Abstract
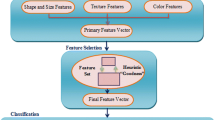
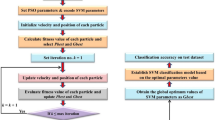
In order to increase the market value and quality of wheat, it is important to separate different types and determine the amount of foreign matter using the visual properties of durum and bread wheat. In this study, the extreme learning machine (ELM) algorithm, which is often preferred in real-time applications, was used to make classifications using features obtained from images containing the wheat kernel and foreign matter. The feature selection process was applied to remove the irrelevant ones from the obtained 236 features. In addition, the Harris hawks’ optimizer (HHO), a novel method in the literature, and the particle swarm optimizer (PSO), one of the well-known algorithms, were used to improve the ELM model. As part of this study, new models called HHO-ELM and PSO-ELM were created and compared with the original ELM model and other artificial neural networks (ANNs) studies published in the literature. As a result, in comparison with other models, the optimized ELM models demonstrated good stability and accuracy, having 99.32% in binary classification and 95.95% in multi-class classification.











Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The experimental dataset are open source and available via references.
References
Igrejas G, Branlard G (2020) The Importance of Wheat. In: Igrejas G, Ikeda TM, Guzmán C (eds) Wheat quality for improving processing and human health. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 1–7
Huebner FR, Bietz JA, Nelsen T et al (1999) Soft wheat quality as related to protein composition. Cereal Chem 76:650–655. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM.1999.76.5.650
Sabanci K, Kayabasi A, Toktas A (2017) Computer vision-based method for classification of wheat grains using artificial neural network. J Sci Food Agric 97:2588–2593. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.8080
Bao Y, Mi C, Wu N et al (2019) Rapid classification of wheat grain varieties using hyperspectral imaging and chemometrics. Appl Sci 9:4119. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194119
Tian H, Wang T, Liu Y et al (2020) Computer vision technology in agricultural automation —a review. Inf Process Agric 7:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inpa.2019.09.006
Mollazade K, Omid M, Arefi A (2012) Comparing data mining classifiers for grading raisins based on visual features. Comput Electron Agric 84:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2012.03.004
Patrício DI, Rieder R (2018) Computer vision and artificial intelligence in precision agriculture for grain crops: a systematic review. Comput Electron Agric 153:69–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2018.08.001
Pourreza A, Pourreza H, Abbaspour-Fard M-H, Sadrnia H (2012) Identification of nine Iranian wheat seed varieties by textural analysis with image processing. Comput Electron Agric 83:102–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2012.02.005
Gunes EO, Aygun S, Kirci M, et al (2014) Determination of the varieties and characteristics of wheat seeds grown in Turkey using image processing techniques. In: 2014 The Third International Conference on Agro-Geoinformatics. IEEE, pp 1–4
Guevara-Hernandez F, Gomez-Gil J (2011) Sistema de visión artificial para la clasificación de granos de trigo y cebada. Spanish J Agric Res 9:672–680. https://doi.org/10.5424/sjar/20110903-140-10
Yasar A, Kaya E, Saritas I (2016) Classification of wheat types by artificial neural network. Int J Intell Syst Appl Eng 4:12–15. https://doi.org/10.18201/ijisae.64198
Aslan MF, Sabancı K, Durdu A (2017) Different wheat species classifier application of ANN and ELM. J Multidiscip Eng Sci Technol 4:2458–9403
Ebrahimi E, Mollazade K, Babaei S (2014) Toward an automatic wheat purity measuring device: a machine vision-based neural networks-assisted imperialist competitive algorithm approach. Measurement 55:196–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2014.05.003
Olgun M, Onarcan AO, Özkan K et al (2016) Wheat grain classification by using dense SIFT features with SVM classifier. Comput Electron Agric 122:185–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2016.01.033
Shrestha BL, Kang Y-M, Yu D, Baik O-D (2016) A two-camera machine vision approach to separating and identifying laboratory sprouted wheat kernels. Biosyst Eng 147:265–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2016.04.008
Singh P, Nayyar A, Singh S, Kaur A (2020) Classification of wheat seeds using image processing and fuzzy clustered random forest. Int J Agric Resour Gov Ecol 16:123–156. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJARGE.2020.109048
JayaBrindha G, Subbu ESG (2018) Ant colony technique for optimizing the order of cascaded SVM classifier for sunflower seed classification. IEEE Trans Emerg Top Comput Intell 2:78–88. https://doi.org/10.1109/TETCI.2017.2772918
Kayabasi A (2018) An application of ANN trained by ABC algorithm for classification of wheat grains. Int J Intell Syst Appl Eng 6:85–91. https://doi.org/10.18201/ijisae.2018637936
Koklu M, Ozkan IA (2020) Multiclass classification of dry beans using computer vision and machine learning techniques. Comput Electron Agric 174:105507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2020.105507
Koklu M, Cinar I, Taspinar YS (2021) Classification of rice varieties with deep learning methods. Comput Electron Agric 187:106285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2021.106285
Ding S, Xu X, Nie R (2014) Extreme learning machine and its applications. Neural Comput Appl 25:549–556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-013-1522-8
Huang G, Huang G-B, Song S, You K (2015) Trends in extreme learning machines: a review. Neural Netw 61:32–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2014.10.001
Murthy CS, Raju PV, Badrinath KVS (2003) Classification of wheat crop with multi-temporal images: performance of maximum likelihood and artificial neural networks. Int J Remote Sens 24:4871–4890. https://doi.org/10.1080/0143116031000070490
Mahesh S, Manickavasagan A, Jayas DS et al (2008) Feasibility of near-infrared hyperspectral imaging to differentiate Canadian wheat classes. Biosyst Eng 101:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2008.05.017
Kaya E, Saritas I (2019) Towards a real-time sorting system: Identification of vitreous durum wheat kernels using ANN based on their morphological, colour, wavelet and gaborlet features. Comput Electron Agric 166:105016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2019.105016
Prasad R, Deo RC, Li Y, Maraseni T (2018) Soil moisture forecasting by a hybrid machine learning technique: ELM integrated with ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Geoderma 330:136–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.05.035
Kouadio L, Deo RC, Byrareddy V et al (2018) Artificial intelligence approach for the prediction of Robusta coffee yield using soil fertility properties. Comput Electron Agric 155:324–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2018.10.014
Sulistyo SB, Wu D, Woo WL et al (2018) Computational deep intelligence vision sensing for nutrient content estimation in agricultural automation. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 15:1243–1257. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASE.2017.2770170
Suchithra MS, Pai ML (2020) Improving the prediction accuracy of soil nutrient classification by optimizing extreme learning machine parameters. Inf Process Agric 7:72–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inpa.2019.05.003
Feng Z, Huang G, Chi D (2020) Classification of the complex agricultural planting structure with a semi-supervised extreme learning machine framework. Remote Sens 12:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223708
Mostafaeipour A, Fakhrzad MB, Gharaat S et al (2020) Machine learning for prediction of energy in wheat production. Agric 10:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10110517
Zhu Q-Y, Qin AK, Suganthan PN, Huang G-B (2005) Evolutionary extreme learning machine. Pattern Recognit 38:1759–1763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2005.03.028
Cao J, Lin Z, Huang G-B (2012) Self-adaptive evolutionary extreme learning machine. Neural Process Lett 36:285–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-012-9236-y
Dash R, Dash PK, Bisoi R (2014) A self adaptive differential harmony search based Optimized extreme learning machine for financial time series prediction. Swarm Evol Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2014.07.003
Yang H, Yi J, Zhao J, Dong Z (2013) Extreme learning machine based genetic algorithm and its application in power system economic dispatch. Neurocomput 102:154–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2011.12.054
Han F, Yao H-F, Ling Q-H (2013) An improved evolutionary extreme learning machine based on particle swarm optimization. Neurocomputing 116:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2011.12.062
Li G, Niu P, Ma Y et al (2014) Tuning extreme learning machine by an improved artificial bee colony to model and optimize the boiler efficiency. Knowledge-Based Syst 67:278–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2014.04.042
Wang M, Chen H, Li H et al (2017) Grey wolf optimization evolving kernel extreme learning machine: application to bankruptcy prediction. Eng Appl Artif Intell 63:54–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2017.05.003
Shariati M, Mafipour MS, Ghahremani B et al (2022) A novel hybrid extreme learning machine–grey wolf optimizer (ELM-GWO) model to predict compressive strength of concrete with partial replacements for cement. Eng Comput 38:757–779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01081-0
Eshtay M, Faris H, Obeid N (2019) Metaheuristic-based extreme learning machines: a review of design formulations and applications. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 10:1543–1561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-018-0833-6
Wang J, Lu S, Wang S-H, Zhang Y-D (2022) A review on extreme learning machine. Multimed Tools Appl 81:41611–41660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11007-7
Heidari AA, Mirjalili S, Faris H et al (2019) Harris hawks optimization: algorithm and applications. Futur Gener Comput Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.02.028
Moayedi H, Osouli A, Nguyen H, Rashid ASA (2021) A novel Harris hawks’ optimization and k-fold cross-validation predicting slope stability. Eng Comput 37:369–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00828-8
Houssein EH, Hosney ME, Elhoseny M et al (2020) Hybrid Harris hawks optimization with cuckoo search for drug design and discovery in chemoinformatics. Sci Rep 10:14439. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71502-z
Wei Y, Lv H, Chen M et al (2020) Predicting entrepreneurial intention of students: an extreme learning machine with Gaussian Barebone Harris Hawks optimizer. IEEE Access 8:76841–76855. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2982796
Huang G-B, Zhu Q-Y, Siew C-K (2006) Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70:489–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126
Schmidt WF, Kraaijveld MA, Duin RPW (1992) Feedforward neural networks with random weights. In: Proceedings, 11th IAPR International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Vol.II. Conference B: Pattern Recognition Methodology and Systems. IEEE Comput. Soc. Press, pp 1–4
Pao Y-H, Park G-H, Sobajic DJ (1994) Learning and generalization characteristics of the random vector functional-link net. Neurocomputing 6:163–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-2312(94)90053-1
Essa FA, Abd Elaziz M, Elsheikh AH (2020) An enhanced productivity prediction model of active solar still using artificial neural network and Harris Hawks optimizer. Appl Therm Eng 170:115020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2020.115020
Shehab M, Mashal I, Momani Z et al (2022) Harris Hawks optimization algorithm: variants and applications. Arch Comput Methods Eng 29:5579–5603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-022-09780-1
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of ICNN’95 - International Conference on Neural Networks. IEEE, pp 1942–1948
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC (1997) A discrete binary version of the particle swarm algorithm. In: 1997 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. Computational Cybernetics and Simulation. pp 4104–4108 vol.5
Shi Y, Eberhart R (1998) A modified particle swarm optimizer. In: 1998 IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Proceedings. IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence (Cat. No.98TH8360). pp 69–73
Zhan Z, Zhang J, Li Y, Chung HS (2009) Adaptive particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B 39:1362–1381. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2009.2015956
Eshtay M, Faris H, Obeid N (2018) Improving extreme learning machine by competitive swarm optimization and its application for medical diagnosis problems. Expert Syst Appl 104:134–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.03.024
Niu P, Ma Y, Li M et al (2016) A kind of parameters self-adjusting extreme learning machine. Neural Process Lett 44:813–830. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-016-9496-z
Kaloop MR, Kumar D, Samui P et al (2019) Particle swarm optimization algorithm-extreme learning machine (PSO-ELM) model for predicting resilient modulus of stabilized aggregate bases. Appl Sci 9:3221. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9163221
Naser MZ, Alavi AH (2021) Error metrics and performance fitness indicators for artificial intelligence and machine learning in engineering and sciences. Archit Struct Constr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s44150-021-00015-8
Ferri C, Hernández-Orallo J, Modroiu R (2009) An experimental comparison of performance measures for classification. Pattern Recognit Lett 30:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2008.08.010
Bui DT, Ngo PTT, Pham TD et al (2019) A novel hybrid approach based on a swarm intelligence optimized extreme learning machine for flash flood susceptibility mapping. CATENA 179:184–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.04.009
Kaya E, Saritas I (2019) Durum Wheat Dataset. In: Towar. a real-time sorting Syst. Identif. Vitr. durum wheat kernels using ANN based their Morphol. colour, wavelet gaborlet Featur. https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/muratkokludataset/durum-wheat-dataset
Johnson KJ, Synovec RE (2002) Pattern recognition of jet fuels: comprehensive GC×GC with ANOVA-based feature selection and principal component analysis. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 60:225–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7439(01)00198-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MD contributed to conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, visualization, writing—original draft, writing review and editing. IAO contributed to methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This research is based in part on the Musa Dogan's master’s thesis under direction of the Ilker Ali Ozkan.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dogan, M., Ozkan, I.A. Determination of wheat types using optimized extreme learning machine with metaheuristic algorithms. Neural Comput & Applic 35, 12565–12581 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-08354-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-08354-x