Abstract
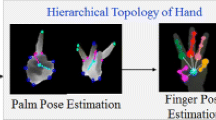
Hand pose estimation is a challenging task in hand-object interaction scenarios due to the uncertainty caused by object occlusions. Inspired by human reasoning from a hand-object interaction video sequence, we propose a hand pose estimation model. It uses three cascaded modules to imitate human’s estimation and observation process. The first module predicts an initial pose based on the visible information and the prior hand knowledge. The second module updates the hand shape memory based on the new information coming from the subsequent frames. The bone’s length updating is initiated by the predicted joint’s reliability. The third module refines the coarse pose according to the hand-object contact state represented by the object’s Signed Distance Function field. Our model gets the mean joints estimation error of 21.3 mm, the Procrustes error of 9.9 mm, and the Trans &Scale error of 22.3 mm on HO3Dv2, and Root-Relative error of 12.3 mm on DexYCB which are superior to other state-of-the-art models.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available within the article or its supplementary materials.
References
Ahmad A, Migniot C, Dipanda A (2019) Hand pose estimation and tracking in real and virtual interaction: a review. Image Vision Comput 89:35–49
Baek S, Kim KI, Kim TK (2020) Weakly-supervised domain adaptation via gan and mesh model for estimating 3d hand poses interacting objects. In: CVPR, pp 6121–6131
Chao YW, Yang W, Xiang Y, et al (2021) Dexycb: A benchmark for capturing hand grasping of objects. In: CVPR, pp 9044–9053
Chen L, Lin SY, Xie Y, et al (2021) Temporal-aware self-supervised learning for 3d hand pose and mesh estimation in videos. In: WACV, pp 1050–1059
Chen Z, Chen S, Schmid C, et al (2023) gsdf: Geometry-driven signed distance functions for 3d hand-object reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 12,890–12,900
Cho W, Park G, Woo W (2020) Bare-hand depth inpainting for 3d tracking of hand interacting with object. In: ISMAR, IEEE, pp 251–259
Doosti B, Naha S, Mirbagheri M, et al (2020) Hope-net: a graph-based model for hand-object pose estimation. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
El-Baz A, Tolba AS (2013) An efficient algorithm for 3d hand gesture recognition using combined neural classifiers. Neural Comput Appl 22(7):1477–1484
Fang L, Wu G, Kang W et al (2019) Feature covariance matrix-based dynamic hand gesture recognition. Neural Comput Appl 31(12):8533–8546
Goudie D, Galata A (2017) 3d hand-object pose estimation from depth with convolutional neural networks. In: FG 2017, IEEE, pp 406–413
Goyal R, Ebrahimi Kahou S, Michalski V, et al (2017) The" something something" video database for learning and evaluating visual common sense. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 5842–5850
Hampali S, Rad M, Oberweger M, et al (2020) Ho3d competition. https://competitions.codalab.org/competitions/22485
Hampali S, Rad M, Oberweger M, et al (2020) Honnotate: a method for 3d annotation of hand and object poses. In: CVPR, pp 3196–3206
Han S, Liu B, Cabezas R et al (2020) Megatrack: monochrome egocentric articulated hand-tracking for virtual reality. ACM Trans Grap 39(4):1–13
Hasan H, Abdul-Kareem S (2014) Retracted article: human-computer interaction using vision-based hand gesture recognition systems: a survey. Neural Comput Appl 25(2):251–261
Hasson Y, Varol G, Tzionas D, et al (2019) Learning joint reconstruction of hands and manipulated objects. In: CVPR, pp 11,807–11,816
Hasson Y, Tekin B, Bogo F, et al (2020) Leveraging photometric consistency over time for sparsely supervised hand-object reconstruction. In: CVPR, pp 571–580
Hasson Y, Varol G, Schmid C et al (2021) Towards unconstrained joint hand-object reconstruction from rgb videos. In: 2021 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), IEEE, pp 659–668
Humphreys GW, Riddoch MJ (1984) Routes to object constancy: implications from neurological impairments of object constancy. Quart J Exp Psychol 36(3):385–415
Kushwaha A, Khare A, Prakash O (2023) Micro-network-based deep convolutional neural network for human activity recognition from realistic and multi-view visual data. Neural Comput Appl 35(18):13321–13341
Li J, Xu C, Chen Z, et al (2021) Hybrik: A hybrid analytical-neural inverse kinematics solution for 3d human pose and shape estimation. In: CVPR, pp 3383–3393
Li R, Liu Z, Tan J (2019) A survey on 3d hand pose estimation: cameras, methods, and datasets. Pattern Recognit 93:251–272
Li X, Lin X, Sun Y (2023) Gecm: graph embedded convolution model for hand mesh reconstruction. Signal Image Video Process 17(3):715–723
Liu C, Li Y, Ma K, et al (2021) Learning 3-d human pose estimation from catadioptric videos. In: IJCAI, pp 852–859
Liu S, Jiang H, Xu J, et al (2021) Semi hand-object. https://github.com/stevenlsw/Semi-Hand-Object
Liu S, Jiang H, Xu J, et al (2021) Semi-supervised 3d hand-object poses estimation with interactions in time. In: CVPR, pp 14687–14697
Liu Z, Chen H, Feng R, et al (2021) Deep dual consecutive network for human pose estimation. In: CVPR, pp 525–534
Logothetis N (1996) Visual object recognition. Ann Rev Neurosci 19(2):577–621
Mishra A, Sharma S, Kumar S et al (2021) Effect of hand grip actions on object recognition process: a machine learning-based approach for improved motor rehabilitation. Neural Comput Appl 33(7):2339–2350
Park JJ, Florence P, Straub J, et al (2019) Deepsdf: Learning continuous signed distance functions for shape representation. In: CVPR, pp 165–174
Romero J, Tzionas D, Black MJ (2017) Embodied hands: Modeling and capturing hands and bodies together. ToG 36(6):1–17
Smith B, Wu C, Wen H et al (2020) Constraining dense hand surface tracking with elasticity. TOG 39(6):1–14
Spurr A, Iqbal U, Molchanov P, et al (2020) Weakly supervised 3d hand pose estimation via biomechanical constraints. In: ECCV, Springer, pp 211–228
Tekin B, Bogo F, Pollefeys M (2019) H+o: Unified egocentric recognition of 3d hand-object poses and interactions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4511–4520
Tekin B, Bogo F, Pollefeys M (2019) H+o: Unified egocentric recognition of 3d hand-object poses and interactions. In: CVPR, pp 4511–4520
Wang C, Xu D, Zhu Y, et al (2019) Densefusion: 6d object pose estimation by iterative dense fusion. In: CVPR, pp 3343–3352
Wei SE, Ramakrishna V, Kanade T, et al (2016) Convolutional pose machines. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 4724–4732
Xiong F, Zhang B, Xiao Y, et al (2019) A2j: Anchor-to-joint regression network for 3d articulated pose estimation from a single depth image. In: CVPR, pp 793–802
Yang J, Chang HJ, Lee S, et al (2020) Seqhand: Rgb-sequence-based 3d hand pose and shape estimation. In: ECCV, Springer, pp 122–139
Yang L, Li K, Zhan X, et al (2022) Artiboost: Boosting articulated 3d hand-object pose estimation via online exploration and synthesis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 2750–2760
Yang L, Li K, Zhan X, et al (2022) Oakink: A large-scale knowledge repository for understanding hand-object interaction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 20,953–20,962
Ye Y, Gupta A, Tulsiani S (2022) What’s in your hands? 3d reconstruction of generic objects in hands. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 3895–3905
Yuan S, Garcia-Hernando G, Stenger B, et al (2018) Depth-based 3d hand pose estimation: From current achievements to future goals. In: CVPR, pp 2636–2645
Yuan Y, Wei SE, Simon T, et al (2021) Simpoe: Simulated character control for 3d human pose estimation. In: CVPR, pp 7159–7169
Zhang Z, Hu L, Deng X, et al (2021) Sequential 3d human pose estimation using adaptive point cloud sampling strategy. In: IJCAI, pp 1330–1337
Zhao Z, Wang T, Xia S, et al (2020) Hand-3d-studio: A new multi-view system for 3d hand reconstruction. In: ICASSP, IEEE, pp 2478–2482
Zhou Y, Habermann M, Xu W, et al (2020) Monocular real-time hand shape and motion capture using multi-modal data. In: CVPR, pp 5346–5355
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.61873046 and No.U1708263).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Lin, X. HRI: human reasoning inspired hand pose estimation with shape memory update and contact-guided refinement. Neural Comput & Applic 35, 21043–21054 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-08884-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-08884-4