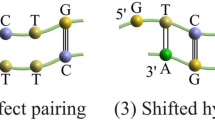
Abstract
Due to its unique properties and excellent sequence design methods, DNA finds wide applications in computing, information storage, molecular circuits, and biological diagnosis. Previous efforts to enhance the efficiency and precision of DNA sequence design have led to the proposal of various universal DNA sequence design methods. These methods optimize the arrangement of the four bases to reduce sequence similarity and meet specific criteria. However, prior investigations have predominantly focused on sequence design within single-scene frameworks, overlooking the complexities associated with designing for multi-scene fusion, such as ion-bridge mismatch, tri-base sequence design, and others. To address this gap, we fused four common scenes and introduced two novel constraint models to facilitate DNA sequence design for multi-scene fusion. Additionally, we developed a dynamic virus spread algorithm as the core for optimizing DNA sequences and evaluated it using 23 well-known benchmark functions. Furthermore, our algorithm outperformed eight popular swarm evolutionary algorithms in eight dominant results. Finally, we simulated the optimization of four distinct scenes, demonstrating that our sequences met expected performance levels in their respective areas. Thus, our work provides a practical tool for designing DNA sequences tailored to various specific applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adleman LM (1994) Molecular computation of solutions to combinatorial problems. Science 266(5187):1021–1024. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7973651
Yang S, Boegels BWA, Wang F, Xu C, Dou HJ, Mann S, Fan CH, de Greef TFA (2024) DNA as a universal chemical substrate for computing and data storage. Nat Rev Chem 8(3):179–194. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-024-00576-4
Chen J, Fu SN, Zhang CY, Liu HY, Su X (2022) DNA logic circuits for cancer theranostics. Small 18(20):2108008. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202108008
Raza MH, Desai S, Aravamudhan S, Zadegan R (2023) An outlook on the current challenges and opportunities in DNA data storage. Biotechnol Adv 66:108155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2023.108155
Yao Y, Liu Y, Liu X, Zhang X, Shi PJ, Zhang XK, Zhang Q, Wei XP (2024) Bubble DNA tweezer: a triple-conformation sensor responsive to concentration-ratios. iScience 27(3):109074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.109074
Xiong XW, Zhu T, Zhu Y, Cao MY, Xiao J, Li L, Wang F, Fan CH, Pei H (2022) Molecular convolutional neural networks with DNA regulatory circuits. Nat Mach Intell 4(7):625–635. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-022-00502-7
Liu SL, Jiang Q, Zhao X, Zhao RF, Wang YN, Wang YM, Liu JB, Shang YX, Zhao S, Wu TT, Zhang YL, Nie GJ, Ding BQ (2021) A DNA nanodevice-based vaccine for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Mater 20(3):421–430. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-020-0793-6
Zhou F, Ni H, Zhu GL, Bershadsky L, Sha RJ, Seeman NC, Chaikin PM (2023) Toward three-dimensional DNA industrial nanorobots. Sci Robot 8(85):eadf1274. https://doi.org/10.1126/scirobotics.adf1274
Todisco M, Ding D, Szostak JW (2024) Transient states during the annealing of mismatched and bulged oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res 52(5):2174–2187. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae091
Hartemink AJ, Gifford DK, Khodor J (1999) Automated constraint based nucleotide sequence selection for DNA computation. Biosystems 52(1–3):227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0303-2647(99)00050-7
Yang GJ, Wang B, Zheng XD, Zhou CJ, Zhang Q (2017) IWO algorithm based on niche crowding for DNA sequence design. Interdiscip Sci 9(3):341–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-016-0160-0
Li X, Wang B, Lv H, Yin Q, Zhang Q, Wei XP (2020) Constraining DNA sequences with a triplet-bases unpaired. IEEE T Nanobiosci 19(2):299–307. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNB.2020.2971644
Zhang Q, Xia X (2013) The quality optimization of DNA sequences with improved genetic algorithm. J Comput Theor Nanos 10(5):1192–1195. https://doi.org/10.1166/jctn.2013.2827
Li X, Wei ZQ, Wang B, Song T (2021) Stable DNA sequence over close-ending and pairing sequences constraint. Front Genet 12:644484. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.644484
Breslauer KJ, Frank R, Blocker HL, Marky A (1986) Predicting DNA duplex stability from the base sequence. P Natl Acad Sci USA 83(11):3746–3750. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.83.11.3746
Zeraati M, Langley DB, Schofield P, Moye AL, Rouet R, Hughes WE, Bryan TM, Dinger ME, Christ D (2018) I-motif DNA structures are formed in the nuclei of human cells. Nat Chem 10:631–637. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-018-0046-3
Zhu DL, Huang ZW, Liao SK, Zhou CJ, Yan SQ, Chen G (2023) Improved bare bones particle swarm optimization for DNA sequence design. IEEE T Nanobiosci 22(3):603–613. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNB.2022.3220795
Liu KQ, Wang B, Lv H, Wei XP, Zhang Q (2019) A BPSON algorithm applied to DNA codes design. IEEE Access 7:88811–88821. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2924708
Yao Y, Ren JK, Bi R, Liu Q (2021) Bacterial foraging algorithm based on activity of bacteria for DNA computing sequence design. IEEE Access 9:2110–2124. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3047469
Yang XW, Zhou CJ (2024) DNA sequences under multiple guanine-cytosine (GC) base pairs constraint. IEEE T Nanobiosci 23(2):252–261. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNB.2023.3316431
Cheng YH, Kuo CN, Lai CM (2016) Effective natural PCR-RFLP primer design for SNP genotyping using teaching–learning-based optimization with elite strategy. IEEE T Nanobiosci 15(7):657–665. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNB.2016.2597867
Zhang X, Xiao WX, Xiao WJ (2020) DeepHE: accurately predicting human essential genes based on deep learning. Plos Comput Biol 16(9):e1008229. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008229
Jiang Z, Shen YY, Liu R (2023) Structure-based prediction of nucleic acid binding residues by merging deep learning- and template-based approaches. Plos Comput Biol 19(9):e1011428. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011428
Zhang C, Ma XY, Zheng XD, Ke YG, Chen KT, Liu DS, Lu ZH, Yang J, Yan H (2022) Programmable allosteric DNA regulations for molecular networks and nanomachines. Sci Adv 8(5):eabl4589. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abl4589
Wei Y, Li BM, Wang X, Duan YX (2014) Magnified fluorescence detection of silver(I) ion in aqueous solutions by using nano-graphite-DNA hybrid and DNase I. Biosens Bioelectron 58:276–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.02.075
Pan LQ, Wang ZY, Li YF, Xu F, Zhang Q, Zhang C (2017) Nicking enzyme-controlled toehold regulation for DNA logic circuits. Nanoscale 9(46):18223–18228. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr06484e
Guo YJ, Yao DB, Zheng B, Sun XB, Zhou X, Wei B, Xiao SY, He M, Li CX, Liang HJ (2020) pH-controlled detachable DNA circuitry and its application in resettable self-assembly of spherical nucleic acids. ACS Nano 14(7):8317–8327. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c02329
Chaves-González JM, Vega-Rodríguez MA (2014) DNA strand generation for DNA computing by using a multi-objective differential evolution algorithm. Biosystems 116:49–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystems.2013.12.005
SantaLucia J, Allawi HT, Seneviratne A (1996) Improved nearest-neighbor parameters for predicting DNA duplex stability. Biochemistry 35(11):3555–3562. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi951907q
Shin SY, Lee IH, Kim DM, Zhang BT (2005) Multiobjective evolutionary optimization of DNA sequences for reliable DNA computing. IEEE T Evolut Comput 9(2):143–158. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2005.844166
Liu F, Ha HD, Han DJ, Seo TS (2013) Photoluminescent graphene oxide microarray for multiplex heavy metal ion analysis. Small 9(20):3410–3414. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201300499
Li MD, Zhao H, Weng XW, Han T (2016) A novel nature-inspired algorithm for optimization: virus colony search. Adv Eng Softw 92:65–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2015.11.004
Al-Betar MA, Alyasseri ZAA, Awadallah MA, Abu Doush I (2020) Coronavirus herd immunity optimizer (CHIO). Neural Comput Appl 33(10):5011–5042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05296-6
Yao Y, Zhang X, Liu X, Liu Y, Zhang X, Zhang Q (2023) Static virus spread algorithm for DNA sequence design. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.02120. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2311.02120
Tellier R, Li YG, Cowling BJ, Tang JW (2019) Recognition of aerosol transmission of infectious agents: a commentary. BMC Infect Dis 19:101. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-019-3707-y
Fine P, Eames K, Heymann DL (2011) "Herd immunity’’: a rough guide. Clin Infect Dis 52(7):911–916. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cir007
Uraki R, Kiso M, Iida S et al (2022) Characterization and antiviral susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2. Nature 607(7917):119–127. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04856-1
Sanjuán R, Domingo-Calap P (2016) Mechanisms of viral mutation. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(23):4433–4448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2299-6
Chu DK, Akl EA, Duda S, Solo K, Yaacoub S, Schunemann HJ (2020) Physical distancing, face masks, and eye protection to prevent person-to-person transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 395(10242):1973–1987. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31142-9
Seyyedabbasi A, Kiani F (2023) Sand cat swarm optimization: a nature-inspired algorithm to solve global optimization problems. Eng Comput-Germany 39(4):2627–2651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-022-01604-x
Zhao WG, Zhang ZX, Wang LY (2020) Manta ray foraging optimization: an effective bio-inspired optimizer for engineering applications. Eng Appl Artif Intel 87:103300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2019.103300
Zhao WG, Wang LY, Zhang ZX (2019) Atom search optimization and its application to solve a hydrogeologic parameter estimation problem. Knowl-Based Syst 163:283–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.08.030
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Grey wolf optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007
Xue JK, Shen B (2020) A novel swarm intelligence optimization approach: sparrow search algorithm. Syst Sci Control Eng 8(1):22–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/21642583.2019.1708830
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2016) The whale optimization algorithm. Adv Eng Softw 95:51–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008
Mirjalili S (2016) SCA: a sine cosine algorithm for solving optimization problems. Knowl-Based Syst 96:120–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2015.12.022
Yao X, Liu Y, Lin GM (1999) Evolutionary programming made faster. IEEE T Evolut Comput 3(2):82–102. https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.771163
Sun AL, Jia FC, Zhang YF, Wang XN (2015) Hybridization-induced Ag(I) dissociation from an immobilization-free and label-free hairpin DNA: toward a novel electronic monitoring platform. Analyst 140(8):2634–2637. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5an00046g
Wang RY, Zhou XH, Shi HC, Luo Y (2016) T-T mismatch-driven biosensor using triple functional DNA-protein conjugates for facile detection of Hg2+. Biosens Bioelectron 78:418–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.11.082
Huang NH, Li RT, Fan C, Wu KY, Zhang Z, Chen JX (2019) Rapid sequential detection of Hg2+ and biothiols by a probe DNA-MOF hybrid sensory system. J Inorg Biochem 197:110690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.04.004
Zhang XK, Zhang Q, Liu Y, Wang B, Zhou SH (2020) A molecular device: a DNA molecular lock driven by the nicking enzymes. Comput Struct Biotec 18:2107–2116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2020.08.004
Qi HJ, Yue SZ, Bi S, Ding CF, Song WL (2018) DNA logic assembly powered by a triplex-helix molecular switch for extracellular pH imaging. Chem Commun 54(61):8498–8501. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cc04615h
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by 111 Project (No. D23006), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62272079), Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (No. 2022-KF-12-14), the Postgraduate Education Reform Project of Liaoning Province (No. LNYJG2022493), the Dalian Outstanding Young Science and Technology Talent Support Program (No. 2022RJ08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human or animal participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (MOV 4215 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Y., Zheng, Y., Cui, S. et al. DNA sequence design model for multi-scene fusion. Neural Comput & Applic 37, 5499–5520 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-10905-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-10905-9