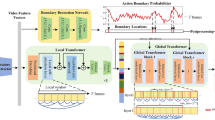
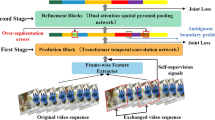
Abstract
Action segmentation is vital for video understanding because it heuristically divides complex untrimmed videos into short semantic clips. Real-world human actions exhibit complex temporal dynamics, encompassing variations in duration, rhythm, and range of motions, etc. While deep networks have been successfully applied to these tasks, they face challenges in effectively adapting to these complex variations due to the inherent difficulty in capturing semantic information from a global perspective. Merely relying on distinguishing visual representations in local regions leads to the issue of over-segmentation. In an attempt to address this practical issue, we propose a novel approach named ASGSA, which aims to obtain smoother segmentation results by extracting instructive semantic information. Our core component, Global Semantic-Aware module, provides an effective way to encode the long-range temporal relation in the long untrimmed video. Specifically, we exploit a hierarchical temporal context aggregation, which is identified by a gated-mechanism selection to control the information passage at different scales. In addition, an adaptive fusion strategy is designed to guide the segmentation with the extracted semantic information. Simultaneously, to obtain higher-quality video representation without extra annotations, we resort to self-supervised training strategy and propose the Video Speed Prediction module. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on all three challenging benchmark datasets (Breakfast, 50Salads, GTEA) and significantly improves the F1 score@50, which represents the reduction of over-segmentation. The code is available at https://github.com/ten000/ASGSA.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Farha YA, Gall J (2019) Ms-tcn: multi-stage temporal convolutional network for action segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3575–3584
Li S-J, AbuFarha Y, Liu Y, Cheng M-M, Gall J (2020) Ms-tcn++: multi-stage temporal convolutional network for action segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 45:6647–6658
Gao S-H, Han Q, Li Z-Y, Peng P, Wang L, Cheng M-M (2021) Global2local: efficient structure search for video action segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 16805–16814
Wang Z, Gao Z, Wang L, Li Z, Wu G (2020) Boundary-aware cascade networks for temporal action segmentation. In: Computer vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, proceedings, part XXV 16. Springer, pp 34–51
Chen M-H, Li B, Bao Y, AlRegib G, Kira Z (2020) Action segmentation with joint self-supervised temporal domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 9454–9463
Li Y, Dong Z, Liu K, Feng L, Hu L, Zhu J, Xu L, Liu S et al (2021) Efficient two-step networks for temporal action segmentation. Neurocomputing 454:373–381
Wang D, Yuan Y, Wang Q (2020) Gated forward refinement network for action segmentation. Neurocomputing 407:63–71
Ishikawa Y, Kasai S, Aoki Y, Kataoka H (2021) Alleviating over-segmentation errors by detecting action boundaries. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision, pp 2322–2331
Yi F, Wen H, Jiang T (2021) Asformer: transformer for action segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.08568
Aziere N, Todorovic S (2022) Multistage temporal convolution transformer for action segmentation. Image Vis Comput 128:104567
Park J, Kim D, Huh S, Jo S (2022) Maximization and restoration: action segmentation through dilation passing and temporal reconstruction. Pattern Recognit 129:108764
Cao J, Xu R, Lin X, Qin F, Peng Y, Shao Y (2023) Adaptive receptive field u-shaped temporal convolutional network for vulgar action segmentation. Neural Comput Appl 35:1–14
Lea C, Flynn MD, Vidal R, Reiter A, Hager GD (2017) Temporal convolutional networks for action segmentation and detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 156–165
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser Ł, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 30
Zhang Y, Ren K, Zhang C, Yan T (2022) SG-TCN: semantic guidance temporal convolutional network for action segmentation. In: 2022 International joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN). IEEE, pp 1–8
Kuehne H, Arslan A, Serre T (2014) The language of actions: recovering the syntax and semantics of goal-directed human activities. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 780–787
Fathi A, Ren X, Rehg JM (2011) Learning to recognize objects in egocentric activities. In: CVPR 2011. IEEE, pp 3281–3288
Stein S, McKenna SJ (2013) Combining embedded accelerometers with computer vision for recognizing food preparation activities. In: Proceedings of the 2013 ACM international joint conference on pervasive and ubiquitous computing, pp 729–738
He K, Fan H, Wu Y, Xie S, Girshick R (2020) Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 9729–9738
Qian R, Meng T, Gong B, Yang M-H, Wang H, Belongie S, Cui Y (2021) Spatiotemporal contrastive video representation learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 6964–6974
Chen T, Kornblith S, Norouzi M, Hinton G (2020) A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: International conference on machine learning. PMLR, pp 1597–1607
He K, Chen X, Xie S, Li Y, Dollár P, Girshick R (2022) Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 16000–16009
Jenni S, Meishvili G, Favaro P (2020) Video representation learning by recognizing temporal transformations. In: Computer vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, proceedings, part XXVIII 16. Springer, pp 425–442
Yao Y, Liu C, Luo D, Zhou Y, Ye Q (2020) Video playback rate perception for self-supervised spatio-temporal representation learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 6548–6557
Wang J, Jiao J, Liu Y-H (2020) Self-supervised video representation learning by pace prediction. In: Computer vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, proceedings, part XVII 16. Springer, pp 504–521
Kim D, Cho D, Kweon IS (2019) Self-supervised video representation learning with space-time cubic puzzles. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence 33:8545–8552
Ahsan U, Madhok R, Essa I (2019) Video jigsaw: unsupervised learning of spatiotemporal context for video action recognition. In: 2019 IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV). IEEE, pp 179–189
Huo Y, Ding M, Lu H, Lu Z, Xiang T, Wen J-R, Huang Z, Jiang J, Zhang S, Tang M, et al (2021) Self-supervised video representation learning with constrained spatiotemporal jigsaw
Jing L, Yang X, Liu J, Tian Y (2018) Self-supervised spatiotemporal feature learning via video rotation prediction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.11387
Xu D, Xiao J, Zhao Z, Shao J, Xie D, Zhuang Y (2019) Self-supervised spatiotemporal learning via video clip order prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 10334–10343
Wang J, Jiao J, Bao L, He S, Liu Y, Liu W (2019) Self-supervised spatio-temporal representation learning for videos by predicting motion and appearance statistics. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4006–4015
Singh B, Marks TK, Jones M, Tuzel O, Shao M (2016) A multi-stream bi-directional recurrent neural network for fine-grained action detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1961–1970
Ding L, Xu C (2017) Tricornet: a hybrid temporal convolutional and recurrent network for video action segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.07818
Ahn H, Lee D (2021) Refining action segmentation with hierarchical video representations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 16302–16310
Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, Hu H, Wei Y, Zhang Z, Lin S, Guo B (2021) Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 10012–10022
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X, Unterthiner T, Dehghani M, Minderer M, Heigold G, Gelly S et al (2020) An image is worth 16 x 16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929
Arnab A, Dehghani M, Heigold G, Sun C, Lučić M, Schmid C (2021) Vivit: a video vision transformer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 6836–6846
Bertasius G, Wang H, Torresani L (2021) Is space-time attention all you need for video understanding? In: ICML 2:4
Zhu X, Su W, Lu L, Li B, Wang X, Dai J (2020) Deformable detr: deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.04159
Liu Z, Ning J, Cao Y, Wei Y, Zhang Z, Lin S, Hu H (2022) Video swin transformer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3202–3211
Feichtenhofer C, Li Y, He K et al (2022) Masked autoencoders as spatiotemporal learners. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 35:35946–35958
Wang R, Chen D, Wu Z, Chen Y, Dai X, Liu M, Jiang Y-G, Zhou L, Yuan L (2022) Bevt: Bert pretraining of video transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 14733–14743
Snoun A, Bouchrika T, Jemai O (2023) Deep-learning-based human activity recognition for Alzheimer’s patients’ daily life activities assistance. Neural Comput Appl 35(2):1777–1802
Kim G-h, Kim E (2022) Stacked encoder-decoder transformer with boundary smoothing for action segmentation. Electron Lett 58:972–974
Souri Y, Farha YA, Despinoy F, Francesca G, Gall J (2022) Fifa: fast inference approximation for action segmentation. In: Pattern recognition: 43rd DAGM German conference, DAGM GCPR 2021, Bonn, Germany, September 28–October 1, 2021, proceedings. Springer, pp 282–296
Xu Z, Rawat Y, Wong Y, Kankanhalli MS, Shah M (2022) Don’t pour cereal into coffee: differentiable temporal logic for temporal action segmentation. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 35:14890–14903
Li M, Chen L, Duan Y, Hu Z, Feng J, Zhou J, Lu J (2022) Bridge-prompt: toward ordinal action understanding in instructional videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 19880–19889
Behrmann N, Golestaneh SA, Kolter Z, Gall J, Noroozi M (2022) Unified fully and timestamp supervised temporal action segmentation via sequence to sequence translation. In: Computer vision–ECCV 2022: 17th European conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022, proceedings, part XXXV. Springer, pp 52–68
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556
Misra I, Zitnick CL, Hebert M (2016) Shuffle and learn: unsupervised learning using temporal order verification. In: Computer vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, proceedings, part I 14. Springer, pp 527–544
Lee H-Y, Huang J-B, Singh M, Yang M-H (2017) Unsupervised representation learning by sorting sequences. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 667–676
Doersch C, Gupta A, Efros AA (2015) Unsupervised visual representation learning by context prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 1422–1430
Larsson G, Maire M, Shakhnarovich G (2017) Colorization as a proxy task for visual understanding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 6874–6883
Carlucci FM, D’Innocente A, Bucci S, Caputo B, Tommasi T (2019) Domain generalization by solving jigsaw puzzles. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2229–2238
Gidaris S, Singh P, Komodakis N (2018) Unsupervised representation learning by predicting image rotations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.07728
Benaim S, Ephrat A, Lang O, Mosseri I, Freeman WT, Rubinstein M, Irani M, Dekel T (2020) Speednet: learning the speediness in videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 9922–9931
Carreira J, Zisserman A (2017) Quo vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 6299–6308
Yang J, Li C, Dai X, Gao J (2022) Focal modulation networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 35:4203–4217
Lea C, Reiter A, Vidal R, Hager GD (2016) Segmental spatiotemporal CNNs for fine-grained action segmentation. In: Computer vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, proceedings, part III 14. Springer, pp 36–52
Wang D, Hu D, Li X, Dou D (2021) Temporal relational modeling with self-supervision for action segmentation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence 35: 2729–2737
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National Key Research and Development Project No.2019YFC1511003, No.2018YFC19008005, and National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) No.61803004 through grants for our project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bian, Q., Zhang, C., Ren, K. et al. ASGSA: global semantic-aware network for action segmentation. Neural Comput & Applic 36, 13629–13645 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-09776-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-09776-x