Abstract
Radioisotope identification presents challenges that can be effectively addressed through pattern recognition and machine learning (ML) techniques. However, further investigation is necessary to assess the accuracy of these algorithms in quantifying mixtures of radioisotopes. The novelty of the study focuses on a hybrid convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture, called Arch, which utilizes numerical values to predict the presence of radioisotopes based on their signals. The feature extraction methods are employed to analyze small-isotope libraries using area-of-interest techniques and low-resolution spectrometers, with fully calibrated detectors ensuring accurate identification complexity. Additionally, this study explores the use of two sets of machine learning approaches for the automated identification of radioisotopes, focusing specifically on the feature extraction method. The Hybrid CNN Arc model, as proposed, achieved a test data accuracy of 95%. Additionally, a recurrent neural network model achieved an accuracy of 92%, while a GBDT model achieved an accuracy of 86%. The precision, recall, and f1-score metrics have been computed for the Hybrid CNN Arch approach, yielding values of 95%, 95%, and 95%, respectively. Similarly, the RNN model achieved precision, recall, and f1-score scores of 89%, 82%, and 81.5%, respectively. Lastly, the GBDT model attained precision, recall, and f1-score values of 84%, 81%, and 74.6%, respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
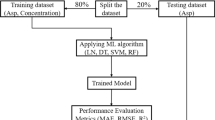
The dataset used for this research is given in Table 1 also and the link for the dataset is provided here. https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1otqCjqRx_r4WZSLYe7L5qN12X4cLmlR7/edit?usp=sharing&ouid=116572301465828671165.
References
Sharma S, Bellinger C, Japkowicz N, Berg R and Ungar K (2012) Anomaly detection in gamma ray spectra: a machine learning perspective. In 2012 IEEE symposium on computational intelligence for security and defence applications (pp. 1–8). IEEE.
Tufail M, Akhtar N (2019) Assessment of environmental radioactivity levels around nuclear power plants in Pakistan using gamma spectroscopy. J Radiation Res Appl Sci 12(1):60–66
Chauhan RPS, Singh NP, Bajwa BS (2017) spectrum deconvolution techniques in gamma spectroscopy. Def Sci J 67(5):541–550
Kamuda M, Stinnett J, Sullivan CJ (2017) Automated isotope identification algorithm using artificial neural networks. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 64(7):1858–1864. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNS.2017.2693152
Gomez-Fernandez M, Wong WK, Tokuhiro A, Welter K, Alhawsawi AM, Yang H, Higley K (2021) Isotope identification using deep learning: an explanation. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect A 988:164925
Alamaniotis M, Mattingly J, Tsoukalas LH (2013) Kernel-based machine learning for background estimation of NaI low-count gamma-ray spectra. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 60(3):2209–2221
Jeon B, Kim J, Lee E, Moon M, Cho G (2021) Pseudo-gamma spectroscopy based on plastic scintillation detectors using multitask learning. Sensors 21(3):684
Kamuda M, Sullivan CJ (2019) An automated isotope identification and quantification algorithm for isotope mixtures in low-resolution gamma-ray spectra. Radiat Phys Chem 155:281–286
Galib SM, Bhowmik PK, Avachat AV, Lee HK (2021) A comparative study of machine learning methods for automated identification of radioisotopes using NaI gamma-ray spectra. Nucl Eng Technol 53(12):4072–4079
Galib S M (2019). Applications of machine learning in nuclear imaging and radiation detection. Missouri University of Science and Technology.
Bilton KJ, Joshi TH, Bandstra MS, Curtis JC, Hellfeld D, Vetter K (2021) Neural network approaches for mobile spectroscopic gamma-ray source detection. J Nucl Eng 2(2):190–206
Kamuda M, Zhao J, Huff K (2020) A comparison of machine learning methods for automated gamma-ray spectroscopy. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect A 954:161385
Khatiwada A, Klasky M, Lombardi M, Matheny J and Mohan A (2023) Machine Learning technique for isotopic determination of radioisotopes using HPGe $\mathrm {\gamma} $-ray spectra. arXiv preprint: arXiv:2301.01415
Bellinger C, Japkowicz N and Drummond C (2015) Synthetic oversampling for advanced radioactive threat detection. In 2015 IEEE 14th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA) (pp. 948–953). IEEE.
Mendes F, Barros M, Vale A, Gonçalves B (2022) Radioactive hot-spot localisation and identification using deep learning. J Radiol Prot 42(1):011516
Daniel G, Ceraudo F, Limousin O, Maier D, Meuris A (2020) Automatic and real-time identification of radionuclides in gamma-ray spectra: a new method based on convolutional neural network trained with synthetic data set. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 67(4):644–653
Elmaghraby EK, Tohamy M, Comsan MNH (2019) Determination of isotopes activity ratio using gamma ray spectroscopy based on neural network model. Appl Radiat Isot 148:19–26
Kamuda M M (2019). Automated isotope identification and quantification using artificial neural networks.
Fayaz J, Medalla M, Torres-Rodas P, Galasso C (2023) A recurrent-neural-network-based generalized ground-motion model for the Chilean subduction seismic environment. Struct Saf 100:102282
Zhan D, Yongqi M, Duan W, Ye M, Song Y, Song Z, Yao K, Sun D, Ding Z (2023) Spatial prediction and mapping of soil water content by TPE-GBDT model in chinese coastal delta farmland with sentinel-2 remote sensing data. Agriculture 13(5):1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051088
Funding
The authors have no affiliation with any organization with a direct or indirect financial interest in the subject matter discussed in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflicts of interest.
Consent for publication
This manuscript has not been submitted to, nor is under review at, another journal or other publishing venue. Co-author has seen and agree with the contents of the manuscript and there is no financial interest to report. We certify that the submission is original work and is not under review at any other publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Paleti, B., Sastry, G.H. Hybrid convolutional neural network approach for optimizing automatic identification of natural isotopes in gamma ray environmental sample spectra. Neural Comput & Applic 36, 19585–19595 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-10221-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-10221-2