Abstract
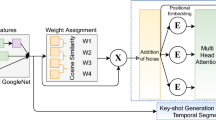
Video summarization deals with the generation of a condensed version of a video by retaining the important information while eliminating redundant data. The performance of video summarization models depends upon the critical task of capturing contextual and temporal information among video frames. This paper presents a supervised Two-stage Attention augmented Fully Convolutional Network for SUMmarization (TAFCN-SUM) model, which exploits separate attention mechanisms to capture the importance of frames at different stages of frame sequence representations. At the first stage, position-aware multi-head attention is employed to learn multiple attentions by densely querying all frames in the sequence. Further, the second-stage attention, embedded inside a fully convolutional network, is applied to model contextual information from temporally encoded frames. In addition, this study also proposes a novel modified tangent loss function that penalizes misclassifications, especially from under-representative classes, heavily. Thus, it provides faster and more stable learning while addressing the class-imbalance issue of the dataset. The experimental study, on benchmark datasets SumMe and TvSum, indicates that the proposed modified tangent loss improves results by up to 4.7% and 0.8% for both datasets, respectively. The proposed model TAFCN-SUM achieves 51.5% and 60.3% score on the SumMe and TvSum datasets, respectively, which is comparable to or superior to the existing state-of-the-art approaches.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
In the present study, all experiments are carried out by utilizing two video summarization datasets named SumMe [10] and TvSum [18]. Both datasets are publicly available at web links:https://gyglim.github.io/me/vsum/index.html and http://people.csail.mit.edu/yalesong/tvsum/, respectively.
References
Srinivas, M., Pai, M.M.M., Pai, R.M.: An improved algorithm for video summarization: a rank based approach. Proced. Comput. Sci. 89, 812–819 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2016.06.065
De Avila, S.E.F., Lopes, A.P.B., Da Luz, A., De Albuquerque Araújo, A.: VSUMM: a mechanism designed to produce static video summaries and a novel evaluation method. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 32(1), 56–68 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2010.08.004
Furini, M., Geraci, F., Montangero, M., Pellegrini, M.: STIMO: STIll and MOving video storyboard for the web scenario. Multimed. Tools Appl. 46(1), 47–69 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-009-0307-7
Gong, B., Chao, W.L., Grauman, K., Sha, F.: Diverse sequential subset selection for supervised video summarization. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 3, 2069–2077 (2014)
Viguier, R., et al.: Automatic video content summarization using geospatial mosaics of aerial imagery. Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Multimed. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISM.2015.124
Lu, Z., Grauman, K.: Story-driven summarization for egocentric video. Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.350
Zhang, K., Chao, W.L., Sha, F., Grauman, K.: Video summarization with long short-term memory. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), vol 9911. Springer (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46478-7_47
Zhang, Y., Zhao, X., Kampffmeyer, M., Tan, M.: DTR-GAN: dilated temporal relational adversarial network for video summarization. ACM Int. Conf. Proc. Ser. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3321408.3322622
Wei, H., Ni, B., Yan, Y., Yu, H., Yang, X.: Video summarization via semantic attended networks. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 32(1), 216–223 (2018)
Gygli, M., Grabner, H., Riemenschneider, H., Van Gool, L.: Creating summaries from user videos. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), vol 8695, pp. 505–520. Springer (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10584-0_33
Zhao, B., Li, X., Lu, X.: Hierarchical recurrent neural network for video summarization. Proc. ACM Multimed. Conf. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3123266.3123328
Zhao, B., Li, X., Lu, X.: HSA-RNN: hierarchical structure-adaptive RNN for video summarization. Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00773
Ji, Z., Xiong, K., Pang, Y., Li, X.: Video summarization with attention-based encoder-decoder networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 30(6), 1709–1717 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2904996
Mahasseni, B., Lam, M., Todorovic, S.: Unsupervised Video Summarization with Adversarial LSTM Networks. Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 202–211 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.318
Rochan, M., Ye, L., Wang, Y.: Video summarization using fully convolutional sequence networks. Proc. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis. (ECCV) (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01258-8_22
Liang, G., Lv, Y., Li, S., Zhang, S., Zhang, Y.: Unsupervised video summarization with a convolutional attentive adversarial network. arXiv preprint, pp. 1–26. http://arxiv.org/abs/2105.11131 (2021)
Ejaz, N., Mehmood, I., Baik, S.W.: Efficient visual attention based framework for extracting key frames from videos. Signal Process. 28(1), 34–44 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.image.2012.10.002
Song, Y., Vallmitjana, J., Stent, A., Jaimes, A.: TVSum: summarizing web videos using titles. Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 07, 5179–5187 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299154
Lee, Y.J., Ghosh, J., Grauman, K.: Discovering important people and objects for egocentric video summarization. Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247820
Etezadifar, P., Farsi, H.: Scalable video summarization via sparse dictionary learning and selection simultaneously. Multimed. Tools Appl. 76(6), 7947–7971 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3433-z
Cai, S., Zuo, W., Davis, L.S., Zhang, L.: Weakly-supervised video summarization using variational encoder-decoder and web prior. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 184–200. Springer (2018)
Zhou, K., Qiao, Y., Xiang, T.: Deep reinforcement learning for unsupervised video summarization with diversity-representativeness reward. In: 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI, pp. 7582–7589 (2018)
Apostolidis, E., Metsai, A.I., Adamantidou, E., Mezaris, V., Patras, I.: A stepwise, label-based approach for improving the adversarial training in unsupervised video summarization. Proc. First Int. Worksh. AI Smart TV Content Prod. Access Deliv (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3347449.3357482
Chen, Y., Tao, L., Wang, X., Yamasaki, T.: Weakly supervised video summarization by hierarchical reinforcement learning. First ACM Int. Conf. Multimed. Asia (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3338533.3366583
Fu, T.J., Tai, S.H., Chen, H.T.: Attentive and adversarial learning for video summarization. Proc. IEEE Winter Conf. Appl. Comput. Vis. WACV (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV.2019.00173
Zhang, K., Grauman, K., Sha, F.: Retrospective encoders for video summarization. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), vol 11212, pp. 391–408. Springer (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01237-3_24
Fajtl, J., Sokeh, H.S., Argyriou, V., Monekosso, D., Remagnino, P.: Summarizing videos with attention. In: Ch, M. (ed.) Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), pp. 39–54. Springer (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-21074-8_4
Zhong, S.H., Wu, J., Jiang, J.: Video summarization via spatio-temporal deep architecture. Neurocomputing 332, 224–235 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.12.040
Ji, Z., Zhao, Y., Pang, Y., Li, X., Han, J.: Deep attentive video summarization with distribution consistency learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(4), 1765–1775 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2991083
Zhao, B., Li, X., Lu, X.: Property-constrained dual learning for video summarization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(10), 3989–4000 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2951680
Zhao, B., Li, H., Lu, X., Li, X.: Reconstructive sequence-graph network for video summarization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 8828, 1–10 (2021)
Vaswani, A., et al.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 5998–6008. Springer (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/2943.974352
Zhang, H., Goodfellow, I., Metaxas, D., Odena, A.: Self-attention generative adversarial networks. Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. 2019, 12744–12753 (2019)
Li, S., Chen, Z., Lu, J., Li, X., Zhou, J.: Neighborhood preserving hashing for scalable video retrieval. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00830
Zhang, Y., Li, K., Li, K., Zhong, B., Fu, Y.: Residual non-local attention networks for image restoration. In: 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR, pp. 1–18 (2019)
Szegedy, C., et al.: Going deeper with convolutions. Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594
Zhang, Y., Qiu, Z., Yao, T., Liu, D., Mei, T.: Fully convolutional adaptation networks for semantic segmentation. Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00712
Potapov, D., et al.: Category-specific video summarization. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 540–555. Springer, Cham (2014)
Friedman, J., Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R.: A note on the group lasso and a sparse group lasso. arXiv , pp. 1–8. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1001.0736.pdf (2010)
Jung, Y., Cho, D., Kim, D., Woo, S., Kweon, I.S.: Discriminative feature learning for unsupervised video summarization. In: 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI 2019, 31st Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference, IAAI 2019 and the 9th AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, EAAI 2019, pp. 8537–8544. Springer (2019). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33018537
Zhang, X., Lu, W., Pan, Y., Wu, H., Wang, R., Yu, R.: Empirical study on tangent loss function for classification with deep neural networks. Comput. Electr. Eng. 90, 107000 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2021.107000
Paszke, A., et al.: “PyTorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol 32. NeurIPS (2019)
Zhong, S., Lin, J., Lu, J., Science, C.: Deep semantic and attentive network for unsupervised video summarization. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 18(2), 21 (2022)
Lin, J., Zhong, S., Fares, A.: Deep hierarchical LSTM networks with attention for video. Comput. Electr. Eng. 97, 107618 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2021.107618
Liu, T., Meng, Q., Huang, J.J., Vlontzos, A., Rueckert, D., Kainz, B.: Video summarization through reinforcement learning with a 3D spatio-temporal U-Net. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 1573–1586 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2022.3143699
Ma, M., Mei, S., Wan, S., Wang, Z., Hua, X.S., Feng, D.D.: Graph convolutional dictionary selection with L2, p Norm for video summarization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 1789–1804 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2022.3146012
Feng, S., Xie, Y., Wei, Y., Yan, J., Wang, Q.: Transformer-based video summarization with spatial-temporal representation. In: BigDIA, pp. 428–433 (2022)
Li, H., Ke, Q., Gong, M., Drummond, T.: Progressive video summarization via multimodal self-supervised learning. Proc. IEEE Winter Conf. Appl. Comput. Vis. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV56688.2023.00554
Chu, X., Tian, Z., Zhang, B., Wang, X., Shen, C.: Conditional positional encodings for vision transformers, pp. 1–19. http://arxiv.org/abs/2102.10882 (2021)
Otani, M., Nakashima, Y., Rahtu, E., Heikkila, J.: Rethinking the evaluation of video summaries. Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00778
Kendall, M.G.: The treatment of ties in ranking problems. Biometrika 33, 239–251 (1945). https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/33.3.239
Funding
This research work is supported by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeITy), Government of India, New Delhi, India through the Visvesvaraya Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Deeksha Gupta wrote the main manuscripts and prepared the figures. Akashdeep Sharma supervised the research work. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by J. Gao.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, D., Sharma, A. A two-stage attention augmented fully convolutional network-based dynamic video summarization. Multimedia Systems 29, 3685–3701 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01154-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01154-2