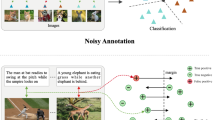
Abstract
Person re-identification (ReID) intends to link people with common identities captured by various cameras spread across a big, fragmented area. Due to the imbalance in the distribution of data between input and output variables and the absence of labeled information in the target domain, cross-domain person re-identification (ReID) is a high demanding assignment. This paper presents a contemporary dual semantic-aligned (DSA) clustering approach, which jointly learns latent semantic subspaces of source and target domains to group target samples. More specifically, we present an innovative subspace learning model which jointly finds intra-domain basis and inter-domain multi-granularity basis. After the subspaces are learned, target samples are correspondingly projected and clustered automatically in each subspace. The clusters allow the model to attribute imaginary labels to the target samples and then impose supervised constraints throughout the training phase. Experiment results on DukeMTMC-reID, Market-1501, and MSMT17 benchmarks validate that our scheme significantly outperformed the state-of-the-art schemes. Our approach obtains performance of 86.82%/63.06% (Duke\(\rightarrow\)Market), 76.3%/58.35% (Market\(\rightarrow\)Duke) and 52.97%/22.44% (Duke\(\rightarrow\)MSMT17) in Rank-1/mAP, correspondingly.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharon, M., Elad, M., Bruckstein, A.: K-svd: an algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans Signal Proc 54(11), 4311–4322 (2006)
Bai Z, Wang Z, Wang J, et al (2021) Unsupervised multi-source domain adaptation for person re-identification. In: CVPR
Cao Z, Simon T, Wei SE, et al (2017) Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In: CVPR
Chang X, Yang Y, Xiang T, et al (2019) Disjoint label space transfer learning with common factorised space. In: AAAI
Chen H, Lagadec B, Bremond F (2021a) Ice: inter-instance contrastive encoding for unsupervised person re-identification. In: ICCV
Chen H, Wang Y, Lagadec B, et al (2021b) Joint generative and contrastive learning for unsupervised person re-identification. In: CVPR
Chen Y, Zhu X, Gong S (2019) Instance-guided context rendering for cross-domain person re-identification. In: ICCV
Cho Y, Kim WJ, Hong S, et al (2022) Part-based pseudo label refinement for unsupervised person re-identification. In: CVPR
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, et al (2009) Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: CVPR
Deng W, Zheng L, Ye Q, et al (2018) Image-image domain adaptation with preserved self-similarity and domain-dissimilarity for person reidentification. In: CVPR
Ester M, Kriegel HP, Sander J, et al (1996) A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters a density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. In: KDD
Fan, H., Zheng, L., Yang, Y.: Unsupervised person re-identification: clustering and fine-tuning. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl 14(4), 1–8 (2018)
Fu Y, Wei Y, Wang G, et al (2019) Self-similarity grouping: a simple unsupervised cross domain adaptation approach for person re-identification. In: ICCV
Goodfellow IJ, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, et al (2014) Generative adversarial nets. In: NeurIPS
Guler RA, Neverova N, Kokkinos I (2018) Densepose: dense human pose estimation in the wild. In: CVPR
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR
Hermans A, Beyer L, Leibe B (2017) In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.07737
Huang H, Yang W, Chen X, et al (2018) Eanet: enhancing alignment for cross-domain person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.11369
Huang Y, Wu Q, Xu J, et al (2019) Sbsgan: suppression of inter-domain background shift for person. In: ICCV
Isobe T, Li D, Tian L, et al (2021) Towards discriminative representation learning for unsupervised person re-identification. In: ICCV
Ji H, Wang L, Zhou S, et al (2021) Meta pairwise relationship distillation for unsupervised person re-identification. In: ICCV
Kalayeh MM, Basaran E, Gokmen M, et al (2018) Human semantic parsing for person re-identification. In: CVPR
Kodirov E, Xiang T, Gong S (2015) Dictionary learning with iterative laplacian regularisation for unsupervised person reidentification. In: BMVC
Li, H., Dong, N., Yu, Z., et al.: Triple adversarial learning and multi-view imaginative reasoning for unsupervised domain adaptation person re-identification. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32(5), 2814–2830 (2022)
Li W, Zhu X, Gong S (2018) Harmonious attention network for person re-identification. In: CVPR
Li YJ, Lin CS, Lin YB, et al (2019) Cross-dataset person re-identification via unsupervised pose disentanglement and adaptation. In: ICCV
Liao S, Hu Y, Zhu X, et al (2015) Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In: CVPR
Lin S, Li H, Li CT, et al (2018) Multi-task mid-level feature alignment network for unsupervised cross-dataset person re-identification. In: BMVC
Lin Y, Xie L, Wu Y, et al (2020) Unsupervised person re-identification via softened similarity learning. In: CVPR
Lisanti, G., Masi, I., Bagdanov, A.D., et al.: Person re-identification by iterative re-weighted sparse ranking. IEEE Trans Patt Analy Mach Intell 37(8), 1629–1642 (2015)
Liu J, Zha ZJ, Chen D, et al (2019) Adaptive transfer network for cross-domain person re-identification. In: CVPR
Long M, Cao Y, Wang J, et al (2015) Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: ICML
Lv J, Chen W, Li Q, et al (2018) Unsupervised cross-dataset person re-identification by transfer learning of spatial-temporal patterns. In: CVPR
Qi L, Wang L, Huo J, et al (2019) A novel unsupervised camera-aware domain adaptation framework for person re-identification. In: ICCV
Qian X, Fu Y, Xiang T, et al (2018) Pose-normalized image generation for person re-identification. In: ECCV
Rubinstein, R., Bruckstein, M.A., et al.: Dictionaries for sparse representation modeling. Proc IEEE 98(6), 1045–1057 (2010)
Song L, Wang C, Zhang L, et al (2018) Unsupervised domain adaptive re-identification: theory and practice. arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.11334
Su C, Zhang S, Xing J, et al (2016) Deep attributes driven multi-camera person re-identification. In: ECCV
Sun B, Saenko K (2016) Deep coral: correlation alignment for deep domain adaptation. In: ECCV
Torralba A, Efros AA (2011) Unbiased look at dataset bias. In: CVPR
Verma A, Subramanyam AV, Wang Z, et al (2021) Unsupervised domain adaptation for person re-identification via individual-preserving and environmental-switching cyclic generation. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia. vol. 25, pp. 364–377
Wang D, Zhang S (2020) Unsupervised person re-identification via multi-label classification. In: CVPR
Wang G, Lai JH, Liang W, et al (2020) Smoothing adversarial domain attack and p-memory reconsolidation for cross-domain person re-identification. In: CVPR
Wang J, Zhu X, Gong S, et al (2018) Transferable joint attribute-identity deep learning for unsupervised person re-identification. In: CVPR
Wei L, Zhang S, Gao W, et al (2018) Person transfer gan to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. In: CVPR
Xuan S, Zhang S (2021) Intra-inter camera similarity for unsupervised person re-identification. In: CVPR
Yang, F., Yan, K., Lu, S., et al.: Attention driven person re-identification. Patt Recogn 86, 143–155 (2019)
Yang F, Zhong Z, Luo Z, et al (2021a) Joint noise-tolerant learning and meta camera shift adaptation for unsupervised person re-identification. In: CVPR
Yang F, Zhong Z, Luo Z, et al (2021b) Joint noise-tolerant learning and meta camera shift adaptation for unsupervised person re-identification. In: CVPR
Yang Q, Yu HX, Wu A, et al (2019b) Patch-based discriminative feature learning for unsupervised person re-identification. In: CVPR
Yu HX, Wu A, Zheng WS (2017) Cross-view asymmetric metric learning for unsupervised person re-identification. In: ICCV
Yu HX, Zheng WS, Wu A, et al (2019) Unsupervised person re-identification by soft multilabel learning. In: CVPR
Zeng K, Ning M, Wang Y, et al (2020) Hierarchical clustering with hard-batch triplet loss for person re-identification. In: CVPR
Zhang, H., Cao, H., Yang, X., et al.: Self-training with progressive representation enhancement for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Proc 30, 5287–5298 (2021)
Zhang X, Cao J, Shen C, et al (2019) Self-training with progressive augmentation for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification. In: ICCV
Zhang X, Li D, Wang Z, et al (2022) Implicit sample extension for unsupervised person re-identification. In: CVPR
Zheng L, Shen L, Tian L, et al (2015) Scalable person re-identification: a benchmark. In: ICCV
Zheng Z, Zheng L, Yang Y (2017) Unlabeled samples generated by gan improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In: ICCV
Zhong Z, Zheng L, Li S, et al (2018) Generalizing a person retrieval model hetero- and homogeneously. In: ECCV
Zhong Z, Zheng L, Luo Z, et al (2019a) Invariance matters: exemplar memory for domain adaptive person re-identification. In: CVPR
Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Zheng, Z., et al.: Camstyle: a novel data augmentation method for person re-identification. IEEE Trans Image Proc 28(3), 1176–1190 (2019)
Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Luo, Z., et al.: Learning to adapt invariance in memory for person re-identification. IEEE Trans Patt Analy Mach Intell 43(8), 2723–2738 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Macao Science and Technology Development Fund Project under contract No.0005/2021/AIR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors discussed the idea of the this work, as well as revised and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Liu, Y., Liu, Q. et al. Dual semantic-aligned clustering for cross-domain person re-identification. Multimedia Systems 29, 2351–2362 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01111-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01111-z