Abstract
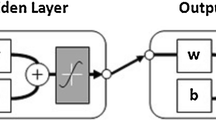
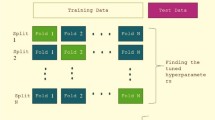
Throughout the published literature for phase equilibrium data of CO2-alkanolamine-H2O and H2S-alkanolamine-H2O systems, it is common to find some discrepant data, called data outliers. The presence of these erroneous values induces inaccuracies and prediction errors in the models and simulation studies developed using such experimental datasets. Hence, it is important that the data outliers are identified and later corrected or removed before developing a model or simulation. This study proposes a modified approach to identifying data outliers present in the phase equilibrium data of CO2-alkanolamine-H2O and H2S-alkanolamine-H2O systems using an artificial neural network and data outlier identification methods. Firstly, the suggested approach correlates the experimental phase equilibrium data (2152 data points) of CO2 and H2S-loaded monoethanolamine, diethanolamine, and N-methyldiethanolamine solutions by developing an artificial neural network. Following this, the data outliers are identified by applying a modified IQR method and compared graphically to 2.5 standard deviation method. The identified data outliers can then be truncated or winsorised for developing reliable and accurate models/simulations. The modified IQR method coupled with a neural network (based on the normalised data values) can robustly identify data outliers within a large experimental dataset. The proposed approach is superior to the previous data outlier identification techniques that used 2.5 standard deviations method, as it alleviates the need for a human decision in determining the congruence of experimental values. The results also indicate that the developed method can be reliably extended to other/larger non-linear experimental datasets having similar correlative complexity.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to the university’s data sharing guidelines but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Rahmanpour O, Zargari MH, Ghayyem MA (2015) Application of artificial neural networks (ANNs) to Predict the rich amine concentration in gas sweetening processing units. Energy Sour A Recov Util Environ Eff 3:118–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2011.578111
Kittel J, Fleury E, Vuillemin B et al (2012) Corrosion in alkanolamine used for acid gas removal: from natural gas processing to CO2 capture. Werkst Korros 63:223–323. https://doi.org/10.1002/maco.201005847
Mokhatab S, Poe WA, Mak JY (2019) Handbook of Natural gas transmission and processing: principles and practices. Gulf Professional Publishing, Cambridge
Kohl AL, Nielsen R (1997) Gas purification. Gulf Publishing Company, Houston
Jou FY, Carroll J, Mather A et al (1993) The solubility of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide in a 35 wt % aqueous solution of Methyldiethanolamine. Can J Chem Eng 71:264–268. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.5450710213
Jou FY, Mather A, Otto F (1982) Solubility of H2S and CO2 in Aqueous Methyldiethanolamine solutions. Ind Eng Chem Process Des Dev 21:539–544. https://doi.org/10.1021/i200019a001
Kuranov G, Rumpf B, Smirnova N et al (1996) Solubility of single gases carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide in aqueous solutions of N-Methyldiethanolamine in the temperature range 313–413 K at pressures up to 5 MPa. Ind Eng Chem Res 35:1959–1966. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie950538r
Lee J, Otto F, Mather A (1976) The measurement and prediction of the solubility of mixtures of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide in a 2.5 N monoethanolamine solution. Can J Chem Eng 54:214–219. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.5450540316
Sidi-Boumedine R, Horstmann S, Fischer K et al (2004) Experimental determination of hydrogen sulfide solubility data in aqueous alkanolamine solutions. Fluid Phase Equilib 218:149–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2003.11.020
Austgen DM, Rochelle GT, Peng X et al (1989) Model of vapor-liquid equilibria for aqueous acid gas-alkanolamine systems using the electrolyte-NRTL equation. Ind Eng Chem Res 28:1060–1073. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie00091a028
Puxty G, Maeder M (2013) A simple chemical model to represent CO2–amine–H2O vapour–liquid-equilibria. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control 17:215–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijggc.2013.05.016
Vrachnos A, Voutsas E, Magoulas K et al (2004) Thermodynamics of acid gas-MDEA-water systems. Ind Eng Chem Res 43:2798–2804. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie030769v
Weiland RH, Chakravarty T, Mather AE (1993) Solubility of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide in aqueous alkanolamines. Ind Eng Chem Res 32:1419–1430. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie00019a016
Suleman H, Maulud A, Man Z (2016) Reconciliation of outliers in CO2-alkanolamine-H2O datasets by robust neural network winsorization. Neural Comput Appl 28:2621–2632. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2213-z
Posey ML, Tapperson KG, Rochelle GT (1996) A simple model for prediction of acid gas solubilities in alkanolamines. Gas Sep Purif 10:181–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/0950-4214(96)00019-9
Suleman H, Maulud A, Man Z (2015) Review and selection criteria of classical thermodynamic models for acid gas absorption in aqueous alkanolamines. Rev Chem Eng 31:599–639. https://doi.org/10.1515/revce-2015-0030
Suleman H, Maulud A, Fosbøl PL et al (2021) A review of semi-empirical equilibrium models for CO2-alkanolamine-H2O solutions and their mixtures at high pressure. J Environ Chem Eng 9:104713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104713
Gabrielsen J, Michelsen ML, Stenby EH et al (2006) Modeling of CO2 absorber using an AMP solution. AIChE J 52:3443–3451. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.10963
Gasca E (2006) Artificial Neural Networks. Dissertation, Toluca: Instituto Tecnologico de Toluca
Xiao G, Li J, Chen Y, Li K (2020) MalFCS: an effective malware classification framework with automated feature extraction based on deep convolutional neural networks. J Parallel Distrib Comput 141:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2020.03.012
Gupta PK, Maiti S (2022) Enhancing data-driven modeling of fluoride concentration using new data mining algorithms. Environ Earth Sci 81:89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10216-z
Maiti S, Ravi Kumar C, Sarkar P et al (2020) Interface depth modelling of gravity data and altitude variations: a Bayesian neural network approach. Neural Comput Appl 32:3183–3202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04276-9
Karmakar M, Maiti S (2019) Short term memory efficient pore pressure prediction via bayesian neural networks at Bering sea slope of IODP expedition 323. Measurement 135:852–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.12.034
Abiodun OI, Jantan A, Omolara AE et al (2018) State-of-the-art in artificial neural network applications: a survey. Heliyon 4:e00938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00938
Mirza S, Zafar MR, Joiya TA et al (2017) Neural network based outlier identification in data values of carbon dioxide loaded 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol solutions. NFC J Eng Sci Res 5(2):7–9. https://doi.org/10.24081/nijesr.2017.2.0002
Barbato G, Barini E, Genta G et al (2011) Features and performance of some outlier detection methods. J Appl Stat 38:2133–2149. https://doi.org/10.1080/02664763.2010.545119
Jones JH, Froning HR, Claytor EE Jr (1959) Solubility of acidic gases in aqueous Monoethanolamine. J Chem Eng Data 4:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1021/je60001a012
Lee JI, Otto F, Mather A (1973) Partial pressures of hydrogen sulfide over aqueous diethanolamine solutions. J Chem Eng Data 18:420. https://doi.org/10.1021/je60059a021
Lee JI, Otto F, Mather A (1974) The solubility of H2S and CO2 in aqueous monoethanolamine solutions. Can J Chem Eng 52:803–805. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.5450520617
Lee J, Otto F, Mather A (1974) The solubility of mixtures of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide in aqueous diethanolamine solutions. Can J Chem Eng 52:125–127. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.5450520121
Lawson JD, Garst AW (1976) Gas sweetening data: equilibrium solubility of hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide in aqueous monoethanolamine and aqueous diethanolamine solutions. J Chem Eng Data 21:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1021/je60068a010
Maddox RN, Bhairi AH, Diers JR et al (1987) Equilibrium Solubility of Carbon Dioxide or Hydrogen Sulfide in Aqueous Solutions of Monoethanolamine, Diglycolamine, Diethanolamine and Methyldiethanolamine, Tulsa: Gas Processors Association. GPA research report, RR-104.
MacGregor RJ, Mather A (1991) Equilibrium Solubility of H2S and CO2 and Their Mixtures in a Mixed Solvent. Can J Chem Eng 69:1357–1366. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.5450690618
Li MH, Shen KP (1993) Solubility of hydrogen sulfide in aqueous mixtures of Monoethanolamine with N-Methyldiethanolamine. J Chem Eng Data 38:105–108. https://doi.org/10.1021/je00009a025
Huang SH, Ng HJ (1998) Solubility of H2S and CO2 in Alkanolamines, Edmonton: Gas Processors Association. GPA research report, RR-155.
Kamps APS, Balaban A, Jodecke M et al (2001) Solubility of single gases carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide in aqueous solutions of N-Methyldiethanolamine at temperatures from 313 to 393 K and pressures up to 7.6 MPa: new experimental data and model extension. Ind Eng Chem Res 40:696–706. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie000441r
Han J, Jin J, Eimer D et al (2012) Density of Water (1) + Monoethanolamine (2) + CO2 (3) from (298.15 to 413.15) K and surface tension of water (1) + Monoethanolamine (2) from (303.15 to 333.15) K). J Chem Eng Data 57:1095–1103. https://doi.org/10.1021/je2010038
Han J, Jin J, Eimer D et al (2012) Density of water (1) + Diethanolamine (2) + CO2 (3) and water (1) + N-Methyldiethanolamine (2) + CO2 (3) from (298.15 to 423.15) K. J Chem Eng Data 57:1843–1850. https://doi.org/10.1021/je300345m
Li Y, Mather AE (1997) Correlation and prediction of the solubility of CO2 and H2S in aqueous solutions of Methyldiethanolamine. Ind Eng Chem Res 36:2760–2765. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie970061e
Rafiq MY, Bugmann G, Easterbrook DJ (2001) Neural network design for engineering applications. Comput Struct 73:1541–1552. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7949(01)00039-6
Nasir Q, Suleman H, Ud Din I et al (2022) A multi-layer perceptron neural network model for predicting the hydrate equilibrium conditions in multi-component hydrocarbon systems. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07284-4
Saghafi H, Arabloo M (2017) Modeling of CO2 solubility in MEA, DEA, TEA, and MDEA aqueous solutions using AdaBoost-decision tree and artificial neural network. Int J Greenh Gas Control 58:256–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijggc.2016.12.014
Balchandani SC, Dey A (2022) Prediction of CO2 solubility in potential blends of ionic liquids with Alkanolamines using statistical non-rigorous and ANN based modeling: a comprehensive simulation study for post combustion CO2 capture. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer 132:105866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105866
Nasir R, Suleman H, Maqsood K (2022) Multiparameter neural network modeling of facilitated transport mixed matrix membranes for carbon dioxide removal. Membranes 12:421. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040421
Seferlis P, Varbanov PS, Papadopoulos AI et al (2021) Sustainable design, integration, and operation for energy high-performance process systems. Energy 224:120158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120158
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Imai, B., Nasir, Q., Maulud, A.S. et al. Neural network-based correlation and statistical identification of data outliers in H2S-alkanolamine-H2O and CO2-alkanolamine-H2O datasets. Neural Comput & Applic 35, 3395–3412 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07904-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07904-z