Abstract
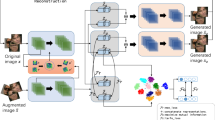
Unsupervised domain-adaptive person re-identification refers to transferring knowledge from labeled to unlabeled datasets, thus alleviating the need for large amounts of labeled data. Existing methods address this problem using clustering methods to generate pseudo-labels. However, the pseudo-labels generated by current existing methods may be unstable and noisy, which will significantly degrade the performance of the method. In this paper, we propose a novel domain-adaptive person re-identification method via domain alignment and mutual pseudo-label refinement. First, we extract discriminative feature from the augmented data using a two-branch structure to enrich the feature diversity; second, we design a distributed adversarial domain alignment module to minimize domain differences; finally, we propose a consistency between local features and global features to refine pseudo-labels predicted by global features to exploit the complementary relationship between local and global features, and thus the noise generated by pseudo-label clustering is effectively reduced. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method can achieve remarkable results on popular benchmark datasets for domain-adaptive person re-identification.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the authors mentioned in the manuscript have agreed for authorship, read, and approved the manuscript, and given consent for submission and subsequent publication of the manuscript.
References
Wei Li, Rui Zhao, Tong Xiao, Xiaogang Wang. Deep ReID: deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2014: 152–159.
Wei Li, Xiatian Zhu, Shaogang Gong. Harmonious attention network for person re-identification. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2018: 2285–2294.
Longhui Wei, Shiliang Zhang, Hantao Yao, Wen Gao, Qi Tian. Glad: global-local-alignment descriptor for pedestrian retrieval. ACM international conference on multimedia, 2017: 420–428.
Yixiao Ge, Dapeng Chen, Feng Zhu, Rui Zhao, Hong sheng Li. Self-paced contrastive learning with hybrid memory for domain adaptive object re-Id. Annual conference on neural information processing systems, 2020: 1–13.
Weijian Deng, Liang Zheng, Qixiang Ye, Guoliang Kang, Yi Yang, Jianbin Jiao. Image-image domain adaptation with preserved self-similarity and domain-dissimilarity for person re-identification. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2018: 994–1003.
Zhun Zhong, Liang Zheng, Shaozi Li,Yi Yang. Generalizing a person retrieval model hetero and homogeneously. European conference on computer vision, 2018: 172–188.
Ying Zhang, Tao Xiang, Timothy M. Hospedales, Huchuan Lu. Deep mutual learning. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2018: 4320–4328.
Shi, Y., Ling, H., Lei, Wu., Shen, J., Li, P.: Learning refined attribute-aligned network with attribute selection for person re-identification. Neurocomputing 402, 124–133 (2020)
Yunpeng Zhai, Qixiang Ye, Shijian Lu, Mengxi Jia, Rongrong Ji, Yonghong Tian. Multiple expert brainstorming for domain adaptive person re-identification. European conference on computer vision, 2020: 594–611.
Liang Zheng, Hengheng Zhang, Shaoyan Sun, Manmohan Chandraker, Yi Yang, Qi Tian. Person re-identification in the wild. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2017: 3346–3355.
Cheng Wang, Bingpeng Ma, Hong Chang, Shiguang Shan, Xilin Chen. TCTS: A task-consistent two stage framework for person search. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2020: 11949–11958.
Yichao Yan, Qiang Zhang, Bingbing Ni, Wendong Zhang, Minghao Xu, Xiaokang Yang. Learning context graph for person search. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2019: 2158–2167.
Di Chen, Shanshan Zhang, Jian Yang, Bernt Schiele. Norm-aware embedding for efficient person search. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2020: 12612–12621.
Zhengjia Li, Duoqian Miao. Sequential end-to-end network for efficient person search. AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2021: 2011–2019.
Yifan Sun, Liang Zheng, Yi Yang, Qi Tian, Shengjin Wang. Beyond part models: person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). European conference on computer vision, 2018: 501–518.
Xuan Zhang, Hao Luo, Xing Fan, Weilai Xiang, Yixiao Sun, Qiqi Xiao, Wei Jiang, Chi Zhang, Jian Sun. Aligned ReID: surpassing human-level performance in person re-identification. CoRRabs/1711.08184, 2017.
Luo, H., Jiang, W., Zhang, X., Fan, X., Qian, J., Zhang, C.: Aligned ReID++: dynamically matching local information for person re-identification. Pattern Recogn. 94, 53–61 (2019)
Luo, H., Jiang, W., Youzhi, Gu., Liu, F., Liao, X., Lai, S., Jianyang, Gu.: A strong baseline and batch normalization neck for deep person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 22(10), 2597–2609 (2020)
Kaiwei Zeng, Munan Ning, Yaohua Wang, Yang Guo. Hierarchical clustering with hard-batch triplet loss for person re-identification. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2020: 13657–13665.
Dongkai Wang and Shiliang Zhang. Unsupervised person re-identification via multi-label classification. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2020: 10981–10990.
Wenhang Ge, Junlong Du, Ancong Wu, Yuqiao Xian, Ke Yan, Feiyue Huang, Weishi Zheng. Lifelong person re-identification by pseudo task knowledge preservation. AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2022: 688–696.
Han, X., Xuehui, Yu., Li, G., Zhao, J., Pan, G., Ye, Q., Jiao, J., Han, Z.: Rethinking sampling strategies for unsupervised person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 32, 29–42 (2023)
Longhui Wei, Shiliang Zhang, Wen Gao, Qi Tian. Person transfer GAN to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2018: 79–88.
Yixiao Ge, Dapeng Chen, Hongsheng Li. Mutual mean-teaching: pseudo label refinery for unsupervised domain adaptation on person re-identification. International conference on learning representations, 2020: 1–15.
Kecheng Zheng, Cuiling Lan, Wenjun Zeng, Zhizheng Zhang, Zhengjun Zha. Exploiting sample uncertainty for domain adaptive person re-identification. AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2021: 3538–3546.
Wang, W., Zhao, F., Liao, S.: Attentive wave block: complementarity-enhanced mutual networks for unsupervised domain adaptation in person re-identification and beyond. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 1532–2154 (2022)
Zhengdong Hu, Yifan Sun, Yi Yang, Jianguang Zhou. Divide-and-regroup clustering for domain adaptive person re-identification AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2022: 980–988.
Yuhang Wu, Tengteng Huang, Haotian Yao, Chi Zhang, Yuanjie Shao, Chuchu Han, Changxin Gao, Nong Sang. Multi-centroid representation network for domain adaptive person re-ID. AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2022: 2750–2758.
Yongxing Dai, Jun Liu, Yifan Sun, Zekun Tong, Chi Zhang, LingYu Duan. IDM: an intermediate domain module for domain adaptive person re-ID. IEEE conference on computer vision, 2021:11864–11874.
Alex Kendall, Yarin Gal:. What uncertainties do we need in bayesian deep learning for computer vision? Annual conference on neural information processing systems, 2017 5574–5584.
Zheng, Z., Yang, Yi.: Rectifying pseudo label learning via uncertainty estimation for domain adaptive semantic segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vision 129(4), 1106–1120 (2021)
Yu, Wu., Lin, Y., Dong, X., Yan, Y., Bian, W., Yang, Yi.: Progressive learning for person re-identification with one example. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(6), 2872–2881 (2019)
Kecheng Zheng, Wu Liu, Lingxiao He, Tao Mei, Jiebo Luo, and Zhengjun Zha. Group-aware label transfer for domain adaptive person re-identification. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2021: 5310–5319.
Liang Zheng, Liyue Shen, Lu Tian, Shengjin Wang, Jingdong Wang, and Qi Tian. Scalable person re-identification: a benchmark. IEEE conference on computer vision, 2015: 1116–1124.
Ergys Ristani, Francesco Solera, Roger Zou, Rita Cucchiara, Carlo Tomasi. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. European conference on computer vision workshops, 2016: 17–35.
Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun. Deep residual learning for image recognition. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2016: 770–778.
Jia Deng, Wei Dong, Richard Socher, Lijia Li, Kai Li, and Feifei Li. Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2009: 248–255.
Yang Fu, Yunchao Wei, Guanshuo Wang, Yuqian Zhou, Honghui Shi, Huang Thomas. Self-similarity Grouping: a simple unsupervised cross domain adaptation approach for person re-identification. IEEE conference on computer vision, 2019: 6111–6120.
Fan, H., Zheng, L., Yan, C., Yang, Yi.: Unsupervised person re-identification: clustering and fine-tuning. ACM Trans Multimedia Comput, Commun, Appl 14(4), 1–18 (2018)
Zhan Zhong, Liang Zheng, Zhiming Luo, Shaozi Li, Yi Yang. Invariance matters: exemplar memory for domain adaptive person re-identification. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2019: 598–607.
Yujhe Li, Cisiang Lin, Yanbo Lin, Yuchiang Frank Wang. Cross dataset person re-identification via unsupervised pose disentanglement and adaptation. IEEE conference on computer vision, 2019: 7918–7928.
Xinyu Zhang, Jiewei Cao, Chunhua Shen, Mingyu You. Self training with progressive augmentation for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification. IEEE conference on computer vision, 2019: 8221–8230.
Dongkai Wang and Shiliang Zhang. Unsupervised person re-identification via multi-label classification. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2020: 10978–10987.
Yunpeng Zhai, Shijian Lu, Qixiang Ye, Xuebo Shan, Jie Chen, Rongrong Ji, Yonghong Tian. ad-cluster: augmented discriminative clustering for domain adaptive person re-identification. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2020: 9018–9027.
Minying Zhang, Kai Liu, Yidong Li, Shihui Guo, Hongtao Duan, Yimin Long, Yi Jin. Unsupervised domain adaptation for person re-identification via heterogeneous graph alignment. AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2021: 3360–3368.
Xin Jin, Cuiling Lan, Wenjun Zeng, Zhibo Chen. Global distance distributions separation for unsupervised person re-identification. European conference on computer vision, 2020: 735–751.
Dai, Y., Liu, J., Bai, Y., Tong, Z., Duan, L.: Dual-refinement: joint label and feature refinement for unsupervised domain adaptive person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 7815–7829 (2021)
Han, J., Li, Y., Wang, S.: Delving into probabilistic uncertainty for unsupervised domain adaptive person re-identification. AAAI Conf Artif Intell 36(1), 790–798 (2022)
Shengming Yu, Shengjin Wang. Consistency mean-teaching for unsupervised domain adaptive person re-identification. International conference on image and graphics processing, 2022: 159–166.
Yutian Lin, Xuanyi Dong, Liang Zheng, Yan Yan, Yi Yang. A bottom-up clustering approach to unsupervised person re-identification. AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2019: 8738–8745.
Zhao, F., Liao, S., Xie, G.-S., Zhao, J., Zhang, K., Shao, L. Unsupervised domain adaptation with noise resistible mutual-training for person re-identification. European conference on computer vision, 2020: 526–544. Springe.
Jianing Li, Shiliang Zhang. Unsupervised domain adaptive person re-identification. European conference on computer vision, 2020: 483–499.
Diederik P Kingma, Jimmy Ba. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. International conference on learning representations, 2015: 1–15.
Michal Lukasik, Srinadh Bhojanapalli, Aditya Menon, and Sanjiv Kumar. Does label smoothing mitigate label noise? In conference on learning representation, 2015: 1–15.
Mingsheng Long, Han Zhu, Jianmin Wang, and Michael I Jordan. Unsupervised domain adaptation with residual transfer networks. In proceedings of the 30th international conference on neural information processing systems, pages 136–144, 2016.
Yaroslav Ganin and Victor Lempitsky. Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropagation. International conference on machine learning, 2015: 1180–1189.
Kuniaki Saito, Kohei Watanabe, Yoshitaka Ushiku, Tatsuya Harada. Maximum classifier discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2018: 3723–3732.
Jingjing Li, Erpeng Chen, Zhengming Ding, Lei Zhu, Ke Lu, Heng Tao Shen. Maximum density divergence for domain adaptation. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 2021, 43(11): 3918–3930.
Paolo Russo, Fabio M Carlucci, Tatiana Tommasi, Barbara Caputo. From source to target and back: symmetric bi-directional adaptive gan. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2018: 8099–8108.
Jingjing Li, Mengmeng Jing, Ke Lu, Lei Zhu, Heng Tao Shen. Locality preserving joint transfer for domain adaptation. IEEE transactions on image processing, 2019, 28(12):6103–6115.
Song, H., Kim, M., Park, D., Shin, Y., Lee, J.-G.: Learning from noisy labels with deep neural networks: a survey. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learning Syst 34(11), 8135–8153 (2023)
Aritra Ghosh, Himanshu Kumar, and P. S. Sastry. Robust loss functions under label noise for deep neural networks. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2017: 1919–1925.
Dan Hendrycks, Mantas Mazeika, Duncan Wilson, and Kevin Gimpel. Using trusted data to train deep networks on labels corrupted by severe noise. Annual conference on neural information processing systems, 2018: 10477–10486.
Haw-Shiuan Chang, Erik G. Learned-Miller, Andrew McCallum. Active bias: training more accurate neural networks by emphasizing high variance samples. Annual conference on neural information processing systems, 2017: 1002–1012.
Funding
The manuscript is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications (No. 221077).
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This declaration is not applicable.
Ethical approval
This declaration is not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by J. Gao.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S., Luo, T. Domain-adaptive person re-identification via domain alignment and mutual pseudo-label refinement. Multimedia Systems 30, 110 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-024-01314-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-024-01314-y