Abstract
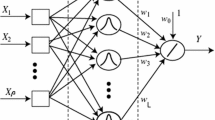
In this paper, an adaptive radial basis function neural network (RBFNN) is investigated and presented for identifying the nonlinear dynamical system. In traditional RBFNN structure, the selections of the activated radius are decided by the designer’s experience to satisfy the best approximation of nonlinear dynamical function. In order to reduce the experience error, an adaptive RBFNN mechanism that can realize auto-regulation of activated radius is proposed in this paper. Taking the lattice points as the center of activated function, we use Taylor expansion to separate the factor of activated radius in local space. In order to ensure that the identification error has the property of fast convergence, the error conversion function is used for shrinking the gain in the error differential equation. Constructing a Lyapunov function to determine the differential equation of the weights and the activated radius, it is shown that the weights and the activated radius will converge to the neighborhood of its true value and the identification error will converge to neighborhood of zero in a periodic or period-like nonlinear dynamical system. To illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed adaptive RBFNN, Vanderpol and Duffing dynamical system are used as test examples, in comparison with traditional RBFNN and wavelet neural networks (WNN). The results show that the proposed method has best accurate identification and approximating effect in all of test algorithms.













Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
Kumar R, Srivastava S, Gupta JRP, Mohindru A (2018) Diagonal recurrent neural network based identification of nonlinear dynamical systems with Lyapunov stability based adaptive learning rates. Neurocomputing 287:102–117
Xu L, Ding F, Yang E (2020) Separable recursive gradient algorithm for dynamical systems based on the impulse response signals. Int J Control Autom Syst 18(12):3167–3177
Denis V, Jossic M, Giraud-Audine C, Chomette B, Renault A, Thomas O (2018) Identification of nonlinear modes using phase-locked-loop experimental continuation and normal form. Mech Syst Signal Process 106:430–452
Zhang S, Wang S, Jing F, Tan M (2019) A sensorless hand guiding scheme based on model identification and control for industrial robot. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 15(9):5204–5213
Gupta V, Mittal M (2020) A novel method of cardiac arrhythmia detection in electrocardiogram signal. Int J Med Eng Inf 12(5):489–499
Deng M, Wang C, Zheng T (2018) Individual identification using a gait dynamics graph. Pattern Recogn 83:287–298
Alexandridis A, Chondrodima E, Giannopoulos N, Sarimveis H (2016) A fast and efficient method for training categorical radial basis function networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(11):2831–2836
Rahimilarki R, Gao Z, Zhang A, Binns R (2019) Robust neural network fault estimation approach for nonlinear dynamic systems with applications to wind turbine systems. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 15(12):6302–6312
Fei J, Lu C (2017) Adaptive sliding mode control of dynamic systems using double loop recurrent neural network structure. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(4):1275–1286
Puscasu G, Codres B, Stancu A, Murariu G (2009) Nonlinear system identification based on internal recurrent neural networks. Int J Neural Syst 19(02):115–125
Pan Y, Wang J (2011) Model predictive control of unknown nonlinear dynamical systems based on recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 59(8):3089–3101
Wu W, Wang C, Yuan C (2019) Deterministic learning from sampling data. Neurocomputing 358:456–466
Kurdila AJ, Narcowich FJ, Ward JD (1995) Persistency of excitation in identification using radial basis function approximants. SIAM J Control Optim 33(2):625–642
Wang C, Hill DJ (2006) Learning from neural control. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17(1):130–146
Wang C, Hill DJ (2010) Deterministic learning and nonlinear observer design. Asian J Control 12(6):714–724
Sanner RM, Slotine J (1992) Gaussian networks for direct adaptive control. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 3(6):837–863
Zheng T, Wang C (2017) Relationship between persistent excitation levels and RBF network structures, with application to performance analysis of deterministic learning. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(10):3380–3392
Schilling RJ, Carroll JJ, Al-Ajlouni AF (2001) Approximation of nonlinear systems with radial basis function neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 12(1):1–15
Luo G, Yang Z, Zhan C, Zhang Q (2021) Identification of nonlinear dynamical system based on raised-cosine radial basis function neural networks. Neural Process Lett 53(1):355–374
Abiyev RH, Kaynak O (2008) Fuzzy wavelet neural networks for identification and control of dynamic plants-a novel structure and a comparative study. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(8):3133–3140
Luo G, Yang Z, Zhang Q (2021) Identification of autonomous nonlinear dynamical system based on discrete-time multiscale wavelet neural network. Neural Comput Appl 33(22):15191–15203
Zeng W, Yuan C (2021) ECG arrhythmia classification based on variational mode decomposition, Shannon energy envelope and deterministic learning. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 12(10):2963–2988
Masood Z, Majeed K, Samar R, Raja MAZ (2017) Design of Mexican Hat Wavelet neural networks for solving Bratu type nonlinear systems. Neurocomputing 221:1–14
Wirkus S, Rand R (2015) The dynamics of two coupled van der pol oscillators with delay coupling. Nonlinear Dyn 30(3):205–221
Zhang Q, Gao J, Dong H, Mao Y (2018) Wpd and de/bbo-rbfnn for solution of rolling bearing fault diagnosis. Neurocomputing 312(27):27–33
Agarwal V, Zheng X, Balachandran B (2018) Influence of noise on frequency responses of softening Duffing oscillators. Phys Lett A 382(46):3355–3364
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank anonymous peer reviewer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors (Guo Luo, Hu Min and Zhi Yang) declare that they have no conflict of financial or non-financial interests in relation to the work in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, G., Min, H. & Yang, Z. Identification of nonlinear dynamical system based on adaptive radial basis function neural networks. Neural Comput & Applic 36, 15617–15629 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-09794-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-09794-9