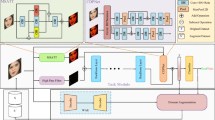
Abstract
Nowadays, numerous synthesized images and videos generated by facial manipulated techniques have become an emerging problem, which promotes facial manipulation detection to be a significant topic. Much concern about the use of synthesized facial digital contents in society is rising due to their deceptive nature and widespread. To detect such manipulated facial digital contents, many methods have been proposed. Most detection methods focus on specific datasets. It is hard for them to detect facial images or videos manipulated by unknown face synthesis algorithms. In this paper, we propose a method to improve the generalization ability of the facial manipulation detection model using one-class domain generalization. We shape the problem into domain generalization. We divide the dataset into several domains according to different manipulation algorithms. We also try to process the images from the perspective of frequency domain. We utilize two-dimensional wavelet transform to preprocess the images to ensure the effect on compressed images. The results of experiments implemented on FaceForensics++ dataset exceed the baselines and recent works. The feature visualization analyses intuitively show that our method can learn robust feature representation that can be generalized to unseen domains.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Akhtar, N., Mian, A.: Threat of adversarial attacks on deep learning in computer vision: a survey. IEEE Access 6, 14410–14430 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2807385
Aneja, S., Nießner, M.: Generalized zero and few-shot transfer for facial forgery detection, (2020). arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.11863. Accessed 30 Nov 2021
Chollet, F.: Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1800–1807 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.195
Chu, X., Jin, Y., Zhu, W., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, S., Mei, H.: DNA: domain generalization with diversified neural averaging. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 162, pp. 4010–4034 (2022)
Dang, H., Liu, F., Stehouwer, J., Liu, X., Jain, A.K.: On the detection of digital face manipulation. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 5780–5789 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00582
Dolhansky, B., Howes, R., Pflaum, B., Baram, N., Ferrer, C.C.: The deepfake detection challenge (dfdc) preview dataset (2019). arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.08854. Accessed 30 Nov 2021
Durall, R., Keuper, M., Keuper, J.: Watch your up-convolution: Cnn based generative deep neural networks are failing to reproduce spectral distributions. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7887–7896 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00791
Frank, J., Eisenhofer, T., Schönherr, L., Fischer, A., Kolossa, D., Holz, T.: Leveraging frequency analysis for deep fake image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 119, pp. 3247–3258 (2020)
Ganin, Y., Lempitsky, V.: Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropagation. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 37, pp. 1180–1189 (2015)
Ganin, Y., Ustinova, E., Ajakan, H., Germain, P., Larochelle, H., Laviolette, F., Marchand, M., Lempitsky, V.: Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 17(1), 2096–2130 (2016)
Geirhos, R., Rubisch, P., Michaelis, C., Bethge, M., Wichmann, F.A., Brendel, W.: Imagenet-trained cnns are biased towards texture; increasing shape bias improves accuracy and robustness, (2018). arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.12231. Accessed 15 Sept 2022
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., Bengio, Y.: Generative adversarial nets. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 27, 1–9 (2014)
Huang, Y., Juefei-Xu, F., Wang, R., Xie, X., Ma, L., Li, J., Miao, W., Liu, Y., Pu, G.: Fakelocator: robust localization of gan-based face manipulations via semantic segmentation networks with bells and whistles, (2020). arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.09598. Accessed 15 Sept 2022
Jung, T., Kim, S., Kim, K.: Deepvision: deepfakes detection using human eye blinking pattern. IEEE Access 8, 83144–83154 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988660
Karras, T., Aila, T., Laine, S., Lehtinen, J.: Progressive growing of gans for improved quality, stability, and variation, (2017). arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10196. Accessed 20 Oct 2022
Karras, T., Laine, S., Aila, T.: A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(12), 4217–4228 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2970919
Karras, T., Laine, S., Aittala, M., Hellsten, J., Lehtinen, J., Aila, T.: Analyzing and improving the image quality of stylegan. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 8107–8116 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00813
Kim, D.-K., Kim, D., Kim, K.: Facial manipulation detection based on the color distribution analysis in edge region, (2021). arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.01381. Accessed 20 Oct 2022
King, D.E.: Dlib-ml: a machine learning toolkit. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 10, 1755–1758 (2009)
Kowalski, M.: Faceswap, (2018). https://github.com/marekkowalski/faceswap
Li, Y., Yang, X., Sun, P., Qi, H., Lyu, S.: Celeb-df: a large-scale challenging dataset for deepfake forensics. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3204–3213 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00327
Liu, D., Dang, Z., Peng, C., Zheng, Y., Li, S., Wang, N., Gao, X.: Fedforgery: generalized face forgery detection with residual federated learning, (2022). arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.09563. Accessed 20 Oct 2022
Liu, Z., Qi, X., Torr, P.H.S.: Global texture enhancement for fake face detection in the wild. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 8057–8066 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00808
Matern, F., Riess, C., Stamminger, M.: Exploiting visual artifacts to expose deepfakes and face manipulations. In: 2019 IEEE Winter Applications of Computer Vision Workshops (WACVW), pp. 83–92 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACVW.2019.00020
Pu, Y., Gan, Z., Henao, R., Yuan, X., Li, C., Stevens, A., Carin, L.: Variational autoencoder for deep learning of images, labels and captions. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 29, 1–9 (2016)
Rangwani, H., Aithal, S.K., Mishra, M., Jain, A., Radhakrishnan, V.B.: A closer look at smoothness in domain adversarial training. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning, vol. 162, pp. 18378–18399, (2022)
Rössler, A., Cozzolino, D., Verdoliva, L., Riess, C., Thies, J., Niessner, M.: Faceforensics++: learning to detect manipulated facial images. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 1–11 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00009
Sun, K., Liu, H., Ye, Q., Gao, Y., Liu, J., Shao, L., Ji, R.: Domain general face forgery detection by learning to weight. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol. 35, pp. 2638–2646 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v35i3.16367
Suwajanakorn, S., Seitz, S.M., Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I.: Synthesizing obama: learning lip sync from audio. ACM Trans. Graph. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3072959.3073640
Thies, J., Zollhöfer, M., Nießner, M.: Deferred neural rendering: image synthesis using neural textures. ACM Trans. Graph. 10(1145/3306346), 3323035 (2019)
Thies, J., Zollhöfer, M., Stamminger, M., Theobalt, C., Nießner, M.: Face2face: real-time face capture and reenactment of rgb videos. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2387–2395 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.262
Tolosana, R., Vera-Rodriguez, R., Fierrez, J., Morales, A., Ortega-Garcia, J.: Deepfakes and beyond: a survey of face manipulation and fake detection. Inf. Fusion 64, 131–148 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2020.06.014
Tora, M.: Deepfakes, (2018). https://github.com/deepfakes/faceswap/tree/v2.0.0
Tran, V.-N., Kwon, S.-G., Lee, S.-H., Le, H.-S., Kwon, K.-R.: Generalization of forgery detection with meta deepfake detection model. IEEE Access 11, 535–546 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3232290
Van Der Maaten, L.: Barnes-hut-sne, (2013). arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10196. Accessed 15 Apr 2021
Yu, P., Fei, J., Xia, Z., Zhou, Z., Weng, J.: Improving generalization by commonality learning in face forgery detection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 17, 547–558 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2022.3146781
Zhang, X., Karaman, S., Chang, S.-F.: Detecting and simulating artifacts in gan fake images. In: 2019 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), pp. 1–6, (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/WIFS47025.2019.9035107
Zhang, X., Wang, S., Liu, C., Zhang, M., Liu, X., Xie, H.: Thinking in patch: towards generalizable forgery detection with patch transformation. In: Duc Nghia Pham, Thanaruk Theeramunkong, Guido Governatori, and Fenrong Liu, editors, PRICAI 2021: Trends in Artificial Intelligence, pp. 337–352, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89370-5_25
Zhao, H., Wei, T., Zhou, W., Zhang, W., Chen, D., Yu, N.: Multi-attentional deepfake detection. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2185–2194, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00222
Zhou, P., Han, X., Morariu, V.I., Davis, L.S.: Two-stream neural networks for tampered face detection. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp. 1831–1839, (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2017.229
Zhu, J.-Y., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 2242–2251, (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.244
Zhuang, W., Chu, Q., Tan, Z., Liu, Q., Yuan, H., Miao, C., Luo, Z., Yu, N.: Uia-vit: unsupervised inconsistency-aware method based on vision transformer for face forgery detection. In: S. Avidan, G. Brostow, M. Cissé, G. Maria Farinella, T. Hassner, editors, Computer Vision – ECCV 2022, pp. 391–407, (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20065-6_23
Zhuang, W., Chu, Q., Yuan, H., Miao, C., Liu, B., Yu, N.: Towards intrinsic common discriminative features learning for face forgery detection using adversarial learning. In: 2022 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), pp. 1–6, (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME52920.2022.9859586
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Research Center of Security Video and Image Processing Engineering Technology of Guizhou (China) under Grant SRC-Open Project ([2020]001]).
Funding
This article is funded by Research Center of Security Video and Image Processing Engineering Technology of Guizhou (China) under Grant SRC-Open Project [2020]001]: Pengxiang Xu, Zhiyuan Ma, Xue Mei.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Huang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, P., Ma, Z., Mei, X. et al. Detecting facial manipulated images via one-class domain generalization. Multimedia Systems 30, 33 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01214-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01214-7