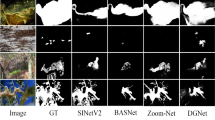
Abstract
Camouflaged object detection (COD) aims to identify and segment items that are seamlessly assimilate into the surroundings. Compared with the traditional image segmentation, the indefinable boundaries of camouflaged objects and high intrinsic similarities between the targets and the surrounding background make COD more challenging. Although many models have been designed to settle this issue, these algorithms suffer from inaccurate contours. Besides, existing COD methods mainly strive to expand the receptive field and excavate rich contextual cues using convolutional layers with large dilation rates. However, the tiny detailed information may be degenerated in this process due to the large “holes” in these dilated convolutional layers. This paper develops a novel boundary-guided context-aware network (BCNet) to deal with these problems. Specifically, we design a high-resolution feature enhancement module to excavate multi-scale information and enlarge the receptive field without destroying the tiny details within the input feature maps. The proposed module is effective in enhancing the single-layer feature and boosting the COD performance. Besides, a boundary-guided feature interaction module is designed to aggregate multi-level features and investigate the complementary relationship between the targets and the corresponding contours. We evaluate BCNet on four benchmark datasets to verify the effectiveness of the key modules. The experimental results demonstrate that BCNet achieves a real-time inference speed (49 FPS) on a Titan XP GPU and surpasses 19 cutting-edge contenders. Source code will be available at https://github.com/clelouch/BCNet.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available in the github repository, https://github.com/clelouch/BCNet.
References
Stevens M, Merilaita S (2009) Animal camouflage: current issues and new perspectives. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 364(1516):423–427. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2008.0217
Fan D, Ji G, Sun G, Cheng M, Shen J, Shao L (2020) Camouflaged object detection. In: CVPR, pp 2774–2784. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00285
Fan D-P, Ji G-P, Cheng M-M, Shao L (2021) Concealed object detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3085766
Mei H, Ji G, Wei Z, Yang X, Wei X, Fan D (2021) Camouflaged object segmentation with distraction mining. In: CVPR, pp 8772–8781
Sun Y,Chen G Zhou T Zhang Y Liu N (2021) Context-aware cross-level fusion network for camouflaged object detection. In: IJCAI, pp 1025–1031. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2021/142
Fan D, Ji G, Zhou T, Chen G, Fu H, Shen J, Shao L (2021) Pranet: parallel reverse attention network for polyp segmentation. In: MICCAI, pp 263–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_26
Fan D, Zhou T, Ji G, Zhou Y, Chen G, Fu H, Shen J, Shao L (2020) Inf-net: automatic COVID-19 lung infection segmentation from CT images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(8):2626–2637. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.2996645
Hall JR, Matthews O, Volonakis TN, Liggins E, Lymer KP, Baddeley R, Cuthill IC, Scott-Samuel NE (2021) A platform for initial testing of multiple camouflage patterns. Defence Technol 17(6):1833–1839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2020.11.004
Chu H, Hsu W, Mitra NJ, Cohen-Or D, Wong T, Lee T (2010) Camouflage images. ACM Trans Graph 29(4):51–1518. https://doi.org/10.1145/1778765.1778788
Wendi Hou Jinping Li JYYH (2011) Detection of the mobile object with camouflage color under dynamic background based on optical flow. Procedia Eng 15:2201–2205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2011.08.412
Sengottuvelan P, Wahi A, Shanmugam A (2008) Performance of decamouflaging through exploratory image analysis. In: ICETET, pp 6–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICETET.2008.232
Xue F, Yong C, Xu S, Dong H, Luo Y, Jia W (2016) Camouflage performance analysis and evaluation framework based on features fusion. Multim Tools Appl 75(7):4065–4082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2946-1
Pan Y, Chen Y, Fu Q, Zhang P, Xu X (2011) Study on the camouflaged target detection method based on 3d convexity. Math Models Methods Appl Sci 5:152
Le T, Nguyen TV, Nie Z, Tran M, Sugimoto A (2019) Anabranch network for camouflaged object segmentation. Comput Vis Image Underst 184:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2019.04.006
Xu X, Zhu M, Yu J, Chen S, Hu X, Yang Y (2021) Boundary guidance network for camouflage object detection. Image Vis Comput 114:104283
Liu J, Hou Q, Cheng M, Feng J, Jiang J (2019) A simple pooling-based design for real-time salient object detection. In: CVPR, pp 3917–3926 . https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00404
Ji G, Fu K, Wu Z, Fan D, Shen J, Shao L (2021) Full-duplex strategy for video object segmentation. In: ICCV, pp 4902–4913 . https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00488
Pang Y, Zhao X, Zhang L, Lu H Multi-scale interactive network for salient object detection. In: CVPR, pp 9410–9419 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00943
Li S, Sui X, Luo X, Xu X, Liu Y, Goh RSM (2021) Medical image segmentation using squeeze-and-expansion transformers. In: Zhou Z. (ed.) IJCAI, pp 807–815. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2021/112
Zhao J, Liu J, Fan D, Cao Y, Yang J, Cheng M (2019) Egnet: edge guidance network for salient object detection. In: ICCV, pp 8778–8787. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00887
Wu Z, Su L, Huang Q (2019) Stacked cross refinement network for edge-aware salient object detection. In: ICCV, pp 7263–7272 . https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00736
Wu Z, Su L, Huang Q (2019) Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection. In: CVPR, pp 3907–3916. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00403
Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, Wang X, Jia J (2017) Pyramid scene parsing network. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, July 21–26, 2017, pp 6230–6239. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.660
Chen L, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille AL (2018) Deeplab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, Atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFS. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834–848. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184
Siricharoen P, Aramvith S, Chalidabhongse TH, Siddhichai S (2010) Robust outdoor human segmentation based on color-based statistical approach and edge combination. In: The 2010 international conference on green circuits and systems, pp 463–468. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICGCS.2010.5543017
Lv Y, Zhang J, Dai Y, Li A, Liu B, Barnes N, Fan D (2021) Simultaneously localize, segment and rank the camouflaged objects. In: CVPR, pp 11591–11601
Yan J, Le T, Nguyen K, Tran M, Do T, Nguyen TV (2021) Mirrornet: bio-inspired camouflaged object segmentation. IEEE Access 9:43290–43300. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3064443
Zhu J, Zhang X, Zhang S, Liu J (2021) Inferring camouflaged objects by texture-aware interactive guidance network. In: AAAI, pp 3599–3607
Ji G-P, Zhu L, Zhuge M, Fu K (2022) Fast camouflaged object detection via edge-based reversible re-calibration network. Pattern Recogn 123:108414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108414
Ren J, Hu X, Zhu L, Xu X, Xu Y, Wang W, Deng Z, Heng P-A (2021) Deep texture-aware features for camouflaged object detection. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3126591
Zhuge M, Lu X, Guo Y, Cai Z, Chen S (2022) Cubenet: X-shape connection for camouflaged object detection. Pattern Recogn 127:108644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2022.108644
Li A, Zhang J, Lv Y, Liu B, Zhang T, Dai Y (2021) Uncertainty-aware joint salient object and camouflaged object detection. In: CVPR, pp 10071–10081
Wang T, Borji A, Zhang L, Zhang P, Lu H (2017) A stagewise refinement model for detecting salient objects in images. In: ICCV, pp 4039–4048. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.433
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: MCCAI, pp 234–241. Springer
Ma Y, Shuai H, Cheng W (2022) Spatiotemporal dilated convolution with uncertain matching for video-based crowd estimation. IEEE Trans Multim 24:261–273. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3050059
Li J, Pan Z, Liu Q, Wang Z (2021) Stacked u-shape network with channel-wise attention for salient object detection. IEEE Trans Multim 23:1397–1409. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2020.2997192
Li H, Chen G, Li G, Yu Y (2019) Motion guided attention for video salient object detection. In: ICCV, pp 7273–7282. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00737
Zhang Z, Lin Z, Xu J, Jin W, Lu S, Fan D (2021) Bilateral attention network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:1949–1961. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3049959
Zhang M, Liu J, Wang Y, Piao Y, Yao S, Ji W, Li J, Lu H, Luo Z(2021) Dynamic context-sensitive filtering network for video salient object detection. In: ICCV, pp 1533–1543. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00158
Wei J, Wang S, Huang Q (2020) F\({^3}\)net: Fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. In: AAAI, pp 12321–12328. https://aaai.org/ojs/index.php/AAAI/article/view/6916
Tu Z, Ma Y, Li C, Tang J, Luo B (2021) Edge-guided non-local fully convolutional network for salient object detection. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 31(2):582–593. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2020.2980853
Ji W, Li J, Zhang M, Piao Y, Lu H Accurate RGB-D salient object detection via collaborative learning. In: Vedaldi A, Bischof H, Brox T, Frahm J (2020) (eds) ECCV, vol 12363, pp 52–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58523-5_4
Zhou H, Xie X, Lai J, Chen Z, Yang L (2020) Interactive two-stream decoder for accurate and fast saliency detection. In: CVPR, pp 9138–9147. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00916
Chen T, Xiao J, Hu X, Zhang G, Wang S (2022) Boundary-guided network for camouflaged object detection. Knowl-Based Syst 248:108901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2022.108901
Chen Q, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Fu K, Zhao Q, Du H (2021) RGB-D salient object detection via 3d convolutional neural networks. In: AAAI, pp 1063–1071. https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/16191
Chen C, Wang G, Peng C, Fang Y, Zhang D, Qin H (2021) Exploring rich and efficient spatial temporal interactions for real-time video salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:3995–4007. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3068644
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2021) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR, pp 770–778 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Chen T, Hu X, Xiao J, Zhang G, Wang S (2021) Binet: bidirectional interactive network for salient object detection. Neurocomputing 465:490–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.09.020
Krähenbühl P, Koltun V (2011) Efficient inference in fully connected crfs with gaussian edge potentials. In: NIPS, pp 109–117
Qiu Z, Yao T, Mei T (2017) Learning spatio-temporal representation with pseudo-3d residual networks. In: ICCV, pp 5534–5542. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.590
Skurowski P, Abdulameer H, Błaszczyk J, Depta T, Kornacki A, Kozieł P Animal Camouflage Analysis. Chameleon Database
Chen T, Xiao J, Hu X, Zhang G, Wang S (2022) Spatiotemporal context-aware network for video salient object detection. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07330-1
Fan D, Cheng M, Liu Y, Li T, Borji A (2017) Structure-measure: a new way to evaluate foreground maps. In: ICCV, pp 4558–4567. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.487
Chen T, Hu X, Xiao J, Zhang G, Wang S (2022) Cfidnet: cascaded feature interaction decoder for rgb-d salient object detection. Neural Comput Appl 34:7547–7563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06845-3
Margolin R, Zelnik-Manor L, Tal A (2014) How to evaluate foreground maps. In: CVPR, pp 248–255. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.39
Fan D, Ji G, Qin X, Cheng M (2021) Cognitive vision inspired object segmentation metric and loss function. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis
Zhai Y, Fan D-P, Yang J, Borji A, Shao L, Han J, Wang L (2021) Bifurcated backbone strategy for rgb-d salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3116793
Kingma D.P, Ba J (2015) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: ICLR
Qin X, Zhang Z.V, Huang C, Gao C, Dehghan M, Jägersand M (2019) Basnet: boundary-aware salient object detection. In: CVPR, pp 7479–7489 . https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00766
Liu N, Han J, Yang M (2018) Picanet: learning pixel-wise contextual attention for saliency detection. In: CVPR, pp 3089–3098. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00326
Gao S, Tan Y, Cheng M, Lu C, Chen Y, Yan S (2020) Highly efficient salient object detection with 100k parameters. ECCV 12351:702–721. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58539-6_42
Zhang J, Fan D, Dai Y, Anwar S, Saleh F.S, Zhang T, Barnes N (2020) Uc-net: uncertainty inspired RGB-D saliency detection via conditional variational autoencoders. In: CVPR, pp 8579–8588. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00861
Luo Z, Mishra A.K, Achkar A, Eichel J.A, Li S, Jodoin P (2017) Non-local deep features for salient object detection. In: CVPR, pp 6593–6601. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.698
Gao S, Cheng M, Zhao K, Zhang X, Yang M, Torr PHS (2021) Res2net: a new multi-scale backbone architecture. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(2):652–662. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2938758
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (under Grant 51807003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, J., Chen, T., Hu, X. et al. Boundary-guided context-aware network for camouflaged object detection. Neural Comput & Applic 35, 15075–15093 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-08502-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-08502-3