Abstract
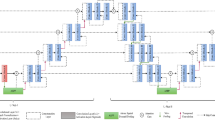
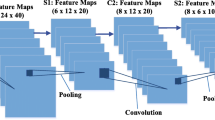
Recently, the introduction of Convolutional Neural Network (CNNs) has advanced the way of solving image segmentation tasks. Semantic image segmentation has considerably benefited from employing various CNN models. The most widely used network in this field is U-Net and its different variations. However, these models require significant number of trainable parameters, floating-point operations per second, and great computational power to be trained. These factors make real-time semantic segmentation in low powered devices very hard. Therefore, in the present paper, we aim to modify particular aspects of the U-Net model to improve its performance through developing a fast U-Net (FU-Net) relying on bottleneck convolution layers in the contraction and expansion paths of the model. The proposed model can be utilized in semantic segmentation applications even on the devices with limited computational power and memory by ensuring the state-of-the-art performance. The amount of memory required by the proposed model is reduced by 23 times when compared with the original U-Net. Moreover, the modifications allowed achieving better performance. In conducted experiments, we assessed the performance of the proposed model on two biomedical image segmentation datasets, namely 2018 Data Science Bowl and ICIS 2018: Skin Lesion Analysis Towards Melanoma Detection. FU-Net demonstrated the state-of-the-art results in biomedical image segmentation, requiring the number of trainable parameters reduced by eight times compared with the original U-Net model. In addition, using bottleneck layers decreased the number of computations, resulting in nearly 30% speed-up at the training, validation and test stages. Furthermore, despite relying on fewer parameters FU-Net achieved a slight improvement of the performance in terms of pixel accuracy, Jaccard index, and dice coefficient evaluation metrics.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Han, C., Duan, Y., Tao, X., Lu, J.: Dense convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Access (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2908685
Florindo, J.B., Lee, Y.-S., Jun, K., et al.: VisGraphNet: a complex network interpretation of convolutional neural features. Inf Sci (Ny) 543, 296–308 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.07.050
Liu, X., Deng, Z., Yang, Y.: Recent progress in semantic image segmentation. Artif. Intell. Rev. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-018-9641-3
Greenhalgh, J., Mirmehdi, M.: Real-time detection and recognition of road traffic signs. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2012.2208909
Maldonado-Bascón, S., Lafuente-Arroyo, S., Gil-Jiménez, P., et al.: Road-sign detection and recognition based on support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2007.895311
Menze, M., Geiger, A.: Object scene flow for autonomous vehicles. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (2015)
Matthaei R, Reschka A, Rieken J, et al.: Autonomous driving. In: Handbook of driver assistance systems: basic information, components and systems for active safety and comfort (2015)
Cohen, A., Rivlin, E., Shimshoni, I., Sabo, E.: Memory based active contour algorithm using pixel-level classified images for colon crypt segmentation. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2014.12.006
Pereira, S., Pinto, A., Alves, V., Silva, C.A.: Brain tumor segmentation using convolutional neural networks in MRI images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2538465
Ibragimov, B., Xing, L.: Segmentation of organs-at-risks in head and neck CT images using convolutional neural networks. Med. Phys. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.12045
Kancherla, K., Mukkamala, S.: Early lung cancer detection using nucleus segementation based features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE symposium on computational intelligence in bioinformatics and computational biology, CIBCB 2013—2013 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence, SSCI 2013 (2013)
Zhou, Y., He, X., Huang, L., et al.: Collaborative learning of semi-supervised segmentation and classification for medical images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (2019)
Wei, S., Wu, W., Jeon, G., et al.: Improving resolution of medical images with deep dense convolutional neural network. Concurr. Comput. 32, 1–11 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.5084
Li, X., Song, D., Leng, S.X.: Link between type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease: From epidemiology to mechanism and treatment. Clin. Interv. Aging 10, 549 (2015)
Liu, F., Chen, L., Lu, L., et al.: Medical image fusion method by using Laplacian pyramid and convolutional sparse representation. Concurr. Comput. 32, 5632 (2019)
Caicedo, J.C., Goodman, A., Karhohs, K.W., et al.: Nucleus segmentation across imaging experiments: the 2018 Data Science Bowl. Nat. Methods (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-019-0612-7
Otsu, N.: Threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. (1979). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076
Malpica, N., De Solórzano, C.O., Vaquero, J.J., et al.: Applying watershed algorithms to the segmentation of clustered nuclei. Cytometry (1997). https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0320(19970801)28:4%3c289::AID-CYTO3%3e3.0.CO;2-7
Chan, T.F., Vese, L.A.: Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Process. (2001). https://doi.org/10.1109/83.902291
Mansouri, B., Housewright, C.D.: The treatment of actinic keratoses—the rule rather than the exception. JAMA Dermatol. 153, 1200 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.3395
Institute NNC: Cancer facts & figures 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 66, 366–367 (2020)
Li, Y., Shen, L.: Skin lesion analysis towards melanoma detection using deep learning network. Sens (Switzerl) (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020556
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) (2015)
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., et al.: Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (2015)
MacQueen, J.: Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In: Proceedings of the fifth Berkeley symposium on mathematical statistics and probability (1967)
Gómez, D.D., Butakoff, C., Ersbøll, B.K., Stoecker, W.: Independent histogram pursuit for segmentation of skin lesions. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2007.910651
Zheng, L., Li, G., Bao, Y.: Improvement of grayscale image 2D maximum entropy threshold segmentation method. In: 2010 international conference on logistics systems and intelligent management, ICLSIM 2010 (2010)
Barghout, L.: Visual taxometric approach to image segmentation using fuzzy-spatial taxon cut yields contextually relevant regions. In: Communications in computer and information science (2014)
Garnavi, R., Aldeen, M., Bailey, J.: Computer-aided diagnosis of melanoma using border- and wavelet-based texture analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITB.2012.2212282
Emre Celebi, M., Wen, Q., Iyatomi, H., et al.: A state-of-the-art survey on lesion border detection in dermoscopy images. Dermoscopy Image Anal. 10, 97–129 (2015)
Drozdzal, M., Vorontsov, E., Chartrand, G., et al.: The importance of skip connections in biomedical image segmentation. In: Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics) (2016)
Yu, L., Chen, H., Dou, Q., et al.: Automated melanoma recognition in dermoscopy images via very deep residual networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2642839
Ibtehaz, N., Rahman, M.S.: MultiResUNet: rethinking the U-Net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural Netw. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2019.08.025
Salido, J.A.A., Ruiz, C.: Using deep learning for melanoma detection in dermoscopy images. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 8, 61–68 (2018). https://doi.org/10.18178/ijmlc.2018.8.1.664
Bisla, D., Choromanska, A., Berman, R.S., et al.: Towards automated melanoma detection with deep learning: Data purification and augmentation. In: IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops (2019)
Smochina, C., Manta, V., Kropatsch, W.: Semantic segmentation of microscopic images using a morphological hierarchy. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) (2011)
Chang, S.W., Liao, S.W.: KUnet: microscopy image segmentation with deep unet based convolutional networks. Conf. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Syst. Man Cybern. 2019, 3561–3566 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/SMC.2019.8914048
Isaksson, J., Arvidsson, I., Aastrom, K., Heyden, A.: Semantic segmentation of microscopic images of H&E stained prostatic tissue using CNN. In: Proceedings of the international joint conference on neural networks (2017)
Minaee, S., Boykov, Y., Porikli, F., et al.: Image segmentation using deep learning: a survey, pp. 1–23 (2020). https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.05566
Shen, D., Wu, G., Suk, H.-I.: Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071516-044442
Rizwan, I., Haque, I., Neubert, J.: Deep learning approaches to biomedical image segmentation. Informatics Med. Unlocked 18, 100297 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2020.100297
Hesamian, M.H., Jia, W., He, X., Kennedy, P.: Deep learning techniques for medical image segmentation: achievements and challenges. J. Dig. Imaging (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-019-00227-x
Ioffe, S., Szegedy, C.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: 32nd international conference on machine learning, ICML 2015 (2015)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (2015)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.L.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: 3rd International conference on learning representations, ICLR 2015—conference track proceedings (2015)
Fu, S., Lu, L., Li, H., Li, Z., Wu, W., Paul, A., Jeon, G., Yang, X.: A real-time super-resolution method based on convolutional neural networks. Circ. Syst. Signal Proc. 39(2), 805–817 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the BK21 Plus project (SW Human Resource Development Program for Supporting Smart Life) funded by the Ministry of Education, School of Computer Science and Engineering, Kyungpook National University, Korea (21A20131600005).
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, OB; data curation, KS; Formal analysis, SD; Funding acquisition, JK; Investigation, AA; Methodology, OB; Project administration, JK; Resources, SK; Software, OB; Validation, AP; Writing—original draft, OB; Writing—review, JK.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olimov, B., Sanjar, K., Din, S. et al. FU-Net: fast biomedical image segmentation model based on bottleneck convolution layers. Multimedia Systems 27, 637–650 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-020-00726-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-020-00726-w