Abstract
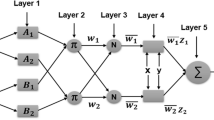
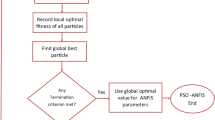
The viability of thermal waste-to-energy (WTE) plants and its optimal performance have informed intelligent predictive modelling of its significant variables critical to optimal energy recovery and plant operational planning using machine learning approach. However, the optimality of hyper-parameters is significant to accurate modelling of combustion enthalpy of waste in neuro-fuzzy models. In this study, the significant effect of hyper-parameters tuning of different clustering techniques, vis-à-vis fuzzy c-means (FCM), subtractive clustering (SC) and grid partitioning (GP), on the performance of the ANFIS model in its standalone and hybridized form was investigated. The ANFIS model was optimized with two evolutionary algorithms, namely particle swarm optimization (PSO) and genetic algorithm (GA), for predicting the lower heating value (LHV) of waste using the city of Johannesburg as a case study. The optimal model for LHV prediction was selected based on minimum error criteria after testing the models’ performance using relevant statistical metrics like root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), mean absolute deviation (MAD), relative mean bias error (rMBE) and coefficient of variation (RCoV). The result revealed a better performance of the hybridized ANFIS model than the standalone ANFIS model. Also, a significant variation in all models’ performance at different clustering technique was noted. However, all GP-clustered models gave the most accurate prediction than others. The most accurate model was obtained using a GP-clustered PSO-ANFIS model with triangular input membership function (tri-MF) giving RMSE, MAD, MAPE, rMBE and RCoV values of 0.139, 0.064, 2.536, 0.071 and 0.181, respectively. This study established the significance of municipality-based LHV prediction model to enhance the efficiency of thermal WTE plants and the robustness of evolutionary-based neuro-fuzzy model for heating value prediction.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Cheng J, Shi F, Yi J, Fu H (2020) Analysis of the factors that affect the production of municipal solid waste in China. J Clean Prod 259:120808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120808
Hoornweg D, Bhada-Tata P (2012) What a waste: A Global Review of Solid Waste Management. Urban papers no. 15. World Bank, Washington, DC. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/17388
Moharir RV, Gautam P, Kumar S (2019) Waste treatment processes/technologies for energy generation. In: Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-64083-3.00004-X
Adeleke O, Akinlabi SA, Jen TC, Dunmade I (2021) Sustainable utilization of energy from waste: a review of potentials and challenges of Waste-to-energy in South Africa. Int J Green Energy. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2021.1914629
Iyamu HO, Anda M, Ho G (2020) A review of municipal solid waste management in the BRIC and high-income countries: A thematic framework for low-income countries. Habitat Int 95:102097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2019.102097
Khan MD, Khan N, Sultana S, Joshi R, Ahmed S, Yu E, Scott K, Ahmad A, Khan MZ (2017) Bioelectrochemical conversion of waste to energy using microbial fuel cell technology. Process Biochem 57:141–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2017.04.001
Awasthi MK, Sarsaiya S, Chen H, Wang Q, Wang M, Awasthi SK, Li J, Liu T, Pandey A, Zhang Z (2019) Global status of waste-to-energy technology. In Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering. Elsevier, Amsterdam https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-64083-3.00003-8
Dadak A, Aghbashlo M, Tabatabaei M, Younesi H (2016) Exergy-based sustainability assessment of continuous photobiological hydrogen production using anaerobic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Clean Prod 139:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.020
Gutierrez-Gomez AC, Gallego AG, Palacios-Bereche R, de Campos T, Leite J, Pereira Neto AM (2021) Energy recovery potential from Brazilian municipal solid waste via combustion process based on its thermochemical characterization. J Clean Prod 293:126145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126145
Ludlow L et al (2021) Organic waste to energy: Resource potential and barriers to uptake in Chile. Sustain Prod Consum 28:1522–1537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.08.017
Mostakim K, Arefin MA, Islam MT, Shifullah KM, Islam AM (2021) Harnessing energy from the waste produced in Bangladesh: evaluating potential technologies. Heliyon 7(10):e08221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08221
Sagastume Gutiérrez A, Cabello Eras JJ, Hens L, Vandecasteele C (2020) The energy potential of agriculture, agroindustrial, livestock, and slaughterhouse biomass wastes through direct combustion and anaerobic digestion. The case of Colombia. J Clean Prod 269:1223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122317
Dalmo FC, Simão NM, Lima HQ, Medina Jimenez AC, Nebra S, Martins G, Palacios-Bereche R, Henriqu P (2019) Energy recovery overview of municipal solid waste in São Paulo State, Brazil. J Clean Prod 212:461–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.016
Anshar M, Negeri P, Pandang U, Nasir F, Universiti A, Anshar M (2015) The energy potential of municipal solid waste for power generation in Indonesia. J Mekanikal 37:42–54
Ibikunle RA, Titiladunayo IF, Akinnuli BO, Dahunsi SO, Olayanju TMA (2019) Estimation of power generation from municipal solid wastes: a case Study of Ilorin metropolis, Nigeria. Energy Rep 5:126–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2019.01.005
Bagheri M, Esfilar R, Sina M, Kennedy CA (2019) A comparative data mining approach for the prediction of energy recovery potential from various municipal solid waste. Renew Sus Energy Rev 116:109423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109423
Birgen C, Magnanelli E, Carlsson P, Skreiberg Ø, Mosby J, Becidan M (2021) Machine learning based modelling for lower heating value prediction of municipal solid waste. Fuel 283:118906
Mateus MM, Bordado JM, Galhano dos Santos R (2021) Simplified multiple linear regression models for the estimation of heating values of refuse derived fuels. Fuel 294:120541
Drudi KCR, Drudi R, Martins G, Antonio GC, Leite JTC (2019) Statistical model for heating value of municipal solid waste in Brazil based on gravimetric composition. Waste Manag 87:782–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.03.012
Khuriati A, Nur M, Istadi I (2015) Modeling the heating value of municipal solid waste based on ultimate analysis using stepwise multiple linear regression. J Eng Appl Sci 12(9):1–8
Amen R, Hameed J, Albashar G, Kamran HW, Hassan M, Shah U, Khaliq M, Zaman U, Mukhtar A, Saqib S, IqbalCh S, Ibrahim M, Ullah S, Al-Sehemi AG, Ahmad SR, Klemeš JJ, Bokhari A, Asif S (2021) Modelling the higher heating value of municipal solid waste for assessment of waste-to-energy potential: a sustainable case study. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125575
Ibikunle RA, Lukman AF, Titiladunayo IF, Akeju EA, Dahunsi SO (2020) Modeling and robust prediction of high heating values of municipal solid waste based on ultimate analysis. Energy Sources Part A Recover Util Environ Eff. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1841343
Qian X, Lee S, Soto AM, Chen G (2018) Regression model to predict the higher heating value of poultry waste from proximate analysis. Resources 7(3):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources7030039
Alrashed AA, Gharibdousti MS, Goodarzi M, de Oliveira LR, Safaei MR, BandarraFilho EP (2018) Effects on thermophysical properties of carbon based nanofluids: experimental data, modelling using regression, ANFIS and ANN. Int J Heat Mass Transf 125:920–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.04.142
Adeleke O, Akinlabi SA, Jen TC, Dunmade I (2021) Application of artificial neural networks for predicting the physical composition of municipal solid waste: an assessment of the impact of seasonal variation. Waste Manag Res 39(8):1058–1068. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X21991642
Khosravi R, Rabiei S, Khaki M, Safaei MR, Goodarzi M (2021) Entropy generation of graphene–platinum hybrid nanofluid flow through a wavy cylindrical microchannel solar receiver by using neural networks. J Therm Anal Calorim 145(4):1949–1967. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-10828-w
Moradikazerouni A, Hajizadeh A, Safaei MR, Afrand M, Yarmand H, Zulkifli NW (2019) Assessment of thermal conductivity enhancement of nano-antifreeze containing single-walled carbon nanotubes: optimal artificial neural network and curve-fitting. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 521:138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2019.01.051
Safaei MR, Hajizadeh A, Afrand M, Qi C, Yarmand H, Zulkifli NW (2019) Evaluating the effect of temperature and concentration on the thermal conductivity of ZnO-TiO2/EG hybrid nanofluid using artificial neural network and curve fitting on experimental data. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 519:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2018.12.010
Wang D, Tang YT, He J, Yang F, Robinson D (2021) Generalized models to predict the lower heating value (LHV) of municipal solid waste (MSW). Energy 216:119279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119279
Adeleke O, Akinlabi SA, Jen TC, Dunmade I (2020) Prediction of the heating value of municipal solid waste: a case study of the city of Johannesburg. Int J Ambient Energy. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2020.1861088
Abidoye LK, Mahdi FM (2014) Novel linear and nonlinear equations for the Higher Heating Values of Municipal Solid Wastes and the implications of carbon to energy ratios. J Energy Technol Policy 4(5):14–27
Shu HY, Lu HC, Fan HJ, Chang MC, Chen JC (2006) Prediction for energy content of taiwan municipal solid waste using multilayer perceptron neural networks. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 56(6):852–858. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2006.10464497
Olatunji OO, Akinlabi S, Madushele N, Adedeji PA, Felix I (2019) Multilayer perceptron artificial neural network for the prediction of heating value of municipal solid waste. AIMS Energy 7(6):944–956. https://doi.org/10.3934/energy.2019.6.944
Sarkheyli A, Mohd A (2015) Robust optimization of ANFIS based on a new modified GA. Neurocomputing 166(357–366):2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.03.060
Azad A, Manoochehri M, Kashi H, Farzin S, Karami H (2019) Comparative evaluation of intelligent algorithms to improve adaptive neuro- fuzzy inference system performance in precipitation modelling. J Hydrol 571:214–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.01.062
Adedeji PA, Akinlabi S, Madushele N, Olatunji OO (2020) Wind turbine power output very short-term forecast: a comparative study of data clustering techniques in a PSO-ANFIS model. J Clean Prod 254:120135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120135
Kumar R, Hynes NRJ (2019) Prediction and optimization of surface roughness in thermal drilling using integrated ANFIS and GA approach. Int J Eng Sci Technol 23(1):30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2019.04.011
Deshwal S, Td A, Kumar IF, Chhabra D (2020) Exercising hybrid statistical tools GA-RSM, GA-ANN and GA-ANFIS to optimize FDM process parameters for tensile strength improvement. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 31:189–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2020.05.009
Yadav HK, Pal Y, Tripathi MM (2019) A novel GA-ANFIS hybrid model for short-term solar PV power forecasting in Indian electricity market. J Optim Inf Sci 2667:377–395. https://doi.org/10.1080/02522667.2019.1580880
Keybondorian E, Soulgani BS, Bemani A (2018) Application of ANFIS-GA algorithm for forecasting oil flocculated asphaltene weight percentage in different operation conditions. Pet Sci Technol 36(12):862–868. https://doi.org/10.1080/10916466.2018.1447960
Zhang Z, Peng B, Luo C, Tai C (2021) ANFIS-GA system for three-dimensional pulse image of normal and string-like pulse in Chinese medicine using an improved contour analysis method. Eur J Integr Med 42:101301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eujim.2021.101301
Semero YK, Zheng D, Zhang J (2021) A PSO-ANFIS based hybrid approach for short term PV power prediction in microgrids. Electr Power Comp Syst 46(1):95–103. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325008.2018.1433733
Catalão JPS, Pousinho HMI, Mendes VMF (2011) Hybrid Wavelet-PSO-ANFIS approach for short-term wind power forecasting in Portugal. IEEE Trans Sustain Energy 2(1):50–59. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSTE.2010.2076359
Zanganeh M (2020) Improvement of the ANFIS-based wave predictor models by the Particle Swarm Optimization. J Ocean Eng Sci 5:84–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joes.2019.09.002
Sajadi A, Dashti A, Raji M, Zarei A, Mohammadi AH (2020) Estimation of cetane numbers of biodiesel and diesel oils using regression and PSO-ANFIS models. Renew Energy 158:465–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.04.146
Olatunji O, Akinlabi S, Madushele N, Adedeji PA (2019) Estimation of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) combustion enthalpy for energy recovery. EAI Endorsed Trans Energy Web 19(23):1–9. https://doi.org/10.4108/eai.11-6-2019.159119
Baghban A, Ebadi T (2019) GA-ANFIS modeling of higher heating value of wastes: application to fuel upgrading. Energy Sources Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 41(1):7–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2017.1344746
Mbuli (2015) Alternative waste treatment technology project Ingwenyama Resort, Mpumulanga Province. A waste report of the city of Johannesburg waste management. City of Johannesburg
Fattahi H (2016) Adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system based on fuzzy c–means clustering algorithm, a technique for estimation of tbm penetration rate. Iran Univ Sci Tech 6(2):159–171
Mustapha M, Mustafa MW, Khalid SN, Abubakar I, Abdilahi AM (2016) Correlation and wavelet-based short-term load forecasting using anfis. Indian J Sci Technol 9(46):1–8. https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i46/107141
Güldal V, Tongal H (2010) Comparison of recurrent neural network, adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system and stochastic models in eġirdir lake level forecasting. Water Resour Manag 24(1):105–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9439-9
Yeom CU, Kwak KC (2018) Performance comparison of ANFIS models by input space partitioning methods. Symmetry 10:700. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10120700
Wang X, Wang Z, Sheng M, Li Q, Sheng W (2021) An adaptive and opposite K-means operation based memetic algorithm for data clustering. Neurocomputing 437:131–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.01.056
Wei M, Bai B, Sung AH, Liu Q, Wang J, Cather ME (2007) Predicting injection profiles using ANFIS. Inf Sci (NY) 177(20):4445–4461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2007.03.021
Abonyi J, Andersen H, Nagy L, Szeifert F (1999) Inverse fuzzy-process-model based direct adaptive control. Math Comput Simul 51(1–2):119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4754(99)00142-1
Keshavarzi A, Sarmadian F, Shiri J, Iqbal M, Tirado-corbalá R, Omran EE (2017) Application of ANFIS-based subtractive clustering algorithm in soil Cation Exchange Capacity estimation using soil and remotely sensed data. Measurement 95:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2016.10.010
Sanikhani H, Kisi O, Nikpour MR, Dinpashoh Y (2012) Estimation of daily pan evaporation using two different adaptive neuro-fuzzy computing techniques. Water Resour Manag 26(15):4347–4365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0148-4
Benmouiza K, Cheknane A (2019) Clustered ANFIS network using fuzzy c-means, subtractive clustering, and grid partitioning for hourly solar radiation forecasting. Theor Appl Climatol 137(1–2):31–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2576-4
Abdulshahed AM, Longstaff AP, Fletcher S (2015) The application of ANFIS prediction models for thermal error compensation on CNC machine tools. Appl Soft Comput J 27:158–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2014.11.012
Eberhart R, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: Proceedings of the sixth international symposium on micro machine and human science. IEEE, pp 39–43. https://doi.org/10.1109/MHS.1995.494215
Arora A, Arabameri A, Pandey M, Siddiqui MA, Shukla UK, Tien D, Narayan V, Bhardwaj A (2021) Optimization of state-of-the-art fuzzy-metaheuristic ANFIS-based machine learning models for flood susceptibility prediction mapping in the Middle Ganga Plain. Sci Total Environ 750:141565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141565
Enayatollahi H, Fussey P, Nguyen BK (2020) Modelling evaporator in organic Rankine cycle using hybrid GD-LSE ANFIS and PSO ANFIS techniques. Therm Sci Eng Prog 19:100570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsep.2020.100570
Kumar R, Jesudoss NR (2020) Prediction and optimization of surface roughness in thermal drilling using integrated ANFIS and GA approach. Eng Sci Technol Int J 23(1):30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2019.04.011
Rezakazemi M, Dashti A, Asghari M, Shirazian S (2017) H2-selective mixed matrix membranes modeling. Intl J Hydrogen Energy 42(22):15211–15225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.04.044
Adedeji PA, Akinlabi S, Madushele N, Olatunji OO (2021) Hybrid neurofuzzy investigation of short-term variability of wind resource in site suitability analysis: a case study in South Africa. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06001-x
Adeleke O, Akinlabi SA, Jen TC, Dunmade I (2020) Prediction of municipal solid waste generation: an clustering techniques and parameters on ANFIS model performance. Environ Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2020.1845819
Pan WT (2009) Forecasting classification of operating performance of enterprises by zscore combining ANFIS and genetic algorithm. Neural Comput Appl 18(8):1005–1011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-009-0243-5
Karami A, Roshani GH, Salehizadeh A, Nazemi E (2017) The fuzzy logic application in volume fractions prediction of the annular three-phase flows. J Nondestruct Eval 36(2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-017-0415-7
Adil O, Ali A, Ali M, Ali AY, Sumait BS (2015) Comparison between the effects of different types of membership functions on fuzzy logic controller performance. Int J Emerg Eng Res Technol 3:76
Alfarraj O, Alkhalaf S (2017) Optimized automatic generation of fuzzy rules for nonlinear system based on subtractive clustering algorithm for medical image segmentation. J Med Imaging Heal Inform 7(2):500–507
Wiharto W, Suryani E (2019) The analysis effect of cluster numbers on fuzzy c-means algorithm for blood vessel segmentation of retinal fundus image. In: International conference on information, communication and computing technology, ICOIACT 2019, pp 106–110. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICOIACT46704.2019.8938583
Zhou K, Yang S (2020) Effect of cluster size distribution on clustering: a comparative study of k-means and fuzzy c-means clustering. Pattern Anal Appl 23(1):455–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-019-00783-6
Hossain M et al (2018) Application of the hybrid ANFIS models for long term wind power density prediction with extrapolation capability. PLoS ONE 13(4):e0193772
Xu A, Chang H, Xu Y, Li R, Li X, Zhao Y (2021) Applying artificial neural networks ( ANNs ) to solve solid waste-related issues: a critical review. Waste Manag 124:385–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.02.029
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the management of the Department of Mechanical Engineering Science, University of Johannesburg, South Africa, for providing workspace and research facilities for this research.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
O.A. involved in conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, writing—review & editing. S.A. took part in conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, writing—review & editing. T.-C.J. involved in conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, writing—review & editing. P.A.A. took part in conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, writing—review & editing. I.D. took part in conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adeleke, O., Akinlabi, S., Jen, TC. et al. Evolutionary-based neuro-fuzzy modelling of combustion enthalpy of municipal solid waste. Neural Comput & Applic 34, 7419–7436 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06870-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06870-2