Abstract
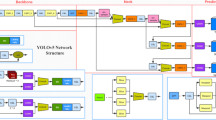
Existing occluded pedestrian re-identification methods mainly utilize convolutional neural networks to realize the feature matching under different camera perspectives. Due to the complex occlusion situation, the accuracy of occluded pedestrian re-identification is not so satisfied where convolutional neural networks are utilized to extract local features. Convolutional neural network is unique in its ability to capture local features, but its global modeling ability is weak. In contrast, Vision Transformer (ViT) can efficiently extract global features from shallow layers with more spatial information and obtain intermediate features with high quality. To deal with the above issues, ViT is here introduced into the residual network to construct a dual-branch hybrid network of residual network and visual converter (DB-ResHViT), where the ViT branch is utilized to reduce training errors, while the residual-ViT branch is utilized to construct the global correlation of feature sequences extracted by the residual network. The proposed network proposes a novel data augmentation module, called partial image patch pre-convolution module (PPPC), which is utilized to input the extracted partial image patches into the pre-convolution network to replace the original image patches to achieve the goal of introducing local features into the ViT branch. In addition, the proposed network designs a novel module integrating residual and mobile vision transformer, called RMV Module, which is utilized to establish the global correlation of local features extracted by the residual network to achieve the goal of reducing the computational cost and improve the re-identification accuracy. Experimental results of a large number of occluded pedestrian re-identification datasets demonstrate that the performance of the proposed method is superior to other advanced methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
This declaration is not applicable.
References
Zheng, L., Yang, Yi., Hauptmann, A.G.: Person re-identification: past, present and future. CoRR 16(10), 1–20 (2016)
He Li, Mang Ye, Cong Wang, and Bo Du. Pyramidal Transformer with Conv-Patchify for Person Re-identification. ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2022: 7317–7326.
Chen, C., Ye, M., Qi, M., Jingjing, Wu., Jiang, J., Lin, C.: Structure-aware positional transformer for visible-infrared person re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 2352–2364 (2022)
Tao, H., Duan, Q., An, J.: An adaptive interference removal framework for video person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 33(9), 5148–5159 (2023)
Tao, H., Bao, W., Duan, Q., Zhenwu, Hu., An, J., Xie, C.: An improved interaction and aggregation network for person re-identification. Multimedia Tools Applications 82(28), 44053–44069 (2023)
Duan, Q., Zhenwu, Hu., Minghao, Lu., Tao, H.: Learning discriminative features for person re-identification via multi-spectral channel attention. Signal Image Video Process 7(6), 3019–3026 (2023)
Huang, P., Zhu, S., Liang, Z.: Cross-modal pedestrian recognition based on triple attention feature aggregation. J Nanjing Univer Posts Telecommun 41(5), 101–112 (2021)
Xiaofu, Wu., Yin, Z., Song, Y., Zhang, L., Xie, B., Zhao, S., Zhang, S.: Progress in the construction of multi-branch deep neural network for pedestrian recognition diversity feature mining. J Nanjing Univer Posts Telecommun 41(1), 78–85 (2021)
Wenjie Luo, Yujia Li, Raquel Urtasun, and Richard S. Zemel:. Understanding the Effective Receptive Field in Deep Convolutional Neural Networks[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2016: 4898–4906.
Shijie Wang, Zhihui Wang, Haojie Li, Jianlong Chang, Wanli Ouyang, and Qi Tian. Accurate Fine-grained Object Recognition with Structure-driven Relation Graph Networks. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2023.
Shijie Wang, Jianlong Chang, Zhihui Wang, Haojie Li, Wanli Ouyang, and Qi Tian. Fine-Grained Retrieval Prompt Tuning. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2023: 2644–2652.
Shijie Wang, Jianlong Chang, Haojie Li, Zhihui Wang, Wanli Ouyang, and Qi Tian. Open-Set Fine-Grained Retrieval via Prompting Vision-Language Evaluator. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2023: 19381–19391.
Tao Wang, Hong Liu, Pinhao Song, Tianyu Guo, and Wei Shi. Pose-Guided Feature Disentangling for Occluded Person Re-Identification Based on Transformer. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2022: 2540–2549.
Boqiang, Xu., He, L., Liang, J., Sun, Z.: Learning feature recovery transformer for occluded person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 4651–4662 (2022)
Wenfeng Liu, Xudong Wang, Lei Tan, Yan Zhang, Pingyang Dai, Yongjian Wu, and Rongrong Ji. Learning Occlusion Disentanglement with Fine-grained Localization for Occluded Person Re-identification. ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2023: 6462–6471.
Zhikang Wang, Feng Zhu, Shixiang Tang, Rui Zhao, Lihuo He, and Jiangning Song. Feature Erasing and Diffusion Network for Occluded Person Re-Identification. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022: 4744–4753.
Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N. Gomez, Lukasz Kaiser, and Illia Polosukhin. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2017: 5998–6008.
Zhizheng Zhang, Cuiling Lan, Wenjun Zeng, Xin Jin, and Zhibo Chen. Relation-aware global attention for person re-identification[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 3186–3195.
Xuesong Chen, Canmiao Fu, Yong Zhao, Feng Zheng, Jingkuan Song, Rongrong Ji, and Yi Yang. Salience-guided cascaded suppression network for person re-identification. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 3300–3310.
Guiwei Zhang, Yongfei Zhang, Tianyu Zhang, Bo Li, and Shiliang Pu. PHA: Patch-Wise High-Frequency Augmentation for Transformer-Based Person Re-Identification. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2023: 14133–14142.
Haocong Rao and Chunyan Miao. TranSG: Transformer-Based Skeleton Graph Prototype Contrastive Learning with Structure Trajectory Prompted Reconstruction for Person Re-Identification. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2023: 22118–22128.
Shang Gao, Jingya Wang, Huchuan Lu, and Zimo Liu. Pose-guided visible part matching for occluded person ReID. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 11744–11752.
Guanan Wang, Shuo Yang, Huanyu Liu, Zhicheng Wang, Yang Yang, Shuliang Wang, Gang Yu, Erjin Zhou, and Jian Sun. High-order information matters: Learning relation and topology for occluded person re-identification. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 6449–6458.
Yang, J., Zhang, C., Tang, Y., Li, Z.: PAFM: pose-drive attention fusion mechanism for occluded person re-identification. Neural Comput. Appl. 34(10), 8241–8252 (2022)
Li, Y., Yang, Z., Chen, Y., Yang, D., Liu, R., Jiao, L.: Occluded person re-identification method based on multiscale features and human feature reconstruction. IEEE Access 10, 98584–98592 (2022)
Zhang, G., Chen, C., Chen, Y., Zhang, H., Zheng, Y.: Fine-grained-based multi-feature fusion for occluded person re-identification. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 87, 103581 (2022)
Alexey Dosovitskiy, Lucas Beyer, Alexander Kolesnikov, Dirk Weissenborn, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Unterthiner, Mostafa Dehghani, Matthias Minderer, Georg Heigold, Sylvain Gelly, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021: 1–12.
Hugo Touvron, Matthieu Cord, Matthijs Douze, Francisco Massa, Alexandre Sablayrolles, and Hervé Jégou. Training data-efficient image transformers and distillation through attention. International Conference on Machine Learning, 2021: 10347–10357.
Shuting He, Hao Luo, Pichao Wang, Fan Wang, Hao Li, and Wei Jiang. Transreid: Transformer-based object re-identification. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision, 2021: 14993–15002.
Jiaxuan Zhuo, Zeyu Chen, Jianhuang Lai, and Guangcong Wang. Occluded Person Re-identification. IEEE Conference on Multimedia and Expo, 2018: 1–6.
Jiaxu Miao, Yu Wu, Ping Liu, Yuhang Ding, and Yi Yang. Pose-Guided Feature Alignment for Occluded Person Re-Identification. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019: 542–551.
Liang Zheng, Liyue Shen, Lu Tian, Shengjin Wang, Jingdong Wang, and Qi Tian. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision, 2015: 1116–1124.
Ergys Ristani, Francesco Solera, Roger S. Zou, Rita Cucchiara, and Carlo Tomasi. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. European conference on computer vision, 2016: 17–35.
Weishi Zheng, Xiang Li, Tao Xiang, Shengcai Liao, Jianhuang Lai, and Shaogang Gong. Partial person re-identification[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision, 2015: 4678–4686.
Lingxiao He, Jian Liang, Haiqing Li, and Zhenan Sun. Deep spatial feature reconstruction for partial person re-identification: Alignment-free approach. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018: 7073–7082.
Liming Zhao, Xi Li, Yueting Zhuang, and Jingdong Wang. Deeply-learned part-aligned representations for person re-identification. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 3219–3228.
Yifan Sun, Liang Zheng, Yi Yang, Qi Tian, and Shengjin Wang. Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline)[C]. European conference on computer vision, 2018: 480–496.
Houjing Huang, Dangwei Li, Zhang Zhang, Xiaotang Chen, and Kaiqi Huang. Adversarially occluded samples for person re-identification. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018: 5098–5107.
Yumin Suh, Jingdong Wang, Siyu Tang, Tao Mei, and Kyoung Mu Lee. Part-aligned bilinear representations for person re-identification. European Conference on Computer Vision, 2018: 402–419.
Yixiao Ge, Zhuowan Li, Haiyu Zhao, Guojun Yin, Shuai Yi, Xiaogang Wang, and Hongsheng Li. Fd-gan: Pose-guided feature distilling gan for robust person re-identification. Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2018: 1230–1241.
He, L., Sun, Z., Zhu, Y., Wang, Y.: Recognizing partial biometric patterns[J]. CoRR 18(10), 1–13 (2018)
Mengxi Jia, Xinhua Cheng, Yunpeng Zhai, Shijian Lu, Siwei Ma, Yonghong Tian, and Jian Zhang. Matching on sets: Conquer occluded person re-identification without alignment. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021: 1673–1681.
Lingxiao He, Yinggang Wang, Wu Liu, He Zhao, Zhenan Sun, and Jiashi Feng. Foreground-aware pyramid reconstruction for alignment-free occluded person re-identification. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision, 2019: 8450–8459.
Yifan Sun, Qin Xu, Yali Li, Chi Zhang, Yikang Li, Shengjin Wang, and Jian Sun. Perceive where to focus: Learning visibility-aware part-level features for partial person re-identification. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: 393–402.
Chunfeng Song, Yan Huang, Wanli Ouyang, and Liang Wang. Mask-guided contrastive attention model for person re-identification. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018: 1179–1188.
Zhou, Mi., Liu, H., Lv, Z., Hong, W., Chen, X.: Motion-aware transformer for occluded person re-identification. CoRR 22(10), 1–20 (2022)
Yulin Li, Jianfeng He, Tianzhu Zhang, Xiang Liu, Yongdong Zhang, and Feng Wu. Diverse Part Discovery: Occluded Person Re-Identification With Part-Aware Transformer. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021: 2898–2907.
Mahdi M. Kalayeh, Emrah Basaran, Muhittin Gökmen, Mustafa E. Kamasak, and Mubarak Shah. Human semantic parsing for person re-identification. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018: 1062–1071.
Kaiyang Zhou, Yongxin Yang, Andrea Cavallaro, and Tao Xiang. Omni-scale feature learning for person re-identification. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision, 2019: 3702–3712.
Kuan Zhu, Haiyun Guo, Zhiwei Liu, Ming Tang, and Jinqiao Wang. Identity-guided human semantic parsing for person re-identification. European Conference on Computer Vision, 2020: 346–363.
Jia, M., Cheng, X., Shijian, Lu., Zhang, J.: Learning disentangled representation implicitly via transformer for occluded person re-identification. CoRR 21(7), 1–10 (2021)
Tan, H., Liu, X., Tian, S., Yin, B., Li, X.: MHSA-net: multi-head self-attention network for occluded person re-identification. CoRR 20(8), 1–11 (2020)
Tao Wang, Hong Liu, Pinhao Song, Tianyu Guo, and Wei Shi. Pose-guided feature disentangling for occluded person re-identification based on transformer. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2022: 2540–2549.
Boqiang, Xu., He, L., Liang, J., Sun, Z.: Learning feature recovery transformer for occluded person re-identification. CoRR 23(1), 1–11 (2023)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SZ and YZ wrote the main manuscript text, and ZL proofread the language description. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
This declaration is not applicable.
Ethical approval
This declaration is not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Zhu, S. Occluded pedestrian re-identification via Res-ViT double-branch hybrid network. Multimedia Systems 30, 5 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01235-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01235-2