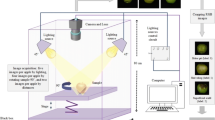
Abstract
The appearance of an object is affected by the color and quality of the light on the surface and the location of the lighting source. Color-balancing methods can solve the problems caused by light changes. Color-balancing models increase the visibility of the image by changing color and clarity. The study aims to examine the images of physiological disorders in apples’ classification performances of images in different light colors with color-balancing models with pre-trained CNN models. Physiological disorders were classified with 0.949 accuracies in the ResNet50V2 model and sharpness data set in the green light color. With the proposed approaches, there was an increase in performance compared to the original data set. The best success in all light colors is in the sharpness data set type. In addition, the quality of the images was measured using MSE, PSNR, and SSIM. PSNR increased in the warm and cold white sharpness data set type and green light CLAHE data set type. Finally, experimental studies have shown that color balancing significantly affects classification success.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abisha, S., Jayasree, T.: Application of image processing techniques and artificial neural network for detection of diseases on brinjal leaf. IETE J. Res. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2019.1696716
Afifi, M., Brown, M.S.: What else can fool deep learning? Addressing color constancy errors on deep neural network performance. Proc. IEEE/CVF Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00033
Akazawa, T., Kinoshita, Y., Kiya, H.: Multi-color balancing for correctly adjusting the intensity of target colors. In: 2021 IEEE 3rd Global Conference on Life Sciences and Technologies (LifeTech), Nara, Japan, 8–12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/LifeTech52111.2021.9391973.
Arici, T., Dikbas, S., Altunbasak, Y.: A histogram modification framework and its application for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 18(9), 1921–1935 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2009.2021548
Bengio, Y.: Practical recommendations for gradient-based training of deep architectures. In: Montavon, G., Orr, G.B., Müller, K.R. (eds.) Neural networks: tricks of the trade, pp. 437–478. Springer, Berlin (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-35289-8_26
Bianco, S., Cusano, C., Napoletano, P., Schettini, R.: Improving CNN-based texture classification by color balancing. J. Imaging 3(3), 33 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging3030033
Bianco, S., Cusano, C., Schettini, R.: Single and multiple illuminant estimation using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(9), 4347–4362 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2713044
Boroumand, M., Fridrich, J.: (2018) Deep learning for detecting processing history of images. Electronic Imaging 7, 213-1–219-9 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2352/ISSN.2470-1173.2018.07.MWSF-213
Bulut, F.: (2022) Değiştirilmiş ayrık haar dalgacık dönüşümü ile yeni bir histogram eşitleme yöntemi. Mühendislik Bilimleri ve Tasarım Dergisi, 10(1): 188–200. https://doi.org/10.21923/jesd.931771
Buyukarikan, B., Ulker, E.: Classification of physiological disorders in apples fruit using a hybrid model based on convolutional neural network and machine learning methods. Neural Comput. Appl. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07350-x
Büyükarıkan, B.: Aydınlatmanın görüntü işleme problemlerine etkisinin yapay zeka teknikleri kullanılarak analizi. Konya Technical University, Konya (2022)
Büyükarıkan, B., Ülker, E.: Using convolutional neural network models illumination estimation according to light colors. Optik 271, 170058 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.170058
Chen, J., Zhang, D., Nanehkaran, Y.A.: Identifying plant diseases using deep transfer learning and enhanced lightweight network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 79(41), 31497–31515 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09669-w
Chen, Y., Yi, H., Liao, C., Huang, P., Chen, Q.: Visual measurement of milling surface roughness based on Xception model with convolutional neural network. Measurement 186, 110217 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110217
Cheng, Y., Pedersen, M., Chen, G.: Evaluation of image quality metrics for sharpness enhancement. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis, 115–120 (2017).
Chollet, F.: Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 1251–1258 (2017).
Cusano, C., Napoletano, P., Schettini, R.: T1K+: a database for benchmarking color texture classification and retrieval methods. Sensors 21(3), 1010 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/s21031010
de Lima, R.P., Duarte, D., Nicholson, C., Slatt, R., Marfurt, K.J.: Petrographic microfacies classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Comput. Geosci. 142, 104481 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2020.104481
Dehesa-González, M., Rosales-Silva, A.J., Gallegos-Funes, F.J., Kinani, J.M.V., Ramos-Díaz, E.: Lighting source classification applied in color images to contrast enhancement. Color. Res. Appl. 45(5), 825–836 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/col.22515
Devlin, K., Chalmers, A., Reinhard, E.: Visual calibration and correction for ambient illumination. ACM Trans. Appl. Percept. (TAP) 3(4), 429–452 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1145/1190036.1190042
Gardner, M.-A., Sunkavalli, K., Yumer, E., Shen, X., Gambaretto, E., Gagné, C., Lalonde, J.-F.: Learning to predict indoor illumination from a single image (2017). arXiv preprint arXiv:170400090
Gasparini, F., Schettini, R.: Color balancing of digital photos using simple image statistics. Pattern Recogn. 37(6), 1201–1217 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2003.12.007
Hariri, M., Avşar, E.: Tipburn disorder detection in strawberry leaves using convolutional neural networks and particle swarm optimization. Multimed. Tools Appl. 81(8), 11795–11822 (2022)
Hayati, M., Muchtar, K., Maulina, N., Syamsuddin, I., Elwirehardja, G.N., Pardamean, B.: Impact of CLAHE-based image enhancement for diabetic retinopathy classification through deep learning. Proc. Comput. Sci. 216, 57–66 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2022.12.111
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In: Computer vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, Proceedings, Part IV 14, 630–645 (2016)
Hegde, R.B., Prasad, K., Hebbar, H., Singh, B.M.K.: Comparison of traditional image processing and deep learning approaches for classification of white blood cells in peripheral blood smear images. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 39(2), 382–392 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2019.01.005
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Van Der Maaten, L., Weinberger, K.Q.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 4700–4708 (2017)
Hussain, M.A., Akbari, A.S.: Color constancy adjustment using sub-blocks of the image. IEEE Access 6, 46617–46629 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2866792
Ince, I.F., Bulut, F., Kilic, I., Yildirim, M.E., Ince, O.F.: Low dynamic range discrete cosine transform (LDR-DCT) for high-performance JPEG image compression. Vis. Comput. 38(5), 1845–1870 (2022)
Iqbal, M., Ali, S.S., Riaz, M.M., Ghafoor, A., Ahmad, A.: Color and white balancing in low-light image enhancement. Optik 209, 164260 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164260
Janowczyk, A., Madabhushi, A.: Deep learning for digital pathology image analysis: a comprehensive tutorial with selected use cases. J. Pathol. Inform. (2016). https://doi.org/10.4103/2153-3539.186902
Jaya, V.L., Gopikakumari, R.: IEM: a new image enhancement metric for contrast and sharpness measurements. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 79(9), 1–9 (2013). https://doi.org/10.5120/13766-1620
Kanabur, V., Harakannanavar, S.S., Purnikmath, V.I., Hullole, P., Torse, D.: Detection of leaf disease using hybrid feature extraction techniques and CNN classifier. Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. Bio Inspired Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-37218-7_127.
Kang, J., Gwak, J.: (2021) Ensemble of multi-task deep convolutional neural networks using transfer learning for fruit freshness classification. Multimed Tools Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11282-4.
Kassani, S.H., Kassani, P.H., Khazaeinezhad, R., Wesolowski, M.J., Schneider, K.A., Deters, R.: Diabetic retinopathy classification using a modified xception architecture. IEEE Int. Symp. Signal Process. Inform. Technol (ISSPIT) 2019, 1–6 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISSPIT47144.2019.9001846
Kaur, M., Kaur, J., Kaur, J.: Survey of contrast enhancement techniques based on histogram equalization. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl (2011). https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2011.020721
Khan, S., Narvekar, M.: Novel fusion of color balancing and superpixel based approach for detection of tomato plant diseases in natural complex environment. J. King Saud Univer. Comput. Inform. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2020.09.006
Kowsari, K., Sali, R., Khan, M.N., Adorno, W., Ali, S.A., Moore, S.R., Amadi, B.C., Kelly, P., Syed, S., Brown, D.E.: Diagnosis of celiac disease and environmental enteropathy on biopsy images using color balancing on convolutional neural networks. Proc. Fut. Technol. Conf. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32520-6_55
Kulkarni, S.G., Kamalapur, S.: Color constancy techniques. Int. J. Eng. Comput. Sci. 3(11), 9147–9150 (2014)
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., Hinton, G.: Deep learning. Nature 521(7553), 436–444 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Liu, J., Wang, X.: Plant diseases and pests detection based on deep learning: a review. Plant Methods 17(1), 1–18 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-021-00722-9
Ma, R., Liao, N., Yan, P., Shinomori, K.: Influences of lighting time course and background on categorical colour constancy with RGB-LED light sources. Color. Res. Appl. 44(5), 694–708 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/col.22392
Ngugi, L.C., Abelwahab, M., Abo-Zahhad, M.: Recent advances in image processing techniques for automated leaf pest and disease recognition–a review. Inform Process. Agric 8(1), 27–51 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inpa.2020.04.004
Pawara, P., Okafor, E., Schomaker, L., Wiering, M.: Data augmentation for plant classification. Int. Conf. Adv. Concepts Intell. Vis. Syst. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70353-4_52
Pedersen, M., Bonnier, N., Hardeberg, J.Y., Albregtsen, F.: Attributes of image quality for color prints. J. Electron. Imaging 19(1), 011016 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.3277145
Pizer, S.M., Amburn, E.P., Austin, J.D., Cromartie, R., Geselowitz, A., Greer, T., ter Haar, R.B., Zimmerman, J.B., Zuiderveld, K.: Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 39(3), 355–368 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0734-189X(87)80186-X
Premaladha, J., Ravichandran, K.: Novel approaches for diagnosing melanoma skin lesions through supervised and deep learning algorithms. J. Med. Syst. 40(4), 1–12 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0460-2
Ragab, D.A., Attallah, O., Sharkas, M., Ren, J., Marshall, S.: A framework for breast cancer classification using multi-DCNNs. Comput. Biol. Med. 131, 104245 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104245
Sachs, J.: Color balancing techniques. Digital Light & Color 1999 (1996).
Setiadi, D.R.I.M.: PSNR vs SSIM: imperceptibility quality assessment for image steganography. Multimed. Tools Appl. 80(6), 8423–8444 (2021)
Sharif, M., Khan, M.A., Iqbal, Z., Azam, M.F., Lali, M.I.U., Javed, M.Y.: Detection and classification of citrus diseases in agriculture based on optimized weighted segmentation and feature selection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 150, 220–234 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2018.04.023
Siddhartha, M., Santra, A.: COVIDLite: A depth-wise separable deep neural network with white balance and CLAHE for detection of COVID-19 (2020). arXiv preprint arXiv:200613873.
Sidorov, O.: Artificial color constancy via GoogleNet with angular loss function. Appl. Artif. Intell. 34(9), 643–655 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/08839514.2020.1730630
Sutskever, I., Martens, J., Dahl, G., Hinton, G.: On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning. In: International conference on machine learning, 1139–1147 (2013)
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., Wojna, Z.: Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2818–2826 (2016)
Tan, Y.M., Chong, R.Q.H., Hargreaves, C.A.: Rheumatoid arthritis: automated scoring of radiographic joint damage. arXiv preprint arXiv:211008812 (2021).
Tao, Y., Chance, L., Liu, B.: Full-scale fruit vision sorting system design-factors and considerations. Proceeding of the food processing automation conference IV, 14–22 (1995).
Thai, B., Deng, G., Ross, R.: A fast white balance algorithm based on pixel greyness. SIViP 11(3), 525–532 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-016-0990-6
Weber, H., Prévost, D., Lalonde, J.-F.: Learning to estimate indoor lighting from 3d objects. In: 2018 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), 199–207 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/3DV.2018.00032.
Xu, B., Liu, J., Hou, X., Liu, B., Qiu, G.: End-to-end illuminant estimation based on deep metric learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 3616–3625 (2020)
Yildirim-Yayilgan, S., Arifaj, B., Rahimpour, M., Hardeberg, J.Y., Ahmedi, L.: Pre-trained CNN based deep features with hand-crafted features and patient data for skin lesion classification. In: Yildirim-Yayilgan S, Bajwa IS, Sanfilippo F (eds) Intelligent Technologies and Application. Springer, pp 151–162 (2021).
Yu, H., Li, X., Lou, Q., Yan, L.: Underwater image enhancement based on color-line model and homomorphic filtering. Signal Image Video Process. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-01960-z
Zhang, B., Huang, W., Li, J., Zhao, C., Fan, S., Wu, J., Liu, C.: Principles, developments and applications of computer vision for external quality inspection of fruits and vegetables: a review. Food Res. Int. 62, 326–343 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.03.012
Funding
This work was supported by the Scientific Research Project at Konya Technical University, Konya, Turkey (No. 201113006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.B.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Implementation, Writing, Review & Editing. E.Ü.: Supervision, Investigation, Writing, Review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants and animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Büyükarıkan, B., Ülker, E. Convolutional neural network-based apple images classification and image quality measurement by light colors using the color-balancing approach. Multimedia Systems 29, 1651–1661 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01084-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01084-z