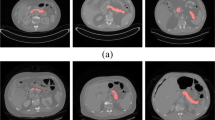
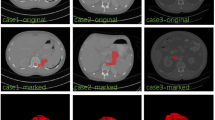
Abstract
Automatic organ segmentation is a prerequisite step for computer-assisted diagnosis (CAD) in clinical application, which can assist in diabetes inspection, organic cancer diagnosis, surgical planning, etc. However, segmenting tiny organs like the pancreas is very challenging. Despite the success of convolutional neural networks (CNN) in automatic pancreas segmentation, the loss of the shape features impedes progress in clinical applications. Therefore, a novel pancreas segmentation network is proposed to extract features in a propagation and fusion manner, named FPF-Net. Firstly, the low-level features and high-level features are combined progressively to preserve and propagate the shape features of the pancreas. Secondly, instead of context-unaware addition or concatenation, we adopt attentional feature fusion (AFF) to alleviate the problems caused by the shape diversity and small size of the pancreas. Finally, a module consisting of Coordinate and multi-scale spatial attention (CMSA) is designed to exploit long-range dependencies and multi-scale spatial features. This module is used to extract salient information for pancreas segmentation. Experimental results validated on two pancreas datasets and a spleen dataset justify the superiority and generalization ability of our method and guarantee the reliability of our approach in clinical application.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, D., Zhang, H., Tang, J., Hua, X.S., Sun, Q.: Self-regulation for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6953–6963 (2021)
Peixoto, S.A., Medeiros, A.G., Hassan, M.M., Dewan, M.A.A., de Albuquerque, V.H.C., Rebouças Filho, P.P.: Floor of log: a novel intelligent algorithm for 3d lung segmentation in computer tomography images. Multimed. Syst. 1–13 (2020)
Tang, W., Zou, D., Yang, S., Shi, J., Dan, J., Song, G.: A two-stage approach for automatic liver segmentation with faster r-cnn and deeplab. Neural Comput. Appl. 32, 6769–78 (2020)
Ali, A.M., Farag, A.A., El-Baz, A.S.: Graph cuts framework for kidney segmentation with prior shape constraints. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 384–392. Springer, New York (2007)
Wang, Z., Bhatia, K.K., Glocker, B., Marvao, A., Dawes, T., Misawa, K., et al.: Geodesic patch-based segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, New York, pp. 666–673 (2014)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3431–3440 (2015)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, New York, pp. 234–241 (2015)
Zhang, D., Zhang, H., Tang, J., Wang, M., Hua, X., Sun, Q.: Feature pyramid transformer. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, New York, pp. 323–339 (2020)
Cai, J., Lu, L., Xie, Y., Xing, F., Yang, L.: Improving deep pancreas segmentation in ctand mri images via recurrent neural contextual learning and direct loss function. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.04912 (2017)
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997)
Oktay, O., Schlemper, J., Folgoc, L.L., Lee, M., Heinrich, M., Misawa, K., et al.: Attention u-net: learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999 (2018)
Roth, H.R., Lu, L., Farag, A., Sohn, A., Summers, R.M.: Spatial aggregation of holistically-nested networks for automated pancreas segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, New York, pp. 451–459 (2016)
Xie, S., Tu, Z.: Holistically-nested edge detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1395–1403 (2015)
Zhou, Y., Xie, L., Shen, W., Wang, Y., Fishman, E.K., Yuille, A.L.: A fixed-point model for pancreas segmentation in abdominal ct scans. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, New York, pp. 693–701 (2017)
Yu, Q., Xie, L., Wang, Y., Zhou, Y., Fishman, E.K., Yuille, A.L.: Recurrent saliency transformation network: incorporating multi-stage visual cues for small organ segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8280–8289 (2018)
Dai, Y., Gieseke, F., Oehmcke, S., Wu, Y., Barnard, K.: Attentional feature fusion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 3560–3569 (2021)
Araújo, R.L., de Araújo, F.H., Silva, R.R.: Automatic segmentation of melanoma skin cancer using transfer learning and fine-tuning. Multimed. Syst. 1–12 (2021)
Liu, Z., Han, K., Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Song, Y., Yao, X., et al.: Automatic liver segmentation from abdominal ct volumes using improved convolution neural networks. Multimed. Syst. 27(1), 111–124 (2021)
Farag, A., Lu, L., Roth, H.R., Liu, J., Turkbey, E., Summers, R.M.: A bottom-up approach for pancreas segmentation using cascaded superpixels and (deep) image patch labeling. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(1), 386–399 (2016)
Xia, Y., Xie, L., Liu, F., Zhu, Z., Fishman, E.K., Yuille, A.L.: Bridging the gap between 2d and 3d organ segmentation with volumetric fusion net. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, New York, pp. 445–453 (2018)
Li, M., Lian, F., Wang, C., Guo, S.: Accurate pancreas segmentation using multi-level pyramidal pooling residual u-net with adversarial mechanism. BMC Med. Imaging 21(1), 1–8 (2021)
Zhu, Z., Xia, Y., Shen, W., Fishman, E., Yuille, A.A.: 3d coarse-to-fine framework for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV). IEEE, pp. 682–690 (2018)
Zhang, D., Zhang, J., Zhang, Q., Han, J., Zhang, S., Han, J.: Automatic pancreas segmentation based on lightweight DCNN modules and spatial prior propagation. Pattern Recognit. 114, 107762 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Wu, J., Liu, Y., Chen, Y., Chen, W., Wu, E.X., et al.: A deep learning framework for pancreas segmentation with multi-atlas registration and 3d level-set. Med. Image Anal. 68, 101884 (2021)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.Y., Kweon, I.S.: Cbam: convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19 (2018)
Hou, Q., Zhou, D., Feng, J.: Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13713–13722 (2021)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Zagoruyko, S., Komodakis, N.: Wide residual networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1605.07146 (2016)
Li, X., Wang, W., Hu, X., Yang, J.: Selective kernel networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 510–519 (2019)
Roth, H.R., Lu, L., Farag, A., Shin, H.C., Liu, J., Turkbey, E.B., et al.: Deeporgan: multi-level deep convolutional networks for automated pancreas segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, New York, pp. 556–564 (2015)
Simpson, A.L., Antonelli, M., Bakas, S., Bilello, M., Farahani, K., Van Ginneken, B., et al.: A large annotated medical image dataset for the development and evaluation of segmentation algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.09063 (2019)
Everingham, M., Van Gool, L., Williams, C.K., Winn, J., Zisserman, A.: The pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 88(2), 303–338 (2010)
Nishio, M., Noguchi, S., Fujimoto, K.: Automatic pancreas segmentation using coarse-scaled 2d model of deep learning: usefulness of data augmentation and deep u-net. Appl. Sci. 10(10), 3360 (2020)
Asaturyan, H., Gligorievski, A., Villarini, B.: Morphological and multi-level geometrical descriptor analysis in CT and MRI volumes for automatic pancreas segmentation. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 75, 1–13 (2019)
Li, M., Lian, F., Guo, S.: Automatic pancreas segmentation using double adversarial networks with pyramidal pooling module. IEEE Access 9, 140965–140974 (2021)
Zheng, H., Chen, Y., Yue, X., Ma, C., Liu, X., Yang, P., et al.: Deep pancreas segmentation with uncertain regions of shadowed sets. Magn. Reson. Imaging 68, 45–52 (2020)
Xie, L., Yu, Q., Zhou, Y., Wang, Y., Fishman, E.K., Yuille, A.L.: Recurrent saliency transformation network for tiny target segmentation in abdominal CT scans. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(2), 514–525 (2019)
Ma, J., Lin, F., Wesarg, S., Erdt, M.: A novel bayesian model incorporating deep neural network and statistical shape model for pancreas segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, New York, pp. 480–487 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFB0804202, 2018YFB0804203), Regional Joint Fund of NSFC (U19A2057), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61876070), Jilin University “Interdisciplinary Integration and Innovation” Young Scholars Free Exploration Project (JLUXKJC2021QZ01), Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan Project (20190303134SF), Anhui University Collaborative Innovation Project Subproject (GXXT-2021-008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Liu, Y. & Shi, Z. FPF-Net: feature propagation and fusion based on attention mechanism for pancreas segmentation. Multimedia Systems 29, 525–538 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-022-00963-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-022-00963-1