Abstract
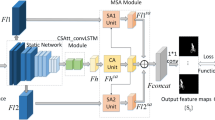
It has been witnessed that there is an increasing interest in video salient object detection (VSOD) in computer vision field. Different from image salient object detection (ISOD), VSOD not only requires appearance information but also needs motion cues. Thus, it is essential to exploit spatiotemporal information to generate accurate saliency results. Existing VSOD models mainly combine an ISOD model with long short-term memory (LSTM) or flow-estimation modules to integrate saliency cues estimated from spatial and temporal domain. However, flow-estimation modules heavily rely on optical flow images; the generation process of which is rather time-consuming and severely limits its applications in practice. Besides, the LSTM can only exploit motion cues via a step-by-step propagation in the time domain and is hard to realize the multi-scale spatiotemporal interaction. In this paper, we propose the SCANet to solve the above problems. Specifically, we develop the pyramid dilated 3D convolutional (PD3C) module to generate rich temporal features by leveraging context information. Besides, a feature aggregation module is designed to effectively integrate spatial and temporal features. Equipped with these modules, the SCANet is capable of generating high-quality saliency maps at more than real-time inference speed (41 FPS on a single Titan Xp GPU). Extensive experimental results on six widely used benchmark datasets prove that SCANet outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of three standard evaluation metrics. Our code will be publicly available at https://github.com/clelouch/SCANet.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qiu W, Gao X, Han B (2018) Eye fixation assisted video saliency detection via total variation-based pairwise interaction. IEEE Trans Image Process 27:10. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2843680
Le TN, Sugimoto A (2018) Video salient object detection using spatiotemporal deep features. IEEE Trans Image Process 27:10. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2849860
Kim W, Jung C, Kim C (2011) Spatiotemporal saliency detection and its applications in static and dynamic scenes. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2011.2125450
Hu YT, Bin Huang J, Schwing AG (2018) Unsupervised video object segmentation using motion saliency-guided spatio-temporal propagation. Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics), vol 11205 LNCS. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01246-5_48
Gorji S, Clark JJ (2018) Going from image to video saliency: augmenting image salience with dynamic attentional push. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00783
Chen C, Li S, Qin H, Pan Z, Yang G (2018) Bilevel feature learning for video saliency detection. IEEE Trans Multimed. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2018.2839523
Xu N, Price B, Cohen S, Yang J, Huang T (2016) Deep interactive object selection. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.47
Hadizadeh H, Bajic IV (2014) Saliency-aware video compression. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2013.2282897
Guo C, Zhang L (2010) A novel multiresolution spatiotemporal saliency detection model and its applications in image and video compression. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2009.2030969
Pan Y, Yao T, Li H, Mei T (2017) Video captioning with transferred semantic attributes. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.111
Xu N et al (2018) YouTube-VOS: sequence-to-sequence video object segmentation. In: Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics), vol 11209 LNCS. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01228-1_36.
Wang W, Shen J, Porikli F (2015) Saliency-aware geodesic video object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol 07-12-June-2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298961
Zhang Z, Fidler S, Urtasun R (2016) Instance-level segmentation for autonomous driving with deep densely connected MRFs. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.79
Yang C, Zhang L, Lu H, Ruan X, Yang MH (2013) Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.407
Wang W, Shen J, Yang R, Porikli F (2018) Saliency-aware video object segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intel. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2662005
Wang W, Shen J, Guo F, Cheng MM, Borji A (2018) Revisiting video saliency: a large-scale benchmark and a new model. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00514.
Wang W, Shen J (2018) Deep visual attention prediction. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2787612
Wang W, Shen J, Shao L (2015) Consistent video saliency using local gradient flow optimization and global refinement. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2460013
Guo F et al (2018) Video saliency detection using object proposals. IEEE Trans Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2017.2761361
Fang Y, Wang Z, Lin W, Fang Z (2014) Video saliency incorporating spatiotemporal cues and uncertainty weighting. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2014.2336549
Chen C, Wang G, Peng C, Fang Y, Zhang D, Qin H (2021) Exploring rich and efficient spatial temporal interactions for real-time video salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3068644
Wu Z, Su L, Huang Q (2019) Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol 2019-June. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00403
Zhao J, Liu JJ, Fan DP, Cao Y, Yang J, Cheng MM (2019) EGNet: edge guidance network for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, vol 2019-October. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00887
Liu JJ, Hou Q, Cheng MM, Feng J, Jiang J (2019) A simple pooling-based design for real-time salient object detection. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00404
Li S, Sui X, Luo X, Xu X, Liu Y, Goh R (2021) Medical image segmentation using squeeze-and-expansion transformers [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2105.09511
Mao Y et al (2021) Transformer transforms salient object detection and camouflaged object detection 14(8):1–15, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2104.10127
Vaswani A et al (2017) Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems, vol. 2017-December
Chen J et al (2021) TransUNet: transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation, pp 1–13, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2102.04306
Dosovitskiy A et al (2021) An image is worth 16 × 16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. ICLR
Li H, Chen G, Li G, Yu Y (2019) Motion guided attention for video salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, vol 2019-October. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00737
Ren S, Han C, Yang X, Han G, He S (2020) TENet: triple excitation network for video salient object detection. Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics), vol 12350 LNCS. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58558-7_13
Song H, Wang W, Zhao S, Shen J, Lam KM (2018) Pyramid dilated deeper ConvLSTM for video salient object detection. In: Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics), vol 11215 LNCS, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01252-6_44
Fan DP, Wang W, Cheng MM, Shen J (2019) Shifting more attention to video salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol. 2019-June. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00875
Chen Z, Xu Q, Cong R, Huang Q (2020) Global context-aware progressive aggregation network for salient object detection. AAAI. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6633
Pang Y, Zhao X, Zhang L, Lu H (2020) Multi-scale interactive network for salient object detection. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr42600.2020.00943
Klein DA, Frintrop S (2021) Center-surround divergence of feature statistics for salient object detection. ICCV
Jiang H, Wang J, Yuan Z, Wu Y, Zheng N, Li S (2013) Salient object detection: a discriminative regional feature integration approach. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.271
Liang J, Zhou J, Tong L, Bai X, Wang B (2018) Material based salient object detection from hyperspectral images. Pattern Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2017.11.024
Shijian L, Joo-Hwee L (2012) Saliency modeling from image histograms. ECCV
Lu S, Tan C, Lim JH (2014) Robust and efficient saliency modeling from image co-occurrence histograms. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2013.158
Zhang J, Ehinger KA, Wei H, Zhang K, Yang J (2017) A novel graph-based optimization framework for salient object detection. Pattern Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.10.025
Wang T, Borji A, Zhang L, Zhang P, Lu H (2017) A stagewise refinement model for detecting salient objects in images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, vol 2017-October. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.433
Chen T, Hu X, Xiao J, Zhang G (2021) BPFINet: boundary-aware progressive feature integration network for salient object detection. Neurocomputing. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.04.078
Zhao T, Wu X (2019) Pyramid feature attention network for saliency detection. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00320
Qin X, Zhang Z, Huang C, Gao C, Dehghan M, Jagersand M (2019) Basnet: Boundary-aware salient object detection. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00766
Feng M, Lu H, Ding E (2019) Attentive feedback network for boundary-aware salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol. 2019-June. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00172
Liu JJ, Hou Q, Cheng MM (2020) Dynamic feature integration for simultaneous detection of salient object, edge, and skeleton. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:8652–8667. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.3017352
Chen Z, Xu Q, Cong R, Huang Q (2020) Global context-aware progressive aggregation network for salient object detection. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6633
Zhao X, Pang Y, Zhang L, Lu H, Zhang L (2020) Suppress and balance: a simple gated network for salient object detection. ECCV
Wu Z, Su L, Huang Q (2019) Stacked cross refinement network for edge-aware salient object detection. ICCV. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00736
Wei J, Wang S, Huang Q (2020) F3Net: fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. AAAI. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6916
Zhu L et al (2020) Aggregating attentional dilated features for salient object detection. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2941017
Tu Z, Ma Y, Li C, Li C, Tang J, Luo B (2020) Edge-guided non-local fully convolutional network for salient object detection. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsvt.2020.2980853
Guo C, Ma Q, Zhang L (2008) Spatio-temporal saliency detection using phase spectrum of quaternion fourier transform. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2008.4587715
Kim H, Kim Y, Sim JY, Kim CS (2015) Spatiotemporal saliency detection for video sequences based on random walk with restart. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2425544
Zhang P, Wang D, Lu H, Wang H, Ruan X (2017) Amulet: aggregating multi-level convolutional features for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, vol. 2017-October. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.31
Luo Z, Mishra A, Achkar A, Eichel J, Li S, Jodoin PM (2017) Non-local deep features for salient object detection. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.698
Liu N, Han J, Yang MH (2018) PiCANet: learning pixel-wise contextual attention for saliency detection. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00326
Zhang X, Wang T, Qi J, Lu H, Wang G (2018) Progressive attention guided recurrent network for salient object detection. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00081
Wang B, Chen Q, Zhou M, Zhang Z, Jin X, Gai K (2020) Progressive feature polishing network for salient object detection. AAAI. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6892
Wang W, Shen J, Shao L (2018) Video salient object detection via fully convolutional networks. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2754941
Li G, Xie Y, Wei T, Wang K, Lin L (2018) Flow guided recurrent neural encoder for video salient object detection. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00342
Dosovitskiy A et al (2015) FlowNet: learning optical flow with convolutional networks. ICCV. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.316.
Gu Y, Wang L, Wang Z, Liu Y, Cheng MM, Lu SP (2020) Pyramid constrained self-attention network for fast video salient object detection. AAAI. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6718
Zheng S et al (2020) Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers. CoRR, vol. abs/2012.15840, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2012.15840
Wang W et al (2021) Pyramid vision transformer: a versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2102.12122
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Hou Q, Cheng MM, Hu X, Borji A, Tu Z, Torr PHS (2019) Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2815688
Zhang L, Dai J, Lu H, He Y, Wang G (2018) A bi-directional message passing model for salient object detection. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00187
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2003.819861
Mattyus G, Luo W, Urtasun R (2017) DeepRoadMapper: extracting road topology from aerial images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, vol. 2017-October. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.372
Wang L et al (2017) Learning to detect salient objects with image-level supervision. CVPR. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.404
Brox T, Malik J (2010) Object segmentation by long term analysis of point trajectories. Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics), vol 6315 LNCS, no Part 5, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15555-0_21
Perazzi F, Pont-Tuset J, McWilliams B, Van Gool L, Gross M, Sorkine-Hornung A (2016) A benchmark dataset and evaluation methodology for video object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol. 2016-December. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.85.
Li J, Xia C, Chen X (2018) A benchmark dataset and saliency-guided stacked autoencoders for video-based salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2762594
Li F, Kim T, Humayun A, Tsai D, Rehg JM (2013) Video segmentation by tracking many figure-ground segments. ICCV. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2013.273
Fan DP, Zhai Y, Borji A, Yang J, Shao L (2020) BBS-Net: RGB-D salient object detection with a bifurcated backbone strategy network. ECCV
Kingma DP, Ba JL (2015) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization
Xi T, Zhao W, Wang H, Lin W (2017) Salient object detection with spatiotemporal background priors for video. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2016.2631900
Liu Z, Li J, Ye L, Sun G, Shen L (2017) Saliency Detection for unconstrained videos using superpixel-level graph and spatiotemporal propagation. IEEE Trans Circ Sys Video Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2016.2595324
Chen C, Li S, Wang Y, Qin H, Hao A (2017) Video Saliency detection via spatial-temporal fusion and low-rank coherency diffusion. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2670143
Li S, Seybold B, Vorobyov A, Lei X, Kuo CCJ (2018) Unsupervised video object segmentation with motion-based bilateral networks. Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics), vol 11207 LNCS, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01219-9_13
Tang Y, Zou W, Jin Z, Chen Y, Hua Y, Li X (2019) Weakly supervised salient object detection with spatiotemporal cascade neural networks. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2018.2859773
Chen Y, Zou W, Tang Y, Li X, Xu C, Komodakis N (2018) SCOM: spatiotemporal constrained optimization for salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2813165
Wang W et al (2019) Learning unsupervised video object segmentation through visual attention. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol. 2019-June. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00318
Zhao W, Zhang J, Li L, Barnes N, Liu N, Han J (2021) Weakly supervised video salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 16826–16835
Chen LC, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille AL (2018) DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184
Zhang Z, Lin Z, Xu J, Da Jin W, Lu SP, Fan DP (2021) Bilateral attention network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3049959
Fan DP et al (2020) PraNet: parallel reverse attention network for polyp segmentation. MICCAI. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_26
Fan DP, Ji GP, Cheng MM, Shao L (2021) Concealed object detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3085766
Howard A et al (2019) Searching for MobileNetV3, CoRR, vol. abs/1905.02244. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1905.02244
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2015) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. ICLR
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (under Grant 51807003).
Funding
This work was supported by the Young Scientists Fund (Grant No. 51807003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T., Xiao, J., Hu, X. et al. Spatiotemporal context-aware network for video salient object detection. Neural Comput & Applic 34, 16861–16877 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07330-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07330-1