Abstract
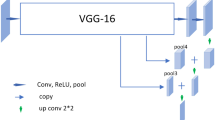
Segmentation of biomedical images is the method of semiautomatic and automatic detection of boundaries within 2D and 3D images. The major challenge of medical image segmentation is the high variability of shape, location, size and texture of the medical images. Manual segmentation is a time-consuming and monotonous process; therefore, a fully automated segmentation process is highly desirable. UNet is deployed as one of the most popular and generic architectures for medical image segmentation. This paper proposes and deploys two variants based on UNet architecture, namely 2DGA-UNet and 3DGA-UNet for the segmentation of 2D and 3D medical images, respectively. The first variant increases the impact of the 2DGA-UNet framework performance by applying transfer learning with the UNet architecture. We use simple convolutional neural networks from the VGG family known as VGG 16 as an encoder in the 2DGA-UNet network. The critical concept of 3DGA-UNet is to supplement a comprehensive contracting network by successive layers, where upsampling operators replace pooling operators. Such layers, therefore, improve the resolution of the output and further be trained end-to-end from very few images, outperforming the state-of-the-art methods. The proposed models are evaluated for 2D and 3D medical images on five benchmark datasets including brain tumor segmentation (BRATS 2018 and BRATS 2019), brain lesion segmentation (MICCAI 2008 multiple sclerosis challenge), lung segmentation (NIH tuberculosis chest X-ray dataset, Shenzhen No. 3 Hospital X-ray set, RSNA pneumonia detection challenge), liver segmentation (3D-IRCADb-01 database). The comprehensive results show remarkable performance considering 14 different evaluation parameters for the segmentation of medical images. Besides, the GA-UNet outperforms traditional methods in terms of ACC, i.e., 97.0% and the DSC of 91.8%.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu X, Guo S, Yang B, Ma S, Zhang H, Li J, Sun C, Jin L, Li X, Yang Q, Fu Y (2018) Automatic organ segmentation for CT scans based on super-pixel and convolutional neural networks. J Digit Imaging 31:748–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-018-0052-4
Cheng J, Liu J, Xu Y, Yin F, Wong DWK, Tan NM, Tao CY, Aung CT, Wong TY (2013) Superpixel classification based optic disc and optic cup segmentation for glaucoma screening. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 32(6):1019–1032
Fu H, Cheng J, Xu Y, Wong D, Liu J, Cao X (2018) Joint optic disc and cup segmentation based on multi-label deep network and polar transformation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 37:1597–1605
Aquino A, Gegúndez-Arias ME, Marín D (2010) Detecting the optic disc boundary in digital fundus images using morphological, edge detection, and feature extraction techniques. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29(11):1860–1869
Makropoulos A, Gousias IS, Ledig C, Aljabar P, Serag A, Hajnal JV, Edwards AD, Counsell SJ, Rueckert D (2014) Automatic whole brain mri segmentation of the developing neonatal brain. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 33(9):1818–1831
Menze BH, Jakab A, Bauer S, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Farahani K, Kirby J, Burren Y, Porz N, Slotboom J, Wiest R et al (2015) The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34(10):1993–2024
Cherukuri V, Ssenyonga P, Warf BC, Kulkarni AV, Monga V, Schiff SJ (2018) Learning based segmentation of CT brain images: application to postoperative hydrocephalic scans. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 65(8):1871–1884
Huang M, Yang W, Wu Y, Jiang J, Chen W, Feng Q (2014) Brain tumor segmentation based on local independent projection-based classification. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 61(10):2633–2645
Kumar S, Conjeti S, Roy AG, Wachinger C, Navab N (2018) Infinet: fully convolutional networks for infant brain mri segmentation. In: 15th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI). IEEE, pp 145–148
Chen W, Smith R, Ji SY, Ward KR, Najarian K (2009) Automated ventricular systems segmentation in brain ct images by combining low level segmentation and high-level template matching. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 9(1):1–14
Wang S, Zhou M, Liu Z, Gu D, Zang Y, Dong D, Gevaert O, Tian J (2017) Central focused convolutional neural networks: developing a data-driven model for lung nodule segmentation. Med Image Anal 40:172–183
Al-Kofahi Y, Lassoued W, Lee W, Roysam B (2010) Improved automatic detection and segmentation of cell nuclei in histopathology images. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(4):841–852
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, pp 234–241
Song T-H, Sanchez V, EIDaly H, Rajpoot NM (2017) Dual-channel active contour model for megakaryocytic cell segmentation in bone marrow trephine histology images. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 64(12):2913–2923
Fu M, Wu W, Hong X, Liu Q, Jiang J, Ou Y, Zhao Y, Gong X (2018) Hierarchical combinatorial deep learning architecture for pancreas segmentation of medical computed tomography cancer images. BMC SystBiol 12(4):56
Roth H, Lu L, Farag A, Shin H, Liu J, Turkbey E, Summers R (2015) Deeporgan: multi-level deep convolutional networks for automated pancreas segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, pp 556–564
Pham DL, Xu C, Prince JL (2000) Current methods in medical image segmentation. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 2(1):315–337
Mesejo P, Valsecchi A, Marrakchi-Kacem L, Cagnoni S, Damas S (2015) Biomedical image segmentation using geometric deformable models and metaheuristics. Comput Med Imaging Graph 43:167–178
Kamnitsas K, Bai W, Ferrante E, McDonagh SG, Sinclair M, Pawlowski N, Rajchl M, Lee M, Kainz B, Rueckert D, Glocker B (2017) Ensembles of multiple models and architectures for robust brain tumour segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention. Multimodal brain tumor segmentation challenge (MICCAI). LNCS
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521(7553):436
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Image net classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 1097–1105
LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P (1998) Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc IEEE 86:2278–2324
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2015) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1409.1556v6
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–9
Long J, Shelhammer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1411.4038v2 [cs.CV]
Kim J, Lee JK, Lee KM (2016) Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In: 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, pp 1646–1654. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.182
Ciresan DC, Giusti A, Gambardella LM, Schmidhuber J (2012) Deep neural networks segment neuronal membranes in electron microscopy images. In: NIPS
Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi S A (2016) V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1606.04797v1 [cs.CV]
Abdulkadir A, Lienkamp SS, Brox T, Ronneberger O (2016) 3D UNet: Learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (Athens), pp 424–432
Kamnitsas K, Ledig C, Newcombe V, Simpson J, Kane A, Menon D, Rueckert D (2017) Efficient multi-scale 3D CNN with fully connected CRF for accurate brain lesion segmentation. Med Image Anal 36:61–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2016.10.004
Havaei M, Davy A, Warde-Farley D (2016) Brain tumor segmentation with deep neural networks. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1505.03540v3 [cs.CV]
Zeiler MD, Fergus R (2014) Visualising and understanding convolutional networks. European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 818–833
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2015) A very deep convolutional networks for large scale image recognition. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1409-1556
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 630–645
Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger K Q (2017) Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4700–4708
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3431–3440
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–9
Zhou T, Ruan S, Canu S (2019) A review: deep learning for medical image segmentation using multi-modality fusion. Array. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.array.2019.100004
LeCun Y, Boser B, Denker JS, Henderson D, Howard RE, Hubbard W, Jackel LD (1989) Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition. Neural Comput 1(4):541–551
Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Ghafoorian M, Laak JAWMV, Ginneken BV, Sanchez CI (2017) A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal 42:60–88
Lin, Bill S, Michael, Kevin, Kalra, Shivam, Tizhoosh, Hamid R (2017). Skin lesion segmentation: U-nets versus clustering. In: 2017 IEEE symposium series on computational intelligence (SSCI). Springer, pp 1–7
Birenbaum A, Greenspay H (2017) Multiview longitudinal CNN for multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation. Eng Appl Artif Intell 65:111–118
Jameson M, Alison M, David K, Zhuowen T (2016). Dense volume-to-volume vascular boundary detection. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, pp 371–379
Setio AA, Traverso A, Bel T, Berens MS, Bogaard CV, Cerello P, Chen H, Dou Q, Fantacci ME, Geurts B, Gugten RV, Heng P, Jansen B, Kaste M, Kotov V, Lin J, Manders J, Sónora-Mengana A, García-Naranjo JC, Prokop M, Saletta M, Schaefer-Prokop C, Scholten ET, Scholten L, Snoeren M, Torres E, Vandemeulebroucke J, Walasek N, Zuidhof GC, Ginneken B, Jacobs C (2017) Validation, comparison, and combination of algorithms for automatic detection of pulmonary nodules in computed tomography images: The LUNA16 challenge. Med Image Anal 42:1–13
Sirinukunwattana K, Pluim J, Chen H, Qi X, Heng P, Guo Y, Wang L, Matuszewski B, Bruni E, Sanchez U, Böhm A, Ronneberger O, Cheikh BB, Racoceanu D, Kainz P, Pfeiffer M, Urschler M, Snead D, Rajpoot N (2017) Gland segmentation in colon histology images: the glas challenge contest. Med Image Anal 35:489–502
Zhou Y, Huang W, Dong P, Xia Y, Wang S (2019) D-UNet: a dimension-fusion U shape network for chronic stroke lesion segmentation. In: IEEE/ACM Transactions on computational biology and bioinformatics
Christ P, Elshaer M, Ettlinger F, Tatavarty S, Bickel M, Bilic P, Rempfler M, Armbruster M, Hofmann F, D'Anastasi M, Sommer W, Ahmadi S, Menze B (2016) Automatic liver and lesion segmentation in CT using cascaded fully convolutional neural networks and 3D conditional random fields. MICCAI
Gu Z, Cheng J, Fu H, Zhou K, Hao H, Zhao Y, Zhang T, Gao S, Liu J (2019) CE-Net: context encoder network for 2D medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38:2281–2292
Roth HR, Lu L, Farag A, Shin HC, Liu J, Turkbey EB, Summers RM (2015) Deeporgan: multi-level deep convolutional networks for automated pancreas segmentation. In: MICCAI
Roth HR, Lu L, Farag A, Sohn A, Summers RM (2016) Spatial aggregation of holistically nested networks for automated pancreas segmentation. In: MICCAI
Havaei M, Davy A, Warde-Farley D, Biard A, Courville AC, Bengio Y, Pal C, Jodoin P, Larochelle H (2017) Brain tumor segmentation with deep neural networks. MIA 35:18–31
Moeskops P, Wolterink JM, vander Velden BHM, Gilhuijs KGA, Leiner T, Viergever MA, Isgum I (2017) Deep learning for multi-task medical image segmentation in multiple modalities. CoRRabs/1704.03379
Wang Y, Zhou Y, Shen W, Park S, Fishman EK, Yuille AL (2018) Abdominal multi-organ segmentation with organ-attention networks and statistical fusion. CoRR abs/1804.08414
Wang Y, Zhou Y, Tang P, Shen W, Fishman EK, Yuille A (2018) Training multi-organ segmentation networks with sample selection by relaxed upper confident bound. In: Proceedings of MICCAI, pp434–442
Brosch T, Tang LY, Yoo Y, Li DK, Traboulsee A, Tam R (2016) Deep 3d convolutional encoder networks with shortcuts for multiscale feature integration applied to multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35:1229–1239. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2528821
Heimann T, Meinzer HP (2009) Statistical shape models for 3D medical image segmentation: a review. Med Image Anal 13(4):543–563
Dolz J, Massoptier L, Vermandel M (2015) Segmentation algorithms of subcortical brain structures on MRI for radiotherapy and radiosurgery: a survey. IRBM 36(4):200–212
Sinha A, Dolz J (2020) Multi-scale self-guided attention for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1906.02849v3
Bernal J, Kushibar K, Asfaw DS, Valverde S, Oliver A, Martí X, Lladóo R (2019) Deep convolutional neural networks for brain image analysis on magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Artif Intell Med 95:64–81
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3431–3440
Alom M, Hasan M, Yakopcic C, Taha T, Asari V (2018) Recurrent residual convolutional neural network based on U-Net (R2U-Net) for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1802.06955 [cs.CV]
Zheng S, Jayasumana S, Romera-Paredes B, Vineet V, Su Z, Du D, Huang C, Torr PH (2015) Conditional random fields as recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 1529–1537
Wang G, Li W, Ourselin S, Vercauteren T (2017) Automatic brain tumor segmentation using cascaded anisotropic convolutional neural networks. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention. Multimodal brain tumor segmentation challenge (MICCAI). LNCS
Isensee F, Kickingereder P, Wick W, Bendszus M, Maier-Hein KH (2018) No newnet. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI 2018). Multimodal brain tumor segmentation challenge (BRATS 2018). BrainLes 2018 workshop. LNCS, Springer
McKinley R, Meier R, Wiest R (2018) Ensembles of densely-connected CNNs with label-uncertainty for brain tumor segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (MICCAI)
Huang G, Liu Z, van der Maaten, L Weinberger, K Q (2017) Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2261–2269
Shakeri M, Tsogkas S, Ferrante E, Lippe S, Kadoury S, Paragios N, Kokkinos I (2016) Sub-cortical brain structure segmentation using FCNN's. In: International symposium on biomedical imaging, pp 269–272
Andermatt S, Pezold S, Cattin P (2016) Multi-dimensional gated recurrent units for the segmentation of biomedical 3D-data. In: Deep learning and data labeling for medical applications. Springer, pp 142–151
Oktay O, Schlemper J, Folgoc LL, Lee MJ, Heinrich M, Misawa K, Mori K, McDonagh SG, Hammerla N, Kainz B, Glocker B, Rueckert D (2018) Attention U-Net: learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1804.03999 [cs.CV]
Kaluva KC, Khened M, Kori A, Krishnamurthi G (2018) 2D-Densely connected convolution neural networks for automatic liver and tumor segmentation. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1802.02182
Li X, Chen H, Qi X, Dou Q, Fu C, Heng P (2018) H-DenseUNet: hybrid densely connected UNet for liver and tumor segmentation from CT Volumes. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 37:2663–2674
Sevastopolsky A (2017) Optic disc and cup segmentation methods for glaucoma detection with modification of u-net convolutional neural network. Pattern Recognit Image Anal 27(3):618–624
Roy AG, Conjeti S, Karri SPK, Sheet D, Katouzian A, Wachinger C, Navab N (2017) Relaynet: retinal layer and fluid segmentation of macular optical coherence tomography using fully convolutional networks. Biomed Opt Express 8(8):3627–3642
Norman B, Pedoia V, Majumdar S (2018) Use of 2d u-net convolutional neural networks for automated cartilage and meniscus segmentation of knee mr imaging data to determine relaxometry and morphometry. Radiology 288:177–185
Skourt BA, El HA, Majda A (2018) Lung ct image segmentation using deep neural networks. Proc Comput Sci 127:109–113
Pasa F, Golkov V, Pfeiffer F, Cremers D, Pfeiffer D (2019) Efficient deep network architectures for fast chest X-ray tuberculosis screening and visualization. Sci Rep 9(1):6268. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42557-4
Sathitratanacheewin S, Sunanta P, Pongpirul K (2020) Deep learning for automated classification of tuberculosis-related chest x-ray: dataset distribution shift limits diagnostic performance generalizability. Heliyon 6(8):e04614
Islam J, Zhang Y (2018) Towards robust lung segmentation in chest radiographs with deep learning. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1811.12638 [cs.CV]
Cui S, Mao L, Jiang J, Liu C, Xiong S (2018) Automatic semantic segmentation of brain gliomas from MRI images using a deep cascaded neural network. J Healthc Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4940593
El-Sherbiny B, Nabil N, El-Naby S H, Emad Y, Ayman N, Mohiy T, AbdelRaouf A (2018) BLB (Brain/Lung cancer detection and segmentation and Breast Dense calculation). In: First International Workshop on Deep and Representation Learning (IWDRL), pp 41–47. Cairo. https://doi.org/10.1109/IWDRL.2018.8358213
Amin J, Sharif M, Anjum MA, Raza M, Bukhari SA (2020) Convolutional neural network with batch normalisation for glioma and stroke lesion detection using MRI. Cogn Syst Res 59:304–311
Lakhani P, Sundaram B (2017) Deep learning at chest radiography: automated classification of pulmonary tuberculosis by using convolutional neural networks. Radiology. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017162326
Myronenko A (2019) 3D MRI brain tumor segmentation using autoencoder regularization. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, multiple sclerosis, stroke and traumatic brain injuries. BrainLes 2018. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 11384. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11726-9_28
Valverde S, Salem M, Cabezas M, Pareto D, Vilanova JC, Ramió-Torrentà L, Rovira A, Salvi J, Oliver A, Lladó X (2019) One-shot domain adaptation in multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation using convolutional neural networks. Neuroimage Clin 21:101638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2018.101638
Xue Y, Xie M, Farhat FG, Boukrina O, Barrett AM, Binder, Usman WR (2020) A multi-path decoder network for brain tumor segmentation. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, multiple sclerosis, stroke and traumatic brain injuries. BrainLes 2019. Lecture notes in computer science 11993. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46643-5_25
Almotairi S, Kareem G, Aouf M, Almutairi B, Salem MA (2020) Liver tumor segmentation in CT scans using modified SegNet. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 20(5):1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051516
Christ P, Ettlinger F, Grün F, Elshaer M, Lipková J, Schlecht S, Ahmaddy F, Tatavarty S, Bickel M, Bilic P, Rempfler M, Hofmann F, D'Anastasi M, Ahmadi S, Kaissis G, Holch J, Sommer W, Braren R, Heinemann V, Menze B (2017) Automatic liver and tumor segmentation of CT and MRI volumes using cascaded fully convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1702.05970 [cs.CV]
Jameson M (2018) Pneumonia detection in chest radiographs. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1811.08939
Yamashita R, Nishio M, Do RKG, Togashi K (2018) Convolutional neural networks: an overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging 9:611–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-018-0639-9
Dhillon A, Verma G (2019) Convolutional neural network: a review of models, methodologies and applications to object detection. Progress Artif Intell 9:85–112
Soffer S, Ben-Cohen A, Shimon O, Amitai MM, Greenspan H, Klang E (2019) Convolutional neural networks for radiologic images: a radiologist’s guide. Radiology 290(3):590–606. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2018180547
Iglovikov V, Shvets A (2018) TernausNet: U-Net with VGG11 encoder pre-trained on ImageNet for image segmentation. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1801.05746
Malla CUP, Hernandez MDCV, Rachmadi MF, Komura T (2019) Evaluation of enhanced learning techniques for segmenting ischaemic stroke lesions in brain magnetic resonance perfusion images using a convolutional neural network scheme. Front Neuroinform 13(33):1–16
Roth HR, Lu L, Farag A, Shin HC, Liu J, Turkbey EB, Summers, RM (2015) Deeporgan: multi-level deep convolutional networks for automated pancreas segmentation. In: MICCAI
Aquino A, Gegundez-Arias ME, Marin D (2010) Detecting the optic disc boundary in digital fundus images using morphological, edge detection, and feature extraction techniques. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29(11):1860–1869
Roth HR, Lu L, Farag A, Sohn A, Summers RM (2016) Spatial aggregation of holistically nested networks for automated pancreas segmentation. In: MICCAI
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2015) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. Int Conf Learn Represent. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2008.09.005
Available at https://towardsdatascience.com/unet-line-by-line-explanation-9b191c76baf5
Ibtehaz N, Rahman MS (2019) MultiResUnet: rethinking the U-Net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. arXiv:1902.04049v1
Bakas S, Akbari H, Sotiras A, Bilello M, Rozycki M, Kirby JS, Freymann JB, Farahani K, Davatzikos C (2017) Advancing the cancer genome atlas glioma mri collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Nat Sci Data 4:170117
Russakovsky O, Deng V, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M, Berg A, Fei-Fei Li (2014) ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1409.0575
Wang G, Li W, Ourselin S, Vercauteren T (2019) Automatic brain tumor segmentation based on cascaded convolutional neural networks with uncertainty estimation. Front Comput Neurosci 13:56. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncom.2019.00056
Chen W, Liu B, Peng S, Sun J, Qiao X (2018) S3D-UNet: separable 3D U-Net for brain tumor segmentation. BrainLes@MICCAI
Havaei M, Davy A, Warde-Farley D, Biard A, Courville A, Bengio Y, Pal C, Jodoin PM, Larochelle H (2017) Brain tumor segmentation with deep neural networks. Med Image Anal 35:18–31
Ben Naceur M, Akil M, Saouli R, Kachouri R (2020) Fully automatic brain tumor segmentation with deep learning-based selective attention using overlapping patches and multi-class weighted cross-entropy. Med Image Anal 63:101692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2020.101692
Mlynarski P, Delingette H, Criminisi A, Ayache N (2019) 3d convolutional neural networks for tumor segmentation using long-range 2d context. Comput Med Imaging Graph 73:60–72
Zhao X, Wu Y, Song G, Li Z, Zhang Y, Fan Y (2018) A deep learning model integrating fcnns and crfs for brain tumor segmentation. Med Image Anal 43:98–111
Kamnitsas K, Ledig C, Newcombe VF, Simpson JP, Kane AD, Menon DK, Rueckert D, Glocker B (2017) Efficient multi-scale 3d cnn with fully connected crf for accurate brain lesion segmentation. Med Image Anal 36:61–78
Ellwaa A, Hussein A, AlNaggar E, Zidan M, Zaki M, Ismail MA, Ghanem NM (2016) Brain tumor segmantation using random forest trained on iteratively selected patients. In International workshop on Brainlesion: glioma, multiple sclerosis, stroke and traumatic brain injuries, pp 129–137. Springer
Ben Naceur M, Saouli R, Akil M, Kachouri R (2018) Fully automatic brain tumor segmentation using end-to-end incremental deep neural networks in mri images. Compu Methods Prog Biomed 166:39–49
Fu J, Liu J, Tian H, Fang Z, Lu H (2019) Dual attention network for scene segmentation. IEEE/CVF Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn (CVPR) 2019:3141–3149
Li H, Xiong P, An J, Wang L (2018) Pyramid attention network for semantic segmentation. In: BMVC. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1805.10180
Wang Y, Dou H, Hu X, Zhu L, Yang X, Xu M, Qin J, Heng PA, Wang T, Ni D (2019) Deep attentive features for prostate segmentation in 3D transrectal ultrasound. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(12):2768–2778. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2913184
Schlemper J, Oktay O, Schaap M, Heinrich M, Kainz B, Glocker B, Rueckert D (2019) Attention gated networks: learning to leverage salient regions in medical images. Med Image Anal 53:197–207
Hamghalam M, Lei B, Wang T (2020) Brain tumor synthetic segmentation in 3D multimodal MRI scans. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, multiple sclerosis, stroke and traumatic brain injuries. BrainLes 2019. Lecture notes in computer science, vol. 11992. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46640-4_15
Li X, Luo G, Wang K (2020) Multi-step cascaded networks for brain tumor segmentation. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, multiple sclerosis, stroke and traumatic brain injuries. BrainLes 2019. Lecture notes in computer science, vol. 11992. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46640-4_16
Jiang Z, Ding C, Liu M, Tao D (2020) Two-stage cascaded U-Net: 1st place solution to BRATS challenge 2019 segmentation task. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, multiple sclerosis, stroke and traumatic brain injuries. BrainLes 2019. Lecture notes in computer science, vol. 11992. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46640-4_22
Xue Y, Xie M, Farhat FG, Boukrina O, Barrett AM, Binder JR, Roshan UW (2020) A multi-path decoder network for brain tumor segmentation. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brainlesion: glioma, multiple sclerosis, stroke and traumatic brain injuries. BrainLes 2019. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 11993. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46643-5_25
Dhillon A, Singh A (2018) Machine Learning in Healthcare Data Analysis: A Survey. J Biol Today’s World 8(2):1–10
Singh G, Singh A (2018) Object detection in fog degraded images. Int J Comput Sci Inform Secur 15(8):174–182
Kaur P, Sharma N, Singh A, Gill B (2018) CI-DPF: a cloud iot based framework for diabetes prediction. In: IEEE 9th annual information technology. Electronics and mobile communication conference (IEMCON) (IEEE)
Sharma N, Singh A (2019) Diabetes detection and prediction using machine learning/IoT: a survey. In: Advanced informatics for computing research. ICAICR communications in computer and information science, vol 955, pp 471–479
Singh G, Singh A (2019) Enhancement methods for low visibility and fog degraded images. In: Advanced informatics for computing research. ICAICR 2018. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 955, pp 489–498
Dhillon A, Singh A, Vohra H, Ellis C, Varghese B, Gill SS (2020) IoTPulse: machine learning based enterprise information system to predict alcohol addiction in Punjab (India) using IoT and fog computing. Enterprise Information System
Singh A, Dhillon A, Kumar N (2020) eDiaPredict: an ensemble based framework for diabetes prediction. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl
Chauhan A, Chauhan D, Rout C (2014) Role of GIST and PHOG features in computer-aided diagnosis of tuberculosis without segmentation. PLoS ONE 9:e112980
Candemir S, Jaeger S, Palaniappan K, Musco JP, Singh RK, Xue Z, Karargyris A, Antani S, Thoma G, McDonald CJ (2014) Lung segmentation in chest radiographs using anatomical atlases with nonrigid registration. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 33(2):577–590
Kalinovsky A, Kovalev V (2016) Lung image segmentation using deep learning methods and convolutional neural networks. In: XIII international conference on pattern recognition and information processing
Rashid R, Akram MU, Hassan T (2018) Fully convolutional neural network for lung segmentation from chest X-rays. In: International conference image analysis and recognition. Springer, Cham, pp 71–80
Islam J, Zhang Y (2018) Towards robust lung segmentation in chest radiographs with deep learning. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1811.12638 [cs.CV]
Pasa F, Golkov V, Pfeiffer F, Cremers D, Pfeiffer D (2019) Efficient deep network architectures for fast chest X-ray tuberculosis screening and visualization. Sci Rep 9:6268. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42557-4
Hwang S, Kim H, Jeong J, Kim H (2016) A novel approach for tuberculosis screening based on deep convolutional neural networks. Proc SPIE 9785:1–8
Jaeger S, Karargyris A, Candemir S, Folio L, Siegelman J, Callaghan F, Xue Z, Palaniappan K, Singh RK, Antani S, Thoma G, Wang YX, Lu PX, McDonald CJ (2013) Automatic tuberculosis screening using chest radiographs. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 33:233–245
Chlebus G, Meine H, Moltz JH, Schenk A (2017) Neural network-Based automatic liver tumor segmentation with random forest-Based candidate filtering. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1706.00842
Christ P, Elshaer M, Ettlinger F, Tatavarty S, Bickel M, Bilic P, Rempfler M, Armbruster M, Hofmann F, D'Anastasi M, Sommer W, Ahmadi S, Menze B (2016) Automatic liver and lesion segmentation in CT using cascaded fully convolutional neural networks and 3D conditional random fields. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1610.02177
Yang D, Xu D, Zhou SK, Georgescu B, Chen M, Grbic S, Metaxas DN, Comaniciu D (2017) Automatic liver segmentation using an adversarial image-To-Image network. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1707.08037
Bi L, Kim J, Kumar A, Feng D (2017) Automatic liver lesion detection using cascaded deep residual networks. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1704.02703
Ke Q, Zhang J, Wei W, Połap D, Wozniak M, Kosmider L, Damaševıcius R (2019) A neuro-Heuristic approach for recognition of lung diseases from X-Ray images. Expert Syst 126:218–232
Yuan Y (2017) Hierarchical convolutional–deconvolutional neural networks for automatic liver and tumor segmentation. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1710.04540
Li W, Jia F, Hu Q (2015) Automatic segmentation of liver tumor in CT images with deep convolutional neural networks. J Comput Commun 3:146–151
Almotairi S, Kareem G, Aouf M, Almutairi B, Salem MAM (2020) Liver tumor segmentation in CT Scans using modified SegNet. Sensors (Basel) 20(5):1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051516
Moghbel M, Mashohor S, Mahmud R, Saripan MIB (2016) Automatic liver tumor segmentation on computed tomography for patient treatment planning and monitoring. EXCLI J 15:406–423
Foruzan AH, Chen YW (2016) Improved segmentation of low-contrast lesions using sigmoid edge model. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11(7):1267–1283
Wu W, Wu S, Zhou Z, Zhang R, Zhang Y (2017). 3D liver tumor segmentation in CT images using improved fuzzy C-means and graph cuts. BioMed Research International, 2017
Christ P, Ettlinger F, Grün F, Elshaer M, Lipková J, Schlecht S, Ahmaddy F, Tatavarty S, Bickel M, Bilic P, Rempfler M, Hofmann F, DAnastasi M, Ahmadi S, Kaissis G, Holch J, Sommer W, Braren R, Heinemann V, Menze B (2017). Automatic liver and tumor segmentation of CT and MRI volumes using cascaded fully convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1702.05970 [cs.CV]
Souplet JC, Lebrun C, Ayache N, Malandain G (2008) An automatic segmentation of T2-FLAIR multiple sclerosis lesions. In: Multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation challenge workshop (MICCAI-2008), New York, NY, USA, pp 1–8
Geremia E, Clatz O, Menze BH, Konukoglu E, Criminisi A, Ayache N (2011) Spatial decision forests for MS lesion segmentation in multi-channel magnetic resonance images. Neuroimage 57(2):378–390
Jesson A, Arbel T (2015) Hierarchical MRF and random forest segmentation of MS lesions and healthy tissues in brain MRI
Guizard N, Coupe P, Fonov VS, Manjon JV, Arnold DL, Collins DL (2015) Rotation-invariant multicontrast non-local means for MS lesion segmentation. NeuroImage Clin 8:376–389
Tomas-Fernandez X, Warfield SK (2015) A model of population and subject (MOPS) intensities with application to multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34(6):1349–1361
Jerman T, Galimzianova A, Pernus F, Lik B, Spiclin Z (2015) Combining unsupervised and supervised methods for lesion segmentation. In: Proceedings the MICCAI 2015 brain lesions workshop, pp 1–12
Brosch T, Lisa YW, Yoo TY, Li DKB, Traboulsee A, Tam R (2016) Deep 3D convolutional encoder networks with shortcuts for multiscale feature integration applied to multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2528821
Geremia E, Menze B H, Clatz O, Konukoglu E, Criminisi A, and Ayache N (2010) Spatial decision forests for MS lesion segmentation in multi-channel MR images. In: Jian T, Navab N, Pluim J, Viergever M (eds) MICCAI 2010, Part I. LNCS, vol 6362, pp 111–118. Springer, Heidelberg
Shiee N, Bazin PL, Ozturk A, Reich DS, Calabresi PA, Pham DL (2010) A topology-preserving approach to the segmentation of brain images with multiple sclerosis lesions. Neuroimage 49(2):1524–1535
Weiss N, Rueckert D, Rao A (2013) Multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation using dictionary learning and sparse coding. In: Mori K, Sakuma I, Sato Y, Barillot C, Navab N (eds) MICCAI 2013, Part I. LNCS, vol 8149, pp 735–742. Springer, Heidelberg
Roura E, Oliver A, Cabezas M, Valverde S, Pareto D, Vilanova JC, Ramio-Torrenta L, Rovira A, Llado X (2013) A toolbox for multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation. Neuroradiology 57(10):1031–1043
Kaur A, Kaur L, Singh A (2020) State-of-the-art segmentation techniques and future directions for multiple sclerosis brain lesions. Arch Comput Methods Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-020-09403-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix

(A) The GA-UNet architecture for IRCAD dataset.

(B) The GA-UNet architecture for Lungs dataset.

(C) The GA-UNet architecture for MICCAI dataset.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, A., Kaur, L. & Singh, A. GA-UNet: UNet-based framework for segmentation of 2D and 3D medical images applicable on heterogeneous datasets. Neural Comput & Applic 33, 14991–15025 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06134-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06134-z