O, Toshev A, Bengio S, Erhan D (2015) Show and tell: a neural image caption generator. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3156–3164
Wei Q (2015) Bayesian fusion of multi-band images: a powerful tool for super-resolution. Ph.D. thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse (INPT)
Wei Q, Dobigeon N, Tourneret JY (2015) Bayesian fusion of multi-band images. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process 9(6):1117–1127
Wu P, Hoi SC, Xia H, Zhao P, Wang D, Miao C (2013) Online multimodal deep similarity learning with application to image retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 21st ACM international conference on multimedia—MM ’13. ACM Press, New York, pp 153–162. https://doi.org/10.1145/2502081.2502112
Wu Q, Teney D, Wang P, Shen C, Dick A, van den Hengel A (2017) Visual question answering: a survey of methods and datasets. Comput Vis Image Underst 163:21–40
Xu K, Ba J, Kiros R, Cho K, Courville A, Salakhutdinov R, Zemel RS, Bengio Y (2015) Show, attend and tell: neural image caption generation with visual attention 2(3):5. arXiv preprint arXiv:150203044
Yan R, Zhao D (2018) Smarter response with proactive suggestion: a new generative neural conversation paradigm. In: IJCAI, pp 4525–4531
Yao L, Zhang Y, Feng Y, Zhao D, Yan R (2017) Towards implicit content-introducing for generative short-text conversation systems. In: Proceedings of the 2017 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, pp 2190–2199
Ye F, Pu J, Wang J, Li Y, Zha H (2017) Glioma grading based on 3d multimodal convolutional neural network and privileged learning. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on bioinformatics and biomedicine (BIBM). IEEE, pp 759–763
Yuksel SE, Wilson JN, Gader PD (2012) Twenty years of mixture of experts. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 23(8):1177–1193
Zhao J, Xie X, Xu X, Sun S (2017) Multi-view learning overview: recent progress and new challenges. Inf Fusion 38:43–54
Zheng Y, Zhang YJ, Larochelle H (2014) Topic modeling of multimodal data: an autoregressive approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1370–1377
Acknowledgements
Arevalo thanks Colciencias for its support through a doctoral Grant in call 617/2013. This research was partially funded by CONACYT Project FC-2016/2410.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arevalo, J., Solorio, T., Montes-y-Gómez, M. et al. Gated multimodal networks. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 10209–10228 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04559-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04559-1