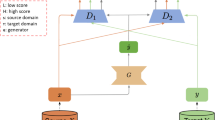
Abstract
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) have been accepted as powerful models in the field of computer vision, speech and language processing, etc. However, a major concern regarding GANs is the requirement of paired images for image-to-image translation, which is not always possible in the case of real-world applications. Moreover, they also suffer from training instability as well as mode collapse problem. These concerns remain open challenging issues for GANs and become more complex in the case of cyclic GAN. Motivated by evolutionary GAN, we hereby propose a novel evolutionary multiobjective cyclic GAN (EMOCGAN) to address the above stated challenges related to cyclic GAN training for the image-to-image translation. In this work, we have also introduced a new approach for model training by integrating the concept of evolutionary computation, multiobjective optimization, cyclic GAN along with different selection mechanisms. To overcome local optima stagnation, metropolis acceptance criteria and Pareto-based selection on two scores (objective functions) are utilized. Evolutionary concepts in training helped to address the instability and mode collapse problems. Extensive experiments on real-world image datasets show that the EMOCGAN outperforms state-of-the-art method in terms of visually realistic appearance and retaining background information as well as salient objects. Quantitative comparisons of our EMOCGAN with the cyclic GAN also show significantly better scores obtained by our model, as indicated by structural similarity index (SSIM) and universal quality index (UQI). The model demonstrated best efficacy in terms of SSIM on Apple\(\leftrightarrow\)Orange, while it shows higher UQI values for Monet\(\leftrightarrow\)Picture and Summer\(\leftrightarrow\)Winter datasets.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Al-Dujaili A, Schmiedlechner T, O’Reilly UM et al (2018) Towards distributed coevolutionary gans. arXiv:180708194
Albuquerque I, Monteiro J, Doan T, Considine B, Falk T, Mitliagkas I (2019) Multi-objective training of generative adversarial networks with multiple discriminators. arXiv:190108680
Arjovsky M, Bottou L (2017) Towards principled methods for training generative adversarial networks. arXiv:170104862
Beume N, Naujoks B, Emmerich M (2007) Sms-emoa: multiobjective selection based on dominated hypervolume. Eur J Oper Res 181(3):1653–1669
Bharti V, Biswas B, Shukla KK (2020) A novel multiobjective gdwcn-pso algorithm and its application to medical data security. ACM Trans Internet Technol (TOIT). https://doi.org/10.1145/3397679
Bharti V, Biswas B, Shukla KK (2020) Recent trends in nature inspired computation with applications to deep learning. In: 2020 10th international conference on cloud computing, data science and engineering (confluence). IEEE, pp 294–299
Brock A, Donahue J, Simonyan K (2018) Large scale gan training for high fidelity natural image synthesis. arXiv:180911096
Chollet F et al (2018) Keras: the python deep learning library. ascl pp ascl–1806
Costa V, Lourenço N, Correia J, Machado P (2019) Coegan: evaluating the coevolution effect in generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the genetic and evolutionary computation conference. pp 374–382
Costa V, Lourenço N, Correia J, Machado P (2021) Demonstrating the evolution of gans through t-sne. arXiv:210200524
Deb K (2001) Multi-objective optimization using evolutionary algorithms, vol 16. Wiley, New York
Efros AA, Leung TK (1999) Texture synthesis by non-parametric sampling. IEEE Proc Seventh IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis 2:1033–1038
Fedus W, Rosca M, Lakshminarayanan B, Dai AM, Mohamed S, Goodfellow I (2017) Many paths to equilibrium: gans do not need to decrease a divergence at every step. arXiv:171008446
Fogel DB (1995) Phenotypes, genotypes, and operators in evolutionary computation. In: Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE international conference evolutionary computation (ICEC-95). pp 193–198
Ghosh A, Kulharia V, Namboodiri VP, Torr PH, Dokania PK (2018) Multi-agent diverse generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 8513–8521
Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, Courville A, Bengio Y (2014) Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 2672–2680
Gulrajani I, Ahmed F, Arjovsky M, Dumoulin V, Courville AC (2017) Improved training of wasserstein gans. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 5767–5777
Heusel M, Ramsauer H, Unterthiner T, Nessler B, Hochreiter S (2017) Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 6626–6637
Hoang Q, Nguyen TD, Le T, Phung D (2018) Mgan: Training generative adversarial nets with multiple generators. In: International conference on learning representations
Isola P, Zhu JY, Zhou T, Efros AA (2017) Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 1125–1134
Kim T, Cha M, Kim H, Lee JK, Kim J (2017) Learning to discover cross-domain relations with generative adversarial networks. arXiv:170305192
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:14126980
Kumar A, Singh SK, Saxena S, Lakshmanan K, Sangaiah AK, Chauhan H, Shrivastava S, Singh RK (2020) Deep feature learning for histopathological image classification of canine mammary tumors and human breast cancer. Inf Sci 508:405–421
Kumar A, Singh SK, Saxena S, Singh AK, Shrivastava S, Lakshmanan K, Kumar N, Singh RK (2021) Comhisp: a novel feature extractor for histopathological image classification based on fuzzy svm with within-class relative density. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 29(1):103–117. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2995968
Li C, Wand M (2016) Combining markov random fields and convolutional neural networks for image synthesis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 2479–2486
Li H, Zhang Q, Deng J (2016) Biased multiobjective optimization and decomposition algorithm. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(1):52–66
Li S, Chen J, Xiang J (2019) Applications of deep convolutional neural networks in prospecting prediction based on two-dimensional geological big data. In: Neural computing and applications. pp 1–17
Liu MY, Breuel T, Kautz J (2017) Unsupervised image-to-image translation networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 700–708
Liu Z, Wang J, Liang Z (2020) Catgan: category-aware generative adversarial networks with hierarchical evolutionary learning for category text generation. In: AAAI. pp 8425–8432
Luijten B, Cohen R, De Bruijn FJ, Schmeitz HA, Mischi M, Eldar YC, Van Sloun RJ (2020) Adaptive ultrasound beamforming using deep learning. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(12):3967–3978. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.3008537
Mirza M, Osindero S (2014) Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv:14111784
Miyato T, Kataoka T, Koyama M, Yoshida Y (2018) Spectral normalization for generative adversarial networks. arXiv:180205957
Mu J, Zhou Y, Cao S, Zhang Y, Liu Z (2020) Enhanced evolutionary generative adversarial networks. In: 2020 39th Chinese control conference (CCC). IEEE, pp 7534–7539
Neyshabur B, Bhojanapalli S, Chakrabarti A (2017) Stabilizing gan training with multiple random projections. arXiv:170507831
Paoletti M, Haut J, Ghamisi P, Yokoya N, Plaza J, Plaza A (2020) U-img2dsm: unpaired simulation of digital surface models with generative adversarial networks. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2020.2997295
Phan DH, Suzuki J (2013) R2-ibea: R2 indicator based evolutionary algorithm for multiobjective optimization. In: 2013 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation. IEEE, pp 1836–1845
Pocock L, (Conference) S (2001) Proceedings of the 28th annual conference on computer graphics and interactive techniques. ACM
Salimans T, Goodfellow I, Zaremba W, Cheung V, Radford A, Chen X (2016) Improved techniques for training gans. arXiv:160603498
Singh R, Ahmed T, Kumar A, Singh AK, Pandey AK, Singh SK (2021) Imbalanced breast cancer classification using transfer learning. IEEE ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinf 18(1):83–93. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2020.2980831
Tan YY, Jiao YC, Li H, Wang XK (2012) A modification to moea/d-de for multiobjective optimization problems with complicated Pareto sets. Inf Sci 213:14–38
Toutouh J, Hemberg E, O’Reilly UM (2019) Spatial evolutionary generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the genetic and evolutionary computation conference. pp 472–480
Wang C, Xu C, Yao X, Tao D (2019) Evolutionary generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 23(6):921–934
Xie J, Lu Y, Gao R, Zhu SC, Wu YN (2018) Cooperative training of descriptor and generator networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42(1):27–45
Xu Z, Moro CF, Bozóky B, Zhang Q (2019) Gan-based virtual re-staining: a promising solution for whole slide image analysis. arXiv:190104059
Yang D, Hong S, Jang Y, Zhao T, Lee H (2019) Diversity-sensitive conditional generative adversarial networks. CoRR abs/1901.09024. http://arxiv.org/abs/1901.09024
Yeh RA, Chen C, Yian Lim T, Schwing AG, Hasegawa-Johnson M, Do MN (2017) Semantic image inpainting with deep generative models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 5485–5493
Yi Z, Zhang H, Tan P, Gong M (2017) Dualgan: Unsupervised dual learning for image-to-image translation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp 2849–2857
Zaltron N, Zurlo L, Risi S (2020) Cg-gan: an interactive evolutionary gan-based approach for facial composite generation. In: AAAI. pp 2544–2551
Zhang Q, Li H (2007) Moea/d: a multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 11(6):712–731
Zhang Y, Dw G, Xy S, Yn G (2017) A pso-based multi-objective multi-label feature selection method in classification. Sci Rep 7(1):1–12
Wang Z, Bovik AC (2002) A universal image quality index. IEEE Signal Process Lett 9(3):81–84. https://doi.org/10.1109/97.995823
Zhu JY, Park T, Isola P, Efros AA (2017a) Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp 2223–2232
Zhu JY, Zhang R, Pathak D, Darrell T, Efros AA, Wang O, Shechtman E (2017b) Toward multimodal image-to-image translation. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 465–476
Zitzler E, Laumanns M, Thiele L (2001) Spea2: Improving the strength Pareto evolutionary algorithm. TIK-report 103
Acknowledgements
The support and the resources provided by PARAM Shivay Facility under the National Supercomputing Mission, Government of India at the Indian Institute of Technology, Varanasi are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bharti, V., Biswas, B. & Shukla, K.K. EMOCGAN: a novel evolutionary multiobjective cyclic generative adversarial network and its application to unpaired image translation. Neural Comput & Applic 34, 21433–21447 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-05975-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-05975-y