Abstract
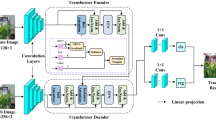
Recently, fully transformer-based trackers have achieved impressive tracking results, but this also brings a great deal of computational complexity. Some researchers have applied token pruning techniques to fully transformer-based trackers to diminish the computational complexity, but this leads to missing contextual information that is important for the regression task in the tracker. In response to the above issue, this paper proposes a token fusion method that speeds up inference while avoiding information loss and thus improving the robustness of the tracker. Specifically, the input of the transformer’s encoder contains search tokens and exemplar tokens, and the search tokens are divided into tracking object tokens and background tokens according to the similarity between search tokens and exemplar tokens. The tokens with greater similarity to the exemplar tokens are identified as tracking object tokens, and those with smaller similarity to the exemplar tokens are identified as background tokens. The tracking object tokens contain the discriminative features of the tracking object, for the sake of making the tracker pay more attention to the tracking object tokens while reducing the computational effort. All the tracking object tokens are kept, and then, the background tokens are weighted and fused to form new background tokens according to the attention weight of the background tokens to prevent the loss of contextual information. The token fusion method presented in this paper not only provides efficient inference of the tracker but also makes the tracker more robust. Extensive experiments are carried out on popular tracking benchmark datasets to verify the validity of the token fusion method.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Data Availability
The dataset that support the findings of this study are openly available in the LaSOT repository at http://vision.cs.stonybrook.edu/~lasot/, in the TrackingNet repository at https://tracking-net.org/, in the GOT-10k repository at http://got-10k.aitestunion.com/, in the COCO repository at https://cocodataset.org/, in the NFS repository at http://ci2cv.net/nfs/index.html, in the TNL2K repository at https://sites.google.com/view/langtrackbenchmark/, in the UAV123 repository at https://cemse.kaust.edu.sa/ivul/uav123.
References
Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Henriques JF, Vedaldi A, Torr PH (2016) Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2016 Workshops: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 8-10 and 15-16, 2016, Proceedings, Part II 14, pp 850–865 Springer
Huang H, Liu G, Zhang Y, Xiong R, Zhang S (2022) Ensemble siamese networks for object tracking. Neural Comput Appl 34:8173–8191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-06911-4
Ke X, Li Y, Guo W, Huang Y (2022) Learning deep convolutional descriptor aggregation for efficient visual tracking. Neural Comput Appl 34:3745–3765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06638-8
Meng F, Gong X, Zhang Y (2023) Rhl-track: visual object tracking based on recurrent historical localization. Neural Comput Appl 35:12611–12625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-08422-2
Wang Q, Zhang L, Bertinetto L, Hu W, Torr PH (2019) Fast online object tracking and segmentation: A unifying approach. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 1328–1338
Voigtlaender P, Luiten J, Torr PH, Leibe B (2020) Siam r-cnn: Visual tracking by re-detection. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 6578–6588
Han W, Dong X, Khan FS, Shao L, Shen J (2021) Learning to fuse asymmetric feature maps in siamese trackers. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition ((CVPR)), pp 16570–16580
Bao J, Chen K, Sun X, Zhao L, Diao W, Yan M (2023) Siamthn: Siamese target highlight network for visual tracking. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol
Yuan D, Chang X, Huang P-Y, Liu Q, He Z (2021) Self-supervised deep correlation tracking. IEEE Trans Image Proc 30:976–985. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.3037518
Yang K, He Z, Pei W, Zhou Z, Li X, Yuan D, Zhang H (2022) Siamcorners: siamese corner networks for visual tracking. IEEE Trans Multimed 24:1956–1967. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3074239
Xie F, Wang C, Wang G, Yang W, Zeng W (2021) Learning tracking representations via dual-branch fully transformer networks. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), pp 2688–2697 https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW54120.2021.00303
Yu B, Tang M, Zheng L, Zhu G, Wang J, Feng H, Feng X, Lu H (2021) High-performance discriminative tracking with transformers. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (CVPR), pp 9856–9865
Zhao M, Okada K, Inaba M (2021) Trtr: Visual tracking with transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.03817
Fu Z, Liu Q, Cai W, Wang Y (2022) Sparsett: Visual tracking with sparse transformers pp 905–912 https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2022/127
Cao Z, Huang Z, Pan L, Zhang S, Liu Z, Fu C (2022) Tctrack: temporal contexts for aerial tracking. In: 2011 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 14798–14808
Zhou X, Yin T, Koltun V, Krähenbühl P (2022) Global tracking transformers. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 8761–8770 https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00857
Song Z, Luo R, Yu J, Chen Y-PP, Yang W (2023) Compact transformer tracker with correlative masked modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.10938
Blatter P, Kanakis M, Danelljan M, Van Gool L (2023) Efficient visual tracking with exemplar transformers. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (CVPR), pp 1571–1581
Ma F, Shou MZ, Zhu L, Fan H, Xu Y, Yang Y, Yan Z (2022) Unified transformer tracker for object tracking. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 8781–8790
Tang W, Kang H, Zhang H, Yu P, Arnold CW, Zhang R (2022) Transformer lesion tracker. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2022: 25th International Conference, Singapore, September 18–22, 2022, Proceedings, Part VI, pp 196–206. Springer
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser Ł, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. Adv Neural Inf Proc Syst 30
Wang N, Zhou W, Wang J, Li H (2021) Transformer meets tracker: Exploiting temporal context for robust visual tracking. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 1571–1580 https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00162
Chen X, Yan B, Zhu J, Wang D, Yang X, Lu H (2021) Transformer tracking. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 8126–8135
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X, Unterthiner T, Dehghani M, Minderer M, Heigold G, Gelly S, et al (2020) An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929
Kim S, Shen S, Thorsley D, Gholami A, Kwon W, Hassoun J, Keutzer K (2022) Learned token pruning for transformers. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp 784–794 https://doi.org/10.1145/3534678.3539260
Yin H, Vahdat A, Alvarez JM, Mallya A, Kautz J, Molchanov P (2022) A-vit: Adaptive tokens for efficient vision transformer. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 10799–10808
Fayyaz M, Kouhpayegani SA, Jafari FR, Sommerlade E, Joze HRV, Pirsiavash H, Gall J (2021) Ats: Adaptive token sampling for efficient vision transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.15667https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01054
Yu H, Wu J (2023) A unified pruning framework for vision transformers. Sci China Inf Sci 66(7):1–2
Song Z, Xu Y, He Z, Jiang L, Jing N, Liang X (2022) Cp-vit: Cascade vision transformer pruning via progressive sparsity prediction. CoRR https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2203.04570
Liang Y, Ge C, Tong Z, Song Y, Wang J, Xie P (2022) Not all patches are what you need: Expediting vision transformers via token reorganizations. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.07800
Wei S, Ye T, Zhang S, Tang Y, Liang J (2023) Joint token pruning and squeezing towards more aggressive compression of vision transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 2092–2101
Thangavel J, Kokul T, Ramanan A, Fernando S (2023) Transformers in single object tracking: an experimental survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.11867
Cui Y, Jiang C, Wang L, Wu G (2022) Mixformer: End-to-end tracking with iterative mixed attention. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 13608–13618
Chen B, Li P, Bai L, Qiao L, Shen Q, Li B, Gan W, Wu W, Ouyang W (2022) Backbone is all your need: a simplified architecture for visual object tracking. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022, Proceedings, Part XXII, pp 375–392 Springer
Lin L, Fan H, Xu Y, Ling H (2022) Swintrack: A simple and strong baseline for transformer tracking. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 35, pp 16743–16754
Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, Hu H, Wei Y, Zhang Z, Lin S, Guo B (2021) Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp 9992–10002 https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00986
Wu Q, Yang T, Liu Z, Wu B, Shan Y, Chan AB (2023) Dropmae: Masked autoencoders with spatial-attention dropout for tracking tasks. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 14561–14571 https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01399
Zhao H, Wang D, Lu H (2023) Representation learning for visual object tracking by masked appearance transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 18696–18705
Ye B, Chang H, Ma B, Shan S, Chen X (2022) Joint feature learning and relation modeling for tracking: A one-stream framework. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022, Proceedings, Part XXII, pp 341–357 Springer
Lan J-P, Cheng Z-Q, He J-Y, Li C, Luo B, Bao X, Xiang W, Geng Y, Xie X (2023) Procontext: Exploring progressive context transformer for tracking. In: ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp 1–5 https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP49357.2023.10094971 . IEEE
Tang Y, Han K, Wang Y, Xu C, Guo J, Xu C, Tao D (2022) Patch slimming for efficient vision transformers. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 12165–12174
Yin H, Vahdat A, Alvarez JM, Mallya A, Kautz J, Molchanov P (2022) A-vit: Adaptive tokens for efficient vision transformer. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 10799–10808 https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01054
Fayyaz M, Koohpayegani SA, Jafari FR, Sengupta S, Joze HRV, Sommerlade E, Pirsiavash H, Gall J (2022) Adaptive token sampling for efficient vision transformers. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp 396–414
Xu Y, Zhang Z, Zhang M, Sheng K, Li K, Dong W, Zhang L, Xu C, Sun X (2022) Evo-vit: Slow-fast token evolution for dynamic vision transformer. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 36, pp 2964–2972
Rao Y, Zhao W, Liu B, Lu J, Zhou J, Hsieh C-J (2021) Dynamicvit: Efficient vision transformers with dynamic token sparsification. Adv Neural Inf Proc Syst 34:13937–13949
Meng L, Li H, Chen B-C, Lan S, Wu Z, Jiang Y-G, Lim S-N (2022) Adavit: Adaptive vision transformers for efficient image recognition. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 12309–12318
Kong Z, Dong P, Ma X, Meng X, Sun M, Niu W, Shen X, Yuan G, Ren B, Qin M, et al (2022) Spvit: Enabling faster vision transformers via latency-aware soft token pruning, pp 620–640. Springer
Fan H, Lin L, Yang F, Chu P, Deng G, Yu S, Bai H, Xu Y, Liao C, Ling H (2019) Lasot: A high-quality benchmark for large-scale single object tracking. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 5374–5383
Muller M, Bibi A, Giancola S, Alsubaihi S, Ghanem B (2018) Trackingnet: A large-scale dataset and benchmark for object tracking in the wild. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp 300–317
Huang L, Zhao X, Huang K (2019) Got-10k: A large high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(5):1562–1577
Lin T-Y, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, Dollár P, Zitnick CL (2014) Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, September 6-12, 2014, Proceedings, Part V 13, pp 740–755 Springer
He K, Chen X, Xie S, Li Y, Dollár P, Girshick R (2022) Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 15979–15988 https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01553
Loshchilov I, Hutter F (2017) Decoupled weight decay regularization. In: International Conference on Learning Representations
Kiani Galoogahi H, Fagg A, Huang C, Ramanan D, Lucey S (2017) Need for speed: A benchmark for higher frame rate object tracking. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp 1134–1143 https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.128
Wang X, Shu X, Zhang Z, Jiang B, Wang Y, Tian Y, Wu F (2021) Towards more flexible and accurate object tracking with natural language: Algorithms and benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 13763–13773
Mueller M, Smith N, Ghanem B (2016) A benchmark and simulator for uav tracking. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, Proceedings, Part I 14, pp 445–461 Springer
He K, Zhang C, Xie S, Li Z, Wang Z (2023) Target-aware tracking with long-term context attention. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.13840
Lin L, Fan H, Zhang Z, Xu Y, Ling H (2022) Swintrack: A simple and strong baseline for transformer tracking. Adv Neural Inf Proc Syst 35:16743–16754
Gao S, Zhou C, Ma C, Wang X, Yuan J (2022) Aiatrack: Attention in attention for transformer visual tracking. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022, Proceedings, Part XXII, pp 146–164 Springer
Mayer C, Danelljan M, Bhat G, Paul M, Paudel DP, Yu F, Van Gool L (2022) Transforming model prediction for tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 8731–8740
Song Z, Yu J, Chen Y-PP, Yang W (2022) Transformer tracking with cyclic shifting window attention. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 8791–8800
Yan B, Peng H, Fu J, Wang D, Lu H (2021) Learning spatio-temporal transformer for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 10448–10457
Zhang Z, Peng H, Fu J, Li B, Hu W (2020) Ocean: Object-aware anchor-free tracking. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part XXI 16, pp 771–787 Springer
Bhat G, Danelljan M, Gool LV, Timofte R (2019) Learning discriminative model prediction for tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 6182–6191
Mayer C, Danelljan M, Paudel DP, Van Gool L (2021) Learning target candidate association to keep track of what not to track. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp 13424–13434 https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.01319
Chen X, Peng H, Wang D, Lu H, Hu H (2023) Seqtrack: Sequence to sequence learning for visual object tracking. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.14394
Gao S, Zhou C, Zhang J (2023) Generalized relation modeling for transformer tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 18686–18695
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by the Scientific and Technological Innovation Leading Talent Project under Grant 2022TSYCLJ0036, in part by the Scientific and Technological Innovation 2030 Major Project under Grant 2022ZD0115800, and in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant U1903213.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Liang Xu was involved in conceptualization, methodology and software. Liejun Wang was responsible for supervision, software and funding acquisition. ZhiQing Guo contributed to supervision, formal analysis and writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, L., Wang, L. & Guo, Z. ATFTrans: attention-weighted token fusion transformer for robust and efficient object tracking. Neural Comput & Applic 36, 7043–7056 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-09444-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-09444-0