Abstract
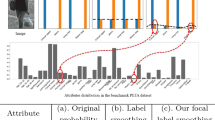
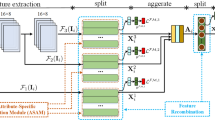
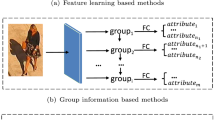
Pedestrian Attribute Recognition (PAR) can provide valuable clues for several innovative surveillance applications. It is also a difficult task because inference of the multiple attributes at a far distance is challenging in real complex scenarios. Most existing methods improve the PAR with visual attention mechanisms or body-part detection modules, which increase the complexity of networks and require manual annotations of the human body. Also, uneven data distribution, leading to a decline in recall values, is still underestimated. This paper presents a novel multi-label optimization algorithm to mitigate these issues, named Multi-label Contrastive Focal Loss (MCFL). Specifically, we first propose a multi-label focal loss to emphasize the error-prone and minority attributes with a separated re-weighting scheme. And then, we introduce a multi-label contrastive learning strategy based on the multi-label divergences to help the deep network to distinguish the hard fine-grained attributes. We conduct extensive experiments on seven PAR benchmarks, and results indicate that the proposed MCFL with the native ResNet-50 backbone surpasses the state-of-the-art comparison methods in mean accuracy and recall.









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Galiyawala H, Raval MS (2021) Person retrieval in surveillance using textual query: a review. Multim Tools Appl 80(18):27343–27383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10983-0
Cheng K, Tao F, Zhan Y, Li M, Li K (2020) Hierarchical attributes learning for pedestrian re-identification via parallel stochastic gradient descent combined with momentum correction and adaptive learning rate. Neural Comput Appl 32(10):5695–5712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04485-2
Lin Y, Zheng L, Zheng Z, Wu Y, Hu Z, Yan C, Yang Y (2019) Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning. Pattern Recognit 95:151–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.06.006
Ji Z, Li S (2020) Multimodal alignment and attention-based person search via natural language description. IEEE Internet Things J 7(11):11147–11156. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.2995148
Li D, Zhang Z, Chen X, Huang K (2019) A richly annotated pedestrian dataset for person retrieval in real surveillance scenarios. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(4):1575–1590. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2878349
Fayyaz M, Yasmin M, Sharif M, Raza M (2021) J-LDFR: joint low-level and deep neural network feature representations for pedestrian gender classification. Neural Comput Appl 33(1):361–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05015-1
Aggarwal S, RADHAKRISHNAN VB, Chakraborty A (2020) Text-based person search via attribute-aided matching. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision, pp 2617–2625. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV45572.2020.9093640
Wu M, Huang D, Guo Y, Wang Y (2020) Distraction-aware feature learning for human attribute recognition via coarse-to-fine attention mechanism. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol. 34, pp 12394–12401. https://aaai.org/ojs/index.php/AAAI/article/view/6925
Sarafianos N, Xu X, Kakadiaris IA (2018) Deep imbalanced attribute classification using visual attention aggregation. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 680–697. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01252-6_42
Park S, Nie BX, Zhu S-C (2018) Attribute and-or grammar for joint parsing of human pose, parts and attributes. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(7):1555–1569. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2731842
Li D, Chen X, Zhang Z, Huang K (2018) Pose guided deep model for pedestrian attribute recognition in surveillance scenarios. In: 2018 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (ICME), pp 1–6 . https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME.2018.8486604. IEEE
Zheng X, Yu Z, Chen L, Shilong Wang FZ (2021) Multi-label contrastive focal loss for pedestrian attribute recognition. In: 25th international conference on pattern recognition, ICPR 2020, Virtual Event / Milan, Italy, January 10-15, 2021, pp 7349–7356 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR48806.2021.9411959
Sudowe P, Spitzer H, Leibe B (2015) Person attribute recognition with a jointly-trained holistic cnn model. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops, pp 87–95
Li D, Chen X, Huang K (2015) Multi-attribute learning for pedestrian attribute recognition in surveillance scenarios. In: 3rd IAPR Asian conference on pattern recognition, ACPR 2015, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, November 3-6, 2015, pp 111–115. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACPR.2015.7486476. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACPR.2015.7486476
Joo J, Wang S, Zhu S (2013) Human attribute recognition by rich appearance dictionary. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision, ICCV 2013, Sydney, Australia, December 1-8, 2013, pp 721–728 . https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2013.95. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2013.95
Liu P, Liu X, Yan J, Shao J (2018) Localization guided learning for pedestrian attribute recognition. In: british machine vision conference 2018, BMVC 2018, Newcastle, UK, September 3-6, 2018, p 142. http://bmvc2018.org/contents/papers/0573.pdf
Liu X, Zhao H, Tian M, Sheng L, Shao J, Yi S, Yan J, Wang X (2017) Hydraplus-net: attentive deep features for pedestrian analysis. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision, ICCV 2017, Venice, Italy, October 22-29, 2017, pp 350–359. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.46. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.46
Sarfraz MS, Schumann A, Wang Y, Stiefelhagen R (2017) Deep view-sensitive pedestrian attribute inference in an end-to-end model. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1707.06089
Tan Z, Yang Y, Wan J, Hang H, Guo G, Li SZ (2019) Attention-based pedestrian attribute analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(12):6126–6140. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2919199
Li Q, Zhao X, He R, Huang K (2019) Pedestrian attribute recognition by joint visual-semantic reasoning and knowledge distillation. In: Kraus, S. (ed.) Proceedings of the 28th international joint conference on artificial intelligence, IJCAI 2019, Macao, China, August 10-16, 2019, pp 833–839. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2019/117. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2019/117
Wu J, Liu H, Jiang J, Qi M, Ren B, Li X, Wang Y (2020) Person attribute recognition by sequence contextual relation learning. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 30(10):3398–3412. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2020.2982962
Ji Z, Hu Z, He E, Han J, Pang Y (2020) Pedestrian attribute recognition based on multiple time steps attention. Pattern Recogn Lett 138:170–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2020.07.018
Yang Y, Tan Z, Tiwari P, Pandey HM, Wan J, Lei Z, Guo G, Li SZ (2021) Cascaded split-and-aggregate learning with feature recombination for pedestrian attribute recognition. Int J Comput Vision 129(10):2731–2744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-021-01499-z
Zhao X, Sang L, Ding G, Han J, Di N, Yan C (2019) Recurrent attention model for pedestrian attribute recognition. In: the thirty-third AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, AAAI 2019, the thirty-first innovative applications of artificial intelligence conference, IAAI 2019, the ninth AAAI symposium on educational advances in artificial intelligence, EAAI 2019, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, January 27 - February 1, 2019, pp 9275–9282. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33019275. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33019275
Tan Z, Yang Y, Wan J, Guo G, Li SZ (2020) Relation-aware pedestrian attribute recognition with graph convolutional networks. In: AAAI, pp 12055–12062. https://aaai.org/ojs/index.php/AAAI/article/view/6883
Fan H, Hu H-M, Liu S, Lu W, Pu S (2020) Correlation graph convolutional network for pedestrian attribute recognition. IEEE Trans Multimed. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2020.3045286
Liu X-Y, Wu J, Zhou Z-H (2008) Exploratory undersampling for class-imbalance learning. IEEE Trans Syst, Man, Cybernet, Part B (Cybernet) 39(2):539–550. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2008.2007853
Ling CX, Sheng VS (2008) Cost-sensitive learning and the class imbalance problem. Encycl Mach Learn 2011:231–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcip.2020.100357
Dong Q, Gong S, Zhu X (2019) Imbalanced deep learning by minority class incremental rectification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(6):1367–1381. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2832629
Huang C, Li Y, Loy CC, Tang X (2020) Deep imbalanced learning for face recognition and attribute prediction. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42(11):2781–2794. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2914680
Hoffer E, Ailon N (2015) Deep metric learning using triplet network. In: Bengio, Y., LeCun, Y. (eds.) 3rd international conference on learning representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, May 7–9, 2015, Workshop Track Proceedings. http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6622
Sohn K (2016) Improved deep metric learning with multi-class n-pair loss objective. In: Lee DD, Sugiyama M, von Luxburg U, Guyon I, Garnett R (eds.) advances in neural information processing systems 29: annual conference on neural information processing systems 2016, December 5-10, 2016, Barcelona, Spain, pp 1849–1857. https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2016/hash/6b180037abbebea991d8b1232f8a8ca9-Abstract.html
Cheng D, Gong Y, Zhou S, Wang J, Zheng N (2016) Person re-identification by multi-channel parts-based CNN with improved triplet loss function. In: 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, CVPR 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, June 27-30, 2016, pp 1335–1344. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.149
Chen L, Yang H, Xu Q, Gao Z (2021) Harmonious attention network for person re-identification via complementarity between groups and individuals. Neurocomputing 453:766–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.07.118
Wang H, Wang Y, Zhou Z, Ji X, Gong D, Zhou J, Li Z, Liu W (2018) Cosface: Large margin cosine loss for deep face recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5265–5274. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00552
Yang J, Fan J, Wang Y, Wang Y, Gan W, Liu L, Wu W (2020) Hierarchical feature embedding for attribute recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 13055–13064. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01307
Tai Y, Yang J, Liu X (2017) Image super-resolution via deep recursive residual network. In: 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, July 21-26, 2017, pp 2790–2798. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.298
Jia J, Huang H, Yang W, Chen X, Huang K (2020) Rethinking of pedestrian attribute recognition: realistic datasets with efficient method. CoRR abs/2005.11909 https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11909
Lin T-Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K, Dollár P (2020) Focal loss for dense object detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42(2):318–327. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826
Deng Y, Luo P, Loy CC, Tang X (2014) Pedestrian attribute recognition at far distance. In: Hua KA, Rui Y, Steinmetz R, Hanjalic A, Natsev A, Zhu W (eds.) Proceedings of the ACM international conference on multimedia, MM ’14, Orlando, FL, USA, November 03 - 07, 2014, pp 789–792. ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/2647868.2654966
Han K, Wang Y, Shu H, Liu C, Xu C, Xu C (2019) Attribute aware pooling for pedestrian attribute recognition. In: Kraus S (ed) Proceedings of the 28th international joint conference on artificial intelligence, IJCAI 2019, Macao, China, August 10-16, 2019, pp. 2456–2462. ijcai.org, ???. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2019/341. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2019/341
Tang C, Sheng L, Zhang Z, Hu X (2019) Improving pedestrian attribute recognition with weakly-supervised multi-scale attribute-specific localization. In: 2019 IEEE/cvf international conference on computer vision, ICCV 2019, Seoul, Korea (South), October 27 - November 2, 2019, pp 4996–5005. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00510
Ji Z, He E, Wang H, Yang A (2019) Image-attribute reciprocally guided attention network for pedestrian attribute recognition. Pattern Recogn Lett 120:89–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2019.01.010
An H, Hu H-M, Guo Y, Zhou Q, Li B (2021) Hierarchical reasoning network for pedestrian attribute recognition. IEEE Trans Multimed 23:268–280. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2020.2975417
Jia J, Chen X, Huang K (2021) Spatial and semantic consistency regularizations for pedestrian attribute recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 962–971
Zeng H, Ai H, Zhuang Z, Chen L (2020) Multi-task learning via co-attentive sharing for pedestrian attribute recognition. In: IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo, ICME 2020, London, UK, July 6-10, 2020, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME46284.2020.9102757
Guo H, Zheng K, Fan X, Yu H, Wang S (2019) Visual attention consistency under image transforms for multi-label image classification. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, CVPR 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, June 16-20, 2019, pp 729–739. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00082
Cai L, Zeng H, Zhu J, Cao J, Wang Y, Ma K-K (2021) Cascading scene and viewpoint feature learning for pedestrian gender recognition. IEEE Internet Things J 8(4):3014–3026. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.3021763
Davis J, Goadrich M (2006) The relationship between precision-recall and ROC curves. In: Cohen WW, Moore AW (eds) Machine Learning, Proceedings of the 23rd international conference (ICML 2006), Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA, June 25-29, 2006. ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, vol. 148, pp 233–240. https://doi.org/10.1145/1143844.1143874
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In: Leibe B, Matas J, Sebe N, Welling M (eds) Computer Vision - ECCV 2016 - 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11-14, 2016, Proceedings, Part IV. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 9908, pp 630–645. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0_38
Jégou S, Drozdzal M, Vázquez D, Romero A, Bengio Y (2017) The one hundred layers tiramisu: Fully convolutional densenets for semantic segmentation. In: 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, CVPR Workshops 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, July 21-26, 2017, pp 1175–1183. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2017.156
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (61902370), and in part by the Chongqing Research Program of Technology Innovation and Application (cstc2019jscx-zdztzxX0019), and is also by the key cooperation project of the Chongqing Municipal Eduction Commission (HZ2021008 and HZ2021017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Song, J., Zhang, X. et al. MCFL: multi-label contrastive focal loss for deep imbalanced pedestrian attribute recognition. Neural Comput & Applic 34, 16701–16715 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07300-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07300-7