Abstract
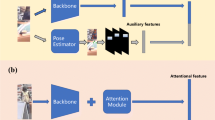
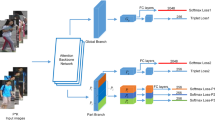
Pedestrians are often occluded by various obstacles in public places, which is a big challenge for person re-identification. To alleviate the occlusion problem, we propose a Pose-drive Attention Fusion Mechanism (PAFM) that jointly fuses the discriminative features with pose-driven attention and spatial attention in an end-to-end framework. To simultaneously use global and local features, a multi-task network is constructed to realize multi-granularity feature representation. After anchoring the region of interest to the un-occluded spatial semantic information in the image through the spatial attention mechanism, some key points of the pedestrian’s body are extracted using pose estimation and then fused with the spatial attention map to eliminate the harm of occlusion to the re-identification. Besides, the identification granularity is increased by matching the local features. We test and verify the effectiveness of the PAFM on Occluded-DukeMTMC, Occluded-REID and Partial-REID. The experimental results show that the proposed method has achieved competitive performance to the state-of-the-art methods.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Availability of data and material
We all make sure that all data and materials support our published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Artacho B, Savakis A (2020) Unipose: Unified human pose estimation in single images and videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p 7035–7044
Cao Z, Simon T, Wei SE, Sheikh Y (2017) Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, p 7291–7299
Chen K, Chen Y, Han C, Sang N, Gao C (2020) Hard sample mining makes person re-identification more efficient and accurate. Neurocomputing 382:259–267
Chen T, Ding S, Xie J, Yuan Y, Chen W, Yang Y, Ren Z, Wang Z (2019) Abd-net: Attentive but diverse person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, p 8351–8361
Chen X, Fu C, Zhao Y, Zheng F, Song J, Ji R, Yang Y (2020) Salience-guided cascaded suppression network for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p 3300–3310
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li LJ, Li K, Fei-Fei L (2009) Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, p 248–255. Ieee
Fang HS, Xie S, Tai YW, Lu C (2017) Rmpe: Regional multi-person pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, p 2334–2343
Gao Z, Gao L, Zhang H, Cheng Z, Hong R (2019) Deep spatial pyramid features collaborative reconstruction for partial person reid. In: MM Proceeding ACM International Conference Multimedia, p 1879–1887
Ge Y, Li Z, Zhao H, Yin G, Yi S, Wang X et al (2018) Fd-gan: Pose-guided feature distilling gan for robust person re-identification. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, p 1222–1233
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, p 770–778
He L, Liang J, Li H, Sun Z (2018) Deep spatial feature reconstruction for partial person re-identification: Alignment-free approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, p 7073–7082
He L, Wang Y, Liu W, Zhao H, Sun Z, Feng J (2019) Foreground-aware pyramid reconstruction for alignment-free occluded person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, p 8450–8459
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, p 7132–7141
Kendall A, Gal Y (2017) What uncertainties do we need in bayesian deep learning for computer vision? In: Advances in neural information processing systems, p 5574–5584
Kendall A, Gal Y, Cipolla R (2018) Multi-task learning using uncertainty to weigh losses for scene geometry and semantics. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, p 7482–7491
Lin TY, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, Dollar P, Zitnick CL (2014) Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In: European conference on computer vision, Springer, p 740–755
Liu J, Ni B, Yan Y, Zhou P, Cheng S, Hu J (2018) Pose transferrable person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p 4099–4108
Lu Y, Wu Y, Liu B, Zhang T, Li B, Chu Q, Yu N (2020) Cross-modality person re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, p 13376–13386
Luo H, Gu Y, Liao X, Lai S, Jiang W (2019) Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, p 0–0
Miao J, Wu Y, Liu P, Ding Y, Yang Y (2019) Pose-guided feature alignment for occluded person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, p 542–551
Peng D, Yu X, Peng W, Lu J (2021) DGFAU-Net: Global feature attention upsampling network for medical image segmentation. Neural Comput Appl 33(18):12023–12037. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-05908-9
Qian X, Fu Y, Jiang YG, Xiang T, Xue X (2017) Multi-scale deep learning architectures for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, p 5399–5408
Ristani E, Solera F, Zou R, Cucchiara R, Tomasi C (2016) Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, p 17–35.
Saquib Sarfraz M, Schumann A, Eberle A, Stiefelhagen R (2018) A pose-sensitive embedding for person re-identification with expanded cross neighborhood re-ranking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p 420–429
Sarfraz MS, Schumann A, Eberle A, Stiefelhagen R (2018) A pose-sensitive embedding for person re-identification with expanded cross neighborhood re-ranking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. p 420–429
Serbetci A, Akgul YS (2020) End-to-end training of CNN ensembles for person re-identification. Pattern Recogn 1(104):107319
Suh Y, Wang J, Tang S, Mei T, Mu Lee K (2018) Part-aligned bilinear representations for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), p 402–419
Sun K, Xiao B, Liu D, Wang J (2019) Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, p 5693–5703
Sun Y, Zheng L, Yang Y, Tian Q, Wang S (2018) Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), p 480–496
Tay CP, Roy S, Yap KH (2019) Aanet: Attribute attention network for person re-identifications. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p 7134–7143
Wang G, Yang S, Liu H, Wang Z, Yang Y, Wang S, Yu G, Zhou E, Sun J (2020) High-order information matters: Learning relation and topology for occluded person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p 6449–6458
Zhang C, Li Z, Wang Z (2018) Joint compressive representation for multi-feature tracking[J]. Neurocomputing 299:32–41
Zhang Z, Lan C, Zeng W, Chen Z (2019) Densely semantically aligned person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p 667–676
Zhao L, Li X, Zhuang Y, Wang J (2017) Deeply-learned part-aligned representations for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, p 3219–3228
Zheng F, Deng C, Sun X, Jiang X, Guo X, Yu Z, Huang F, Ji R (2019) Pyramidal person re-identification via multi-loss dynamic training. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p 8514–8522
Zheng L, Shen L, Tian L, Wang S, Wang J, Tian Q (2015) Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International conference on computer vision, p 1116–1124
Zheng WS, Li X, Xiang T, Liao S, Lai J, Gong S (2015) Partial person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, p 4678–4686
Zhou K, Yang Y, Cavallaro A, Xiang T (2019) Omni-scale feature learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, p 3702–3712
Zhou S, Wang J, Wang J, Gong Y, Zheng N (2017) Point to set similarity based deep feature learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, p 3741–3750
Zhuo J, Chen Z, Lai J, Wang G (2018) Occluded person re-identification. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME),IEEE, p 1–6
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.61866004, 61966004, 61962007), the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (Nos.2018GXNSFDA281009, 2019GXNSFDA245018,2018GXNSFDA294001), Research Fund of Guangxi Key Lab of Multi-source Information Mining and Security (No.20-A-03-01), Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education JXXYYJSCXXM-2021-013, and Guangxi “Bagui Scholar” Teams for Innovation and Research Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Not applicable
Code availability
Not applicable
Ethics approval
This paper strictly abides by the moral standards of this journal.
Consent to participate
All the authors of this paper have reviewed and agreed to contribute to your journal by consensus.
Consent for publication
Once this paper is hired, we agree to publish it in your journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Zhang, C., Tang, Y. et al. PAFM: pose-drive attention fusion mechanism for occluded person re-identification. Neural Comput & Applic 34, 8241–8252 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-06903-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-06903-4