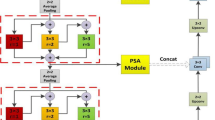
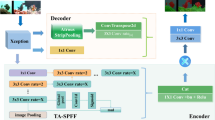
Abstract
The armor layer unit of the breakwater is a commonly used structure in ocean engineering. They are usually densely arranged and often have complex occlusion and overlap. These factors make traditional segmentation methods difficult to meet the requirements of high precision and efficiency. Unlike existing approaches to generic target segmentation, we propose a specific target segmentation method characterized by segmenting small and dense instances with similar characteristics. Our approach called the attention-guided enhanced feature pyramid network (AE-FPN) for breakwater armor layer unit segmentation, consists of two major components. The first component is an attention-guided (AM) module. Comprising both a channel context attention module (CCAM) and a spatial context attention module (SCAM), the AM module uses contextual information to allow the model to learn information about the region containing the target. The second component is semantic feature enhancement (SFE), wherein pyramid-like structures are employed to enhance semantic information. To assess the performance of the AE-FPN, a task-specific breakwater armor unit dataset named SUD2022 was released. Without any bells and whistles, the proposed AE-FPN achieved 75.2% AP on this dataset, which represents a 9.1% improvement over that of the Mask R-CNN. We also performed ablation experiments on the Cifar10 and COCO datasets to verify the generalization of our designed module. Large-scale experimental results on SUD2022 and COCO datasets demonstrate that the AE-FPN not only achieves excellent performance on breakwater armor layer unit segmentation but can also improve the performance of generic object segmentation.












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data are available from the authors upon request.
References
Hough, G., Phelp, D.: Digital image technology and a measurement tool in physical models. In: 26th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, pp 1–12 (2006)
Herrera-Charles, R., Vergara, M.A., Hernandez, C.A., et al.: Identification of breakwater damage by processing video with the surf algorithm. In: Applications of Digital Image Processing XLII, p 111370I (2019)
Sousa, P.J., Cachaço, A., Barros, F., et al.: Structural monitoring of a breakwater using uavs and photogrammetry. Proc. Struct. Integr. 37, 167–172 (2022)
Wang, H., Xu, Y., He, Y., et al.: Yolov5-fog: a multiobjective visual detection algorithm for fog driving scenes based on improved yolov5. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 71, 1–12 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2022.3196954
De Brabandere, B., Neven, D., Van Gool, L.: Semantic instance segmentation for autonomous driving. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). IEEE, Honolulu, HI, pp 478–480, (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2017.66
Zhao, M., Jha, A., Liu, Q., et al.: Faster mean-shift: Gpu-accelerated clustering for cosine embedding-based cell segmentation and tracking. Med. Image Anal. 71, 102048 (2021)
Hollandi, R., Moshkov, N., Paavolainen, L., et al.: Nucleus segmentation: towards automated solutions. Trends Cell Biol. 32(4), 295–310 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2021.12.004
Scharr, H., Minervini, M., Fischbach, A., et al.: Annotated image datasets of rosette plants. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6–12. Zürich, Suisse (2014)
Zheng, Z., Hu, Y., Guo, T., et al.: Aghrnet: an attention ghost-hrnet for confirmation of catch-and-shake locations in jujube fruits vibration harvesting. Comput. Electron. Agric. 210, 107921 (2023)
Everingham, M., Van Gool, L., Williams, C.K.I., et al.: The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 88(2), 303–338 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4
Lin, T.Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., et al.: Microsoft coco: common objects in context. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 740–755 (2014)
He, K., Gkioxari, G., Dollár, P., et al.: Mask r-cnn. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 386–397 (2017)
Deng, C., Wang, M., Liu, L., et al.: Extended feature pyramid network for small object detection. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 24, 1968–1979 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3074273
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.Y., et al.: Cbam: convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19 (2018)
Krizhevsky, A., Hinton, G.: Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. (2009). https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/learning-features-2009-TR.pdf
Liu, W., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., et al.: Ssd: single shot multibox detector. In: In European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 21–37 (2015)
Fu, C.Y., Liu, W., Ranga, A., et al.: Dssd: deconvolutional single shot detector. arXiv preprint (2017)
Shen, Z., Zhuang, L., Li, J., et al.: Dsod: learning deeply supervised object detectors from scratch. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 1919–1927 (2017)
Lin, T.Y., Dollar, P., Girshick, R., et al.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2117–2125 (2017)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., et al.: Faster r-cnn: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(6), 1137–1149 (2017)
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: Yolov3: an incremental improvement. arXiv prints (2018)
Lin, T.Y., Goyal, P., Girshick, R., et al.: Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2980–2988 (2017)
Cai, Z., Vasconcelos, N.: Cascade r-cnn: delving into high quality object detection. In: IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell, pp. 6154–6162 (2017)
Liu, S., Qi, L., Qin, H., et al.: Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 8759–8768 (2018)
Ghiasi, G., Lin, T.Y., Le, Q.V.: Nas-fpn: Learning scalable feature pyramid architecture for object detection. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7029–7038 (2019)
Tan, M., Pang, R., Le, Q.V.: Efficientdet: scalable and efficient object detection. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 10778–10787 (2020)
Guo, C., Fan, B., Zhang, Q., et al.: Augfpn: Improving multi-scale feature learning for object detection. In: EEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12595–12604 (2019)
Larochelle, H., Hinton, G.E.: Learning to combine foveal glimpses with a third-order boltzmann machine. In: Proc. of Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), pp. 1–7 (2010)
Bahdanau, D., Cho, K., Bengio, Y.: Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. In: 3rd International Conference on Learning Representation (2015)
Mnih, V., Heess, N., Graves, A., et al.: Recurrent models of visual attention. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 3, 2204–2212 (2014)
Fei, W., Jiang, M., Chen, Q., et al.: Residual attention network for image classification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3156–3649 (2017)
Chen, L.C., Yi, Y., Jiang, W., et al.: Attention to scale: scale-aware semantic image segmentation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3640–3649 (2016)
Ren, M., Zemel, R.S.: End-to-end instance segmentation with recurrent attention. In: Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, pp. 6656–6664 (2017)
Jie, H., Li, S., Gang, S., et al.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 42(8), 2011–2023 (2019)
Zhang, Z., Wang, Z., Zhe, L., et al.: Image super-resolution by neural texture transfer. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7982–7991 (2019)
Shi, W., Caballero, J., Huszár, F., et al.: Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1874–1883 (2016)
Zhou, B., Khosla, A., Lapedriza, A., et al.: Learning deep features for discriminative localization, pp. 2921–2929 (2016)
You, Q., Luo, J., Jin, H., et al.: Building a large scale dataset for image emotion recognition: The fine print and the benchmark. In: AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 308–314 (2016)
Zhou, B., Lapedriza, A., Xiao, J., et al.: Learning deep features for scene recognition using places database. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 39, 487–495 (2014)
Huang, Z., Huang, L., Gong, Y., et al.: Mask scoring r-cnn. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2019)
Bolya, D., Zhou, C., Xiao, F., et al.: Yolact: real-time instance segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44, 9157–9166 (2019)
Xie, E., Sun, P., Song, X., et al.: Polarmask: single shot instance segmentation with polar representation. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 12193–12202 (2020)
Chen, L.C., Hermans, A., Papandreou, G., et al.: Masklab: instance segmentation by refining object detection with semantic and direction features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4013–4022 (2018)
Tian, Z., Shen, C., Chen, H., et al.: Fcos: fully convolutional one-stage object detection. In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 9627-9636 (2019)
Selvaraju, R.R., Cogswell, M., Das, A., et al.: Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 618–626 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by China National Key R &D Program (2022YFE0104500), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52001149, 52039005), and the Research Funds for the Central Universities (TKS20210102, TKS20220301, TKS20230205).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Authors’ contributions: Linchun Gao performed the methodology, writing - original draft and visualization; Shoujun Wang performed the supervision; Songgui Chen performed the writing - review & editing and funding acquisition; Yuanye Hu performed the formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest and competing interests.
Consent for publication
All participants provided written consent for publication of their data.
Additional information
Communicated by J. Gao.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, L., Wang, S., Chen, S. et al. AF-FPN: an attention-guided enhanced feature pyramid network for breakwater armor layer unit segmentation. Multimedia Systems 30, 18 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01243-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01243-2