Abstract
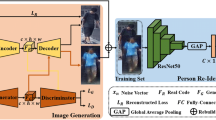
Person re-identification (Re-ID) aims to match a person of interest across multiple non-overlapping camera views. This is a challenging task, partly because a person captured in surveillance video often undergoes intense pose variations. Consequently, differences in their appearance are typically obvious. In this paper, we propose a pose variation aware data augmentation (\(\hbox {PA}^4\)) method, which is composed of a pose transfer generative adversarial network (PTGAN) and person re-identification with improved hard example mining (Pre-HEM). Specifically, PTGAN introduces a similarity measurement module to synthesize realistic person images that are conditional on the pose, and with the original images, form an augmented training dataset. Pre-HEM presents a novel method of using the pose-transferred images with the learned pose transfer model for person Re-ID. It replaces the invalid samples that are caused by pose variations and constrains the proportion of the pose-transferred samples in each mini-batch. We conduct extensive comparative evaluations to demonstrate the advantages and superiority of our proposed method over state-of-the-art approaches on Market-1501, DukeMTMC-reID, and CUHK03 dataset.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Zheng L, Yang Y, Hauptmann AG (2016) Person re-identification: past, present and future. arXiv preprintarXiv:1610.02984
Wang Z, Ruimin H, Yi Y, Jiang J, Liang C, Wang J (2016) Scale-adaptive low-resolution person re-identification via learning a discriminating surface. In: IJCAI, vol 2, p 6
Bedagkar-Gala A, Shah SK (2014) A survey of approaches and trends in person re-identification. Image Vis Comput 32(4):270–286
Vezzani R, Baltieri D, Cucchiara R (2013) People reidentification in surveillance and forensics: a survey. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 46(2):1–37
Gao J, Qing L, Li L, Cheng Y, Peng Y (2021) Multi-scale features based interpersonal relation recognition using higher-order graph neural network. Neurocomputing 456:243–252
Hongyang G, Guangyuan F, Li J, Zhu J (2021) Auto-reid+: searching for a multi-branch convnet for person re-identification. Neurocomputing 435:53–66
Chen L, Yang H, Qiling X, Gao Z (2021) Harmonious attention network for person re-identification via complementarity between groups and individuals. Neurocomputing 453:766–776
Zhao Q (2011) 10 scientific problems in virtual reality. Commun ACM 54(2):116–118
Liao S, Yang H, Zhu X, Li Stan Z (2015) Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2197–2206
Yan Y, Ni B, Song Z, Ma C, Yan Y, Yang X (2016) Person re-identification via recurrent feature aggregation. In: European conference on computer vision, pp 701–716. Springer
Zhang L, Xiang T, Gong S (2016) Learning a discriminative null space for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1239–1248
Chi S, Li J, Zhang S, Xing J, Gao W, Tian Q (2017) Pose-driven deep convolutional model for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 3960–3969
Jiang Na, Liu Junqi, Sun Chenxin, Wang Yuehua, Zhou Zhong, Wei Wu (2018) Orientation-guided similarity learning for person re-identification. In: 2018 24th International conference on pattern recognition (ICPR), pp 2056–2061. IEEE
Zheng Z, Zheng L, Yang Y (2017) Unlabeled samples generated by gan improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 3754–3762
Zheng L, Liyue SL, Tian SW, Wang J, Tian Q (2015) Scalable person re-identification: a benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 1116–1124
Li W, Zhao R, Xiao T, Wang X (2014) Deepreid: deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 152–159
Radford A, Metz L, Chintala S (2015) Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprintarXiv:1511.06434
Zhong Z, Zheng L, Zheng Z, Li S, Yang Y (2018) Camera style adaptation for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5157–5166
Liu J, Ni B, Yan Y, Zhou P, Cheng S, Hu J (2018) Pose transferrable person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4099–4108
Qian X, Fu Y, Xiang T, Wang W, Qiu J, Yang W, Jiang Y-G, Xue X (2018) Pose-normalized image generation for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 650–667
Mignon A, Pcca FJ A new approach for distance learning from sparse pairwise constraints. In: 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Zhao R, Ouyang W, Wang X (2013) Unsupervised salience learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3586–3593
Yi D, Lei Z, Liao S, Li S Z (2014) Deep metric learning for person re-identification. In: 2014 22nd International conference on pattern recognition, pp 34–39. IEEE
Varior R R, Haloi M, Wang G (2016) Gated siamese convolutional neural network architecture for human re-identification. In: European conference on computer vision, pp 791–808. Springer
Imani Z, Soltanizadeh H (2018) Histogram of the node strength and histogram of the edge weight: two new features for rgb-d person re-identification. Sci China Inf Sci 61(9):1–14
Zhao H, Tian M, Sun S, Shao J, Yan J, Yi S, Wang X, Tang X (2017) Spindle net: person re-identification with human body region guided feature decomposition and fusion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1077–1085
Sun Y, Zheng L, Yang Y, Tian Q, Wang S (2018) Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 480–496
Sun Y, Qin X, Li Y, Zhang C, Li Y, Wang S, Sun J (2019) Perceive where to focus: Learning visibility-aware part-level features for partial person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 393–402
Zhu K, Guo H, Liu Z, Tang M, Wang J (2020) Identity-guided human semantic parsing for person re-identification. arXiv preprintarXiv:2007.13467
Sun Y, Zheng L, Deng W, Wang S (2017) Svdnet for pedestrian retrieval. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 3800–3808
Li DW, Huang KQ et al (2018) Adversarially occluded samples for person re-identification
Zheng M, Karanam S, Ziyan W, Radke RJ (2019) Re-identification with consistent attentive siamese networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5735–5744
Zheng Z, Zheng L, Yang Y (2017) A discriminatively learned cnn embedding for person reidentification. ACM Trans Multimedia Comput, Commun, Appl (TOMM) 14(1):1–20
Varior RR, Shuai B, Lu J, Xu D, Wang G (2016) A siamese long short-term memory architecture for human re-identification. In: European conference on computer vision, pps 135–153. Springer
Deng W, Zheng L, Ye Q, Kang G, Yang Y, Jiao J (2018) Image-image domain adaptation with preserved self-similarity and domain-dissimilarity for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 994–1003
Schroff F, Kalenichenko D, Philbin J (2015) Facenet: a unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 815–823
Bin H, Jiwei X, Wang X (2021) Learning generalizable deep feature using triplet-batch-center loss for person re-identification. Sci China Inf Sci 64(2):1–2
Zhou J, Bing S, Ying W (2020) Online joint multi-metric adaptation from frequent sharing-subset mining for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2909–2918
Ioffe S, Szegedy C (2015) Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv preprintarXiv:1502.03167
Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Salakhutdinov R (2014) Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J Mach Learn Res 15(1):1929–1958
McLaughlin N, Del Rincon JM, Miller P (2015) Data-augmentation for reducing dataset bias in person re-identification. In: 2015 12th IEEE International conference on advanced video and signal based surveillance (AVSS), pp 1–6. IEEE
Zhong Z, Zheng L, Kang G, Li S, Yang Y (2020) Random erasing data augmentation. In: AAAI, pp 13001–13008
Huang Houjing, Li Dangwei, Zhang Zhang, Chen Xiaotang, Huang Kaiqi (2018) Adversarially occluded samples for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 5098–5107
Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Bing X, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, Courville A, Bengio Y (2014) Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 2672–2680
Mirza M, Osindero S (2014) Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv preprintarXiv:1411.1784
Isola P, Zhu J-Y, Zhou T, Efros Alexei A (2017) Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1125–1134
Wei L, Zhang S, Gao W, Tian Q (2018) Person transfer gan to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 79–88
Zheng Z, Yang X, Zhiding Y, Zheng L, Yang Y, Kautz J (2019) Joint discriminative and generative learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2138–2147
Cao Z, Simon T, Wei S-E, Sheikh Y (2017) Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 7291–7299
Zhang Y, Zhong Q, Ma L, Xie D, Shiliang P (2019) Learning incremental triplet margin for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol 33, pp 9243–9250
Wang X, Doretto G, Sebastian T, Rittscher J, Peter T (2007) Shape and appearance context modeling. In: 2007 ieee 11th international conference on computer vision, pp 1–8. Ieee
Luo H, Gu Y, Liao X, Lai S, Jiang W (2019) Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp 0–0
Siarohin A, Sangineto E, Lathuilière S, Sebe N (2018) Deformable gans for pose-based human image generation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3408–3416
Zhong Z, Zheng L, Cao D, Li S (2017) Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1318–1327
Ge Y, Li Z, Zhao H, Yin G, Yi S, Wang X et al (2018) Fd-gan: pose-guided feature distilling gan for robust person re-identification. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 1222–1233
Suh Y, Wang J, Tang S, Mei T, Kyoung ML (2018) Part-aligned bilinear representations for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 402–419
Wang C, Zhang Q, Huang C, Liu W, Wang X (2018) Mancs: a multi-task attentional network with curriculum sampling for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 365–381
Wang G, Gong S, Cheng J, Hou Z (2020) Faster person re-identification. In: European conference on computer vision, pp 275–292. Springer
Hong P, Tao W, Ancong W, Han X, Zheng W-S (2021) Fine-grained shape-appearance mutual learning for cloth-changing person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 10513–10522
Nguyen Binh X, Nguyen Binh D, Do T, Tjiputra E, Tran Quang D, Nguyen A (2021) Graph-based person signature for person re-identifications. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3492–3501
Chen T, Ding S, Xie J, Yuan Y, Chen W, Yang Y, Ren Z, Wang Z (2019) Abd-net: attentive but diverse person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 8351–8361
Chen X, Canmiao F, Zhao Y, Zheng F, Song J, Ji R, Yang Y (2020) Salience-guided cascaded suppression network for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3300–3310
Lin Y, Zheng L, Zhedong Zheng YW, Zhilan H, Yan C, Yang Y (2019) Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning. Pattern Recogn 95:151–161
Chen B, Deng W, Jiani H (2019) Mixed high-order attention network for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 371–381
Quan R, Xuanyi Dong YW, Zhu L, Yang Y (2019) Auto-reid: searching for a part-aware convnet for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 3750–3759
Zhang Z, Lan C, Zeng W, Chen Z (2019) Densely semantically aligned person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 667–676
Zheng F, Deng C, Sun X, Jiang X, Guo X, Zongqiao Y, Huang F, Ji R (2019) Pyramidal person re-identification via multi-loss dynamic training. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 8514–8522
Quispe R, Pedrini H (2021) Top-db-net: top dropblock for activation enhancement in person re-identification. In: 2020 25th International conference on pattern recognition (ICPR), pp 2980–2987. IEEE
Zhang S, Zhang L, Wang W, Xiaofu W (2020) Asnet: asymmetrical network for learning rich features in person re-identification. IEEE Signal Process Lett 27:850–854
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFB2100603) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61872024). The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Jiang, N., Diao, Q. et al. Person Re-identification with pose variation aware data augmentation. Neural Comput & Applic 34, 11817–11830 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07071-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07071-1