Abstract
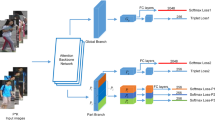
In many person re-identification application scenarios, such as supermarkets, subway stations, and streets, it is necessary to solve an occlusion problem. We propose a dual branch named Dual structural Features Network to solve the problem. Our method obtains features embedding from two types of structural data, that is, Euclidean structural data and non-Euclidean structural data. We argue that the features of these two structures are equally important to ease the occlusion problem. In our first branch, we introduce a Position Attention Drop Block to extract the Euclidean structural feature. This branch focuses on the information that pixels can represent within a certain receptive field. In order to better target our network at the occlusion problem, we propose a drop method based on the pixel attention score of the person image, in which the area with the highest score is lost. In this way, we design a network that pays more attention to other more detailed information. In the other branch, a new U-shaped Residual Graph Convolutional Network is used to extract the features from non-Euclidean structural data, which is an effective multilayer graph convolution. We argue that good non-Euclidean structural data can express more topological correlation information, thereby reducing the interference of the occluded part. From the experimental results, we have achieved competitive performance with state-of-the-art methods, and our method is especially effective for person re-identification with occluded body parts.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The datasets used in this paper are public datasets. The data that support the fundings of the study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Zhu J, Zeng H, Liao S et al (2018) Deep hybrid similarity learning for person re-identification. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 28(11):3183–3193. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2017.2734740
Li W, Zhu X, Gong S (2018b) Harmonious attention network for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 2285–2294
Ahmed E, Jones M, Marks TK (2015) An improved deep learning architecture for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Hermans A, Beyer L, Leibe B (2017) In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.07737
Luo H, Gu Y, Liao X, et al (2019) Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, pp. 0–0
Zhong Z, Zheng L, Cao D, et al (2017) Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 1318–1327
Ristani E, Solera F, Zou R, et al (2016a) Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp. 17–35
Zheng L, Shen L, Tian L, et al (2015a) Scalable person re-identification: a benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 1116–1124
Huang H, Yang W, Chen X, et al (2018b) Eanet: enhancing alignment for cross-domain person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.11369
Fu Y, Wei Y, Wang G, et al (2019) Self-similarity grouping: A simple unsupervised cross domain adaptation approach for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp. 6112–6121
Chen Y, Zhu X, Gong S (2019) Instance-guided context rendering for cross-domain person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp. 232–242
Huang Z, Wang Z, Tsai CC et al (2021) Dotscn: group re-identification via domain-transferred single and couple representation learning. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 31(7):2739–2750. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2020.3031303
Zhang X, Luo H, Fan X, et al (2017) Alignedreid: Surpassing human-level performance in person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.08184
Yang Q, Wu A, Zheng WS (2019) Person re-identification by contour sketch under moderate clothing change. In: IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence
Miao J, Wu Y, Liu P, et al (2019) Pose-guided feature alignment for occluded person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp. 542–551
Zhuo J, Chen Z, Lai J, et al (2018) Occluded person re-identification. In: 2018 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (ICME). IEEE, pp. 1–6
Luo H, Jiang W, Gu Y et al (2020) A strong baseline and batch normalization neck for deep person re-identification. IEEE Trans Multimed 22(10):2597–2609. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2019.2958756
Wang G, Yuan Y, Chen X, et al (2018) Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM international conference on Multimedia
Gong X, Yao Z, Li X, et al (2021) Lag-net: Multi-granularity network for person re-identification via local attention system. In: IEEE transactions on multimedia pp 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3050082
Sun Y, Zheng L, Yang Y, et al (2018) Beyond part models: person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp. 480–496
Gao S, Wang J, Lu H, et al (2020) Pose-guided visible part matching for occluded person reid. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 11744–11752
Yang J, Zhang C, Tang Y et al (2022) Pafm: pose-drive attention fusion mechanism for occluded person re-identification. Neural Comput Appl 34(10):8241–8252
Zhang L, Jiang N, Diao Q, et al (2022) Person re-identification with pose variation aware data augmentation. In: Neural computing and applications, pp. 1–14
Wang G, Yang S, Liu H, et al (2020) High-order information matters: Learning relation and topology for occluded person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 6449–6458
Pan H, Bai Y, He Z et al (2022) Aagcn: adjacency-aware graph convolutional network for person re-identification. Knowl Based Syst 236(107):300
Zheng L, Yang Y, Hauptmann AG (2016) Person re-identification: past, present and future. arXiv preprint arXiv:1610.02984
Alemu LT, Pelillo M, Shah M (2019) Deep constrained dominant sets for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 9855–9864
Chen H, Wang Y, Shi Y, et al (2018) Deep transfer learning for person re-identification. In: 2018 IEEE fourth international conference on multimedia big data (BigMM), IEEE, pp 1–5
Zhang S, Wen L, Bian X, et al (2018) Occlusion-aware r-cnn: Detecting pedestrians in a crowd. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp. 637–653
Pang Y, Xie J, Khan MH, et al (2019) Mask-guided attention network for occluded pedestrian detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp. 4967–4975
Liu S, Huang D, Wang Y (2019) Adaptive nms: Refining pedestrian detection in a crowd. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 6459–6468
Zheng WS, Li X, Xiang T, et al (2015b) Partial person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 4678–4686
He L, Liang J, Li H, et al (2018a) Deep spatial feature reconstruction for partial person re-identification: Alignment-free approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 7073–7082
Fan X, Luo H, Zhang X, et al (2018) Scpnet: Spatial-channel parallelism network for joint holistic and partial person re-identification. In: Asian conference on computer vision, Springer, pp. 19–34
Sun Y, Xu Q, Li Y, et al (2019) Perceive where to focus: learning visibility-aware part-level features for partial person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 393–402
Zhao Y, Zhu S, Wang D, et al (2022) Short range correlation transformer for occluded person re-identification. In: Neural computing and applications, pp. 1–13
Niepert M, Ahmed M, Kutzkov K (2016) Learning convolutional neural networks for graphs. In: International conference on machine learning, PMLR, pp. 2014–2023
Bronstein MM, Bruna J, LeCun Y et al (2017) Geometric deep learning: going beyond euclidean data. IEEE Signal Process Mag 34(4):18–42
Kipf TN, Welling M (2016) Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.02907
Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A et al (2014) Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J Mach Learn Res 15(1):1929–1958
Ghiasi G, Lin TY, Le QV (2018) Dropblock: A regularization method for convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.12890
Dai Z, Chen M, Gu X, et al (2019) Batch dropblock network for person re-identification and beyond. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp. 3691–3701
Fu J, Liu J, Tian H et al (2019). Dual attention network for scene segmentation. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00326
Li S, Bak S, Carr P, et al (2018a) Diversity regularized spatiotemporal attention for video-based person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 369–378
Wu D, Ye M, Lin G, et al (2021) Person re-identification by context-aware part attention and multi-head collaborative learning. In: IEEE transactions on information forensics and security
Chen P, Liu W, Dai P, et al (2021) Occlude them all: Occlusion-aware attention network for occluded person re-id. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp. 11833–11842
Tompson J, Goroshin R, Jain A, et al (2015) Efficient object localization using convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 648–656
Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, et al (2016) Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 2818–2826
Wen Y, Zhang K, Li Z, et al (2016) A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp. 499–515
Cao Z, Hidalgo G, Simon T et al (2019) Openpose: realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(1):172–186
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 7132–7141
Zhong Z, Zheng L, Kang G, et al (2020) Random erasing data augmentation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp. 13001–13008
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 770–778
Zheng Z, Zheng L, Yang Y (2017) Unlabeled samples generated by gan improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 3754–3762
Ristani E, Solera F, Zou R, et al (2016b) Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In: European conference on computer vision workshop on benchmarking multi-target tracking
Li W, Zhao R, Xiao T, et al (2014) Deepreid: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In: CVPR
Zhao L, Li X, Zhuang Y, et al (2017) Deeply-learned part-aligned representations for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 3219–3228
He L, Wang Y, Liu W, et al (2019) Foreground-aware pyramid reconstruction for alignment-free occluded person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp. 8450–8459
He L, Sun Z, Zhu Y, et al (2018b) Recognizing partial biometric patterns. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.07399
Huang H, Li D, Zhang Z, et al (2018a) Adversarially occluded samples for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 5098–5107
Zhong Z, Zheng L, Cao D, et al (2017) Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding. In: 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 3652–3661, https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.389
Yang J, Zhang J, Yu F, et al (2021) Learning to know where to see: a visibility-aware approach for occluded person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp. 11885–11894
Wang P, Ding C, Shao Z, et al (2022) Quality-aware part models for occluded person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.00107
Zheng F, Deng C, Sun X, et al (2019) Pyramidal person re-identification via multi-loss dynamic training. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 8514–8522
Wang G, Lai J, Huang PY, et al (2019) Spatial-temporal person re-identification. ArXiv abs/1812.03282
Wieczorek M, Rychalska B, Dabrowski J (2021) On the unreasonable effectiveness of centroids in image retrieval. In: ICONIP
Qi L, Huo J, Wang L, et al (2018a) Maskreid: a mask based deep ranking neural network for person re-identification. ArXiv abs/1804.03864
Yin J, Xie J, Ma Z, Guo J (2022) Mpccl: multiview predictive coding with contrastive learning for person re-identification. Pattern Recognit 129:108710
Qi L, Huo J, Wang L, et al (2018b) Maskreid: a mask based deep ranking neural network for person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03864
Wattenberg M, Viégas F, Johnson I (2016) How to use t-sne effectively. Distill https://doi.org/10.23915/distill.00002, http://distill.pub/2016/misread-tsne
Acknowledgements
This work is partly supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61876158) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2682021ZTPY030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The research described in the article was performed with funding from The National Natural Science Foundation of China. Dr. Gong is a principal of the Foundation. However, none of these foundation is described or presented in this article. The foundation is used to promote the development of basic research in the natural sciences. The Institute receives research grants from The National Natural Science Foundation of China. However, there are no other conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Y., Gong, X. & He, Y. DSF-net: occluded person re-identification based on dual structure features. Neural Comput & Applic 35, 3537–3550 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07927-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07927-6