Abstract
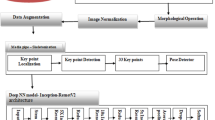
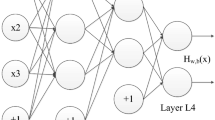
This paper provides an in-depth analysis and study of the simulation of 3D human animation visualization techniques by enhancing machine learning algorithms. Based on the statistical analysis of the data obtained from different measurement methods, the extraction of human body feature parameters based on millimeter-wave point cloud data is realized, and the 3D reconstruction and simulation of the human body are realized using parametric human modeling software. In video-based action recognition, most methods are data-driven and use deep networks to automatically learn features of the entire video image. In this process, specific research on human actions is not included or reflected. However, human action recognition is a processing of the semantic level of video content. Realizing universal human action recognition requires a semantic understanding of human behavior. Firstly, the geometric feature analysis of the 3D scanned human model is performed to extract the human body shape characteristic parameters, and the research on the analysis and estimation methods of body shape characteristic parameters is carried out to establish the human body shape parameter relationship model; then, the millimeter-wave point cloud is calculated and measured, the Li group features extracted using the group skeletal representation model with high data dimensionality, to be able to process the high-dimensional data, while reducing the complexity of the recognition process and speeding up the computation, feature learning and classification are performed with convolutional neural networks. To verify the better library portability and robustness of the method in this paper, the method was tested on a self-built human action database in the laboratory, and an average recognition rate of 97.26% was achieved. Meanwhile, this paper investigates the natural interaction application of virtual characters in a virtual learning environment based on human action recognition. Four testers tested the virtual human–computer interaction system of this paper, respectively, and the final test results show that the system has flexibility and stability.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Change history
28 April 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07267-5
References
Alexopoulos K, Nikolakis N, Chryssolouris G (2020) Digital twin-driven supervised machine learning for the development of artificial intelligence applications in manufacturing. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 33(5):429–439
Yang J, Wang C, Jiang B et al (2020) Visual perception enabled industry intelligence: state of the art, challenges and prospects. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 17(3):2204–2219
Ghana S, Singh S, Jalali A et al (2020) Adaptive visual learning using augmented reality and machine learning techniques. J Comput Theor Nanosci 17(11):4952–4956
Tian Y, Li Y, Pan L et al (2020) Research on group animation design technology based on artificial fish swarm algorithm. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 38(2):1137–1145
Myszczynska MA, Ojamies PN, Lacoste AMB et al (2020) Applications of machine learning to diagnosis and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurol 16(8):440–456
Liu MY, Huang X, Yu J et al (2021) Generative adversarial networks for image and video synthesis: algorithms and applications. Proc IEEE 109(5):839–862
Smith B, Wu C, Wen H et al (2020) Constraining dense hand surface tracking with elasticity. ACM Trans Graph (TOG) 39(6):1–14
Puzyrev D, Harth K, Trittel T et al (2020) Machine learning for 3D particle tracking in granular gases. Microgravity Sci Technol 32(5):897–906
Ukrit MF, Nithyakani P (2020) The systematic review on gait analysis: trends and developments. Eur J Mol Clin Med 7(6):1636–1654
Siddique S, Chow JCL (2021) Machine learning in healthcare communication. Encyclopedia 1(1):220–239
Mourdi Y, Sadgal M, Fathi WB et al (2020) A machine learning based approach to enhance MOOC users’ classification. Turk Online J Distance Educ 21(2):47–68
Khan SA, Khan MA, Song OY et al (2020) Medical imaging fusion techniques: a survey benchmark analysis, open challenges and recommendations. J Med Imaging Health Inf 10(11):2523–2531
Carrozzino MA, Galdieri R, Machidon OM et al (2020) Do virtual humans dream of digital sheep? IEEE Comput Graphics Appl 40(4):71–83
de Belen RAJ, Bednarz T, Sowmya A et al (2020) Computer vision in autism spectrum disorder research: a systematic review of published studies from 2009 to 2019. Transl Psychiatry 10(1):1–20
Fu K, Peng J, He Q et al (2021) Single image 3D object reconstruction based on deep learning: a review. Multimed Tools Appl 80(1):463–498
Shimada S, Golyanik V, Xu W et al (2020) Physcap: physically plausible monocular 3d motion capture in real time. ACM Trans Graph (TOG) 39(6):1–16
Sagayam KM, Timothy AJ, Ho CC et al (2020) Augmented reality-based solar system for e-magazine with 3-D audio effect. Int J Simul Process Model 15(6):524–534
Wang ZJ, Turko R, Shaikh O et al (2020) CNN explainer: learning convolutional neural networks with interactive visualization. IEEE Trans Visual Comput Graph 27(2):1396–1406
Mahayuddin ZR, Saif AFMS (2020) A comprehensive review towards segmentation and detection of cancer cell and tumor for dynamic 3D reconstruction. Asia-Pacific J Inf Technol Multimed 9(1):28–39
Devi PRS, Baskaran R (2021) SL2E-AFRE: personalized 3D face reconstruction using autoencoder with simultaneous subspace learning and landmark estimation. Appl Intell 51(4):2253–2268
Zhang S, Callaghan V (2021) Real-time human posture recognition using an adaptive hybrid classifier. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 12(2):489–499
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by High-level Science Foundation of Qingdao Agricultural University (Grant number 6631121712).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, H., Lee, J.H. & Zhang, S. Research on simulation of 3D human animation vision technology based on an enhanced machine learning algorithm. Neural Comput & Applic 35, 4243–4254 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07083-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07083-x