Abstract
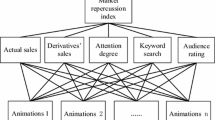
The diversity and dynamics of quality index information bring challenges to quality assessment of experience products. This paper proposes a three-stage quality assessment method based on grounded theory, association analysis, combined weighting, sentiment analysis and cloud model. Firstly, based on online reviews, the true quality indicators of animation are recognized by grounded theory, and the relationships among quality indicators are identified by association analysis. Secondly, by introducing the principle of gaming, the combined weighting based on network opinion leader and network opinion follower is proposed. Finally, an animation comprehensive quality evaluation model based on cloud model and sentiment analysis is proposed. The feasibility and practicability of the method are verified on multiple animation datasets, and the quality levels of different sales products are obtained, providing a direction for animation quality improvement. Meanwhile, this paper further demonstrates the method's superiority by comparing it with other methods.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Nelson, P.: Information and consumer behavior. J Polit Econ 78, 311–329 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1086/259630
Tang, Z., Wang, T., Cui, J., Han, B., He, B.: Predicting total sales volume interval of an experiential product with short life cycle before production: similarity comparison in attribute relationship patterns. Manag. Decis. 59, 2528–2548 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1108/md-03-2020-0320
Business Brand Institute. Prospective report on Chinese animation going to sea in 2023 (2023). https://www.hanghangcha.com/pdf.html. Accessed 22 Oct 2023
Enlightent. Analysis of long video platform animation webcast in the first half of 2023 (2023). https://www.hanghangcha.com/pdf.html. Accessed 22 Oct 2023
Liang, H., Sit, J., Chang, J., Zhang, J.: Computer animation data management: review of evolution phases and emerging issues. Int. J. Inf. Manage. 36, 1089–1100 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2016.07.008
Seshadrinathan, K., Bovik, A.C.: Automatic prediction of perceptual quality of multimedia signals-a survey. Multimed. Tools Appl. 51, 163–186 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-010-0625-9
Kim, H.J., Choi, S.G.: QoE assessment model for multimedia streaming services using QoS parameters. Multimed. Tools Appl. 72, 2163–2175 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1507-8
Huang, P., Lurie, N.H., Mitra, S.: Searching for experience on the web: an empirical examination of consumer behavior for search and experience goods. J. Mark. 73, 55–69 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1509/jmkg.73.2.55
Ghose, A., Ipeirotis, P.G.: Estimating the helpfulness and economic impact of product reviews: mining text and reviewer characteristics. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 23, 1498–1512 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/tkde.2010.188
Hong, H., Xu, D., Wang, G.A., Fan, W.: Understanding the determinants of online review helpfulness: a meta-analytic investigation. Decis. Support. Syst. 102, 1–11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2017.06.007
Yakubu, H., Kwong, C.K.: Forecasting the importance of product attributes using online customer reviews and google trends. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 171, 120983 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120983
Lan, H., Ma, X., Qiao, W., Ma, L.: On the causation of seafarers’ unsafe acts using grounded theory and association rule. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 223, 108498 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2022.108498
Yu, D., Fang, A., Xu, Z.: Topic research in fuzzy domain: based on LDA topic modelling. Inf Sci (N Y) 648, 119600 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2023.119600
Wei, C., Meng, J., Zhu, L., Han, Z.: Assessing progress towards sustainable development goals for chinese urban land use: a new cloud model approach. J. Environ. Manage. 326, 116826 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116826
Wen, X., Nie, Y., Du, Z., Huang, L.: Operational safety assessment of straddle-type monorail vehicle system based on cloud model and improved CRITIC method. Eng. Fail. Anal. 139, 106463 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106463
Yang, T., Dang, Y., Wu, J.: Dynamic perceived quality analysis using social media data at macro- and micro-levels. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 123, 1465–1495 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1108/imds-08-2022-0478
MandalMaiti, S.: A network promoter score (NePS): an indicator of product sales in e-commerce retailing sector. Electron. Mark. 32, 1327–1349 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12525-021-00503-1
Agryzkov, T., Oliver, J.L., Tortosa, L., Vicent, J.F.: An algorithm for ranking the nodes of an urban network based on the concept of PageRank vector. Appl. Math. Comput. 219, 2186–2193 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2012.08.064
Liu, Y., Liu, Z., Li, S., Guo, Y., Liu, Q., Wang, G.: Cloud-cluster: an uncertainty clustering algorithm based on cloud model. Knowl. Based Syst. 263, 110261 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2023.110261
Phillips, T., Abdulla, W.: Developing a new ensemble approach with multi-class SVMs for manuka honey quality classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 111, 107710 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107710
Tuttle, J.F., Blackburn, L.D., Powell, K.M.: On-line classification of coal combustion quality using nonlinear SVM for improved neural network NOx emission rate prediction. Comput. Chem. Eng. 141, 106990 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2020.106990
Fu, Y., Gao, P.P., Gao, X., Zhang, Y.: Quality evaluation of resistance spot welding based on dynamic reactance signal and radar diagram method. IEEE Sens. J. 24, 6666–6676 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2024.3352632
Jiang, Z., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Cao, H.: A new method for recognition and classification of power quality disturbances based on IAST and RF. Electr. Pow. Syst. Res. 226, 109939 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2023.109939
Hoi, K.I., Yuen, K.V., Mok, K.M.: Improvement of the multilayer perceptron for air quality modelling through an adaptive learning scheme. Comput. Geosci. 59, 148–155 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2013.06.002
He, J., Liu, D., Chen, X.: Wearable exercise electrocardiograph signal quality assessment based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation algorithm. Comput. Commun. 151, 86–97 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2019.12.051
Li, D., Liu, C., Gan, W.: A new cognitive model: cloud model. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 24, 357–375 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/int.20340
Zhang, L., Zhang, T., Lang, Y., Li, J., Ji, F.: Research on patent quality evaluation based on rough set and cloud model. Expert Syst. Appl. 235, 121057 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121057
Guo, M., Zhao, J., Pan, D., Sun, M., Zhou, Y., Yan, B.: Normal cloud model theory-based comprehensive fuzzy assessment of wooden pagoda safety. J. Cult. Herit. 55, 1–10 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2022.02.001
Xu, J., Ding, R., Li, M., Dai, T., Zheng, M., Yu, T., Sui, Y.: A new Bayesian network model for risk assessment based on cloud model, interval type-2 fuzzy sets and improved D-S evidence theory. Inf. Sci. (N Y) 618, 336–355 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2022.11.011
Chen, H., Shen, Q., Feng, Z., Liu, Y.: Vulnerability assessment in urban metro systems based on an improved cloud model and a Bayesian network. Sustain. Cities Soc. 98, 104823 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2023.104823
Thompson, J.J., Leung, B.H., Blair, M.R., Taboada, M.: Sentiment analysis of player chat messaging in the video game StarCraft 2: extending a lexicon-based model. Knowl. Based Syst. 137, 149–162 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2017.09.022
Liu, A., Mazumdar, T., Li, B.: Counterfactual decomposition of movie star effects with star selection. Manage. Sci. 61, 1704–1721 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.2014.1923
He, D., Tang, Z., Chen, Q., Han, Z., Zhao, D., Sun, F.: A two-stage deep graph clustering method for identifying the evolutionary patterns of the time series of animation view counts. Inf. Sci. (N Y) 642, 119155 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2023.119155
Sharma, M., Basu, S., Chakraborty, S., Bose, I.: Determining the optimal release time of movies: a study of movie and market characteristics. Decis. Support. Syst. 165, 113893 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2022.113893
Yalcinkaya, G., Aktekin, T.: Brand extension effects and core attributes of experience product franchises: a Bayesian approach. J. Prod. Innovat. Manag. 32, 731–746 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12164
Weia, Y.M.: The similarity network of motion pictures. Manage. Sci. 66, 1647–1671 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.2018.3261
Bharadwaj, N., Noble, C.H., Tower, A., Smith, L.M., Dong, Y.: Predicting innovation success in the motion picture industry: the influence of multiple quality signals. J. Prod. Innovat. Manag. 34, 659–680 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12404
Yeh, C.C.: Online word-of-mouth as a predictor of television rating. Online Inform. Rev. 39, 831–847 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1108/oir-01-2015-0033
Bayo-Moriones, A., Etayo, C., Sánchez-Tabernero, A.: Political orientation and perceived quality of television channels. J. Serv. Theor. Pract. 25, 813–835 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1108/jstp-09-2014-0217
Papathanassis, A., Knolle, F.: Exploring the adoption and processing of online holiday reviews: a grounded theory approach. Tour. Manag. 32, 215–224 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2009.12.005
Yu, S., Liu, Y., Tang, Y., Li, X., Li, W., Li, C., Zhang, Y., Lan, H.: Non-destructive quality assessment method for Korla fragrant pears based on electrical properties and adaptive neural-fuzzy inference system. Comput. Electron. Agric. 203, 107492 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2022.107492
Ruan, D., Bian, J., Wang, Q., Wu, J., Yu, Y., Gu, Z.: Application of modified cloud model-level eigenvalue method in water quality evaluation. J. Hydrol. (Amst) 603, 126980 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126980
Ye, Q., Zhang, Z., Law, R.: Sentiment classification of online reviews to travel destinations by supervised machine learning approaches expert. Syst. Appl. 36(6527), 6535 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.07.035
Gomes, L., da Silva, T.R., Côrtes, M.L.: BERT- and TF-IDF-based feature extraction for long-lived bug prediction in FLOSS: a comparative study. Inf. Softw. Technol. 160, 107217 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2023.107217
Liu, D., Zou, Z.: Water quality evaluation based on improved fuzzy matter-element method. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 24, 1210–1216 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(11)60938-8
Zhao, E., Kuo, Y.M., Chen, N.: Assessment of water quality under various environmental features using a site-specific weighting water quality index. Sci. Total. Environ. 783, 146868 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146868
Mandal, S., Maiti,: A social promoter score (SPS) and review network: a method and a tool for predicting financial health of an online shopping brand. ArXiv (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1804.04464
Mandal, S., Maiti,: A rating prediction with review network feedback: a new direction in recommendation. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 9, 740–750 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcss.2021.3108007
Newman, M.E.J., Forrest, S., Balthrop, J.: Email networks and the spread of computer viruses. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Phys. Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip. Topics (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevE.66.035101
Newman, M.E.J.: A measure of betweenness centrality based on random walks. Soc. Networks 27, 39–54 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socnet.2004.11.009
Freeman, L.C.: Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification. Soc Networks 1, 215–239 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-8733(78)90021-7
Bonacich, P.: Power and centrality: a family of measures. Am. J. Sociol. 92, 1170–1182 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1086/228631
Gama Dessavre, D., Ramirez-Marquez, J.E., Barker, K.: Multidimensional approach to complex system resilience analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 149, 34–43 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2015.12.009
Lv, L., Zhang, K., Zhang, T., Li, X., Sun, Q., Zhang, L., Xue, W.: Eigenvector-based centralities for multilayer temporal networks under the framework of tensor computation. Expert Syst. Appl. 184, 115471 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115471
Lian, X., Zhu, H., Zhang, X., Jin, Y., Zhou, H., He, B., Li, Z.: Recognition of typical environmental control behavior patterns of indoor occupants based on temporal series association analysis. Build. Environ. 234, 110170 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2023.110170
Yürüşen, N.Y., Uzunoğlu, B., Talayero, A.P., Estopiñán, A.L.: Apriori and k-means algorithms of machine learning for spatio-temporal solar generation balancing. Renew. Energy 175, 702–717 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.04.098
Lin, D.-I., Kedem, Z.M.: Pincer-search: an efficient algorithm for discovering the maximum frequent set. Ieee T Knowl Data En 14, 553–566 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/tkde.2002.1000342
Pei, J., Han, J., Member, S., Mortazavi-Asl, B., Wang, J., Pinto, H., Chen, Q., Dayal, U., Hsu, M.S.: Mining sequential patterns by pattern-growth: the PrefixSpan approach. IEEE T Knowl Data En 16, 1424–1440 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/tkde.2004.77
Wąs, T., Skibski, O.: Axiomatic characterization of PageRank. Artif. Intell. 318, 103900 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artint.2023.103900
Liu, C., Wang, J., Xia, R.: Node importance evaluation in multi-platform avionics architecture based on TOPSIS and PageRank. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Proc. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13634-023-00979-3
Zhao, L., Yang, W., Wang, Z., Liang, Y., Zeng, Z.: Long-term safety evaluation of soft rock tunnel structure based on knowledge decision-making and data-driven models. Comput. Geotech. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2024.106244
Kan, Z., Wei, Y., Zhao, T., Cao, J.: Risk evaluation of submarine pipelines in FMEA by combination of gray relation projection and VIKOR method. Ocean Eng. 302, 117695 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.117695
Wang, H.L., Zhao, X.F., Chen, H.J., Yi, K., Xie, W.C., Xu, Y.: Evaluation of toppling rock slopes using a composite cloud model with DEMATEL–CRITIC method. Water Sci. Eng. 16, 280–288 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2023.04.002
Deshpande, K.V., Kumar, D.: Time and memory scalable algorithms for clustering tendency assessment of big data. Inf. Sci. (N Y) 664, 120324 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2024.120324
Xie, X., Zhang, J., Lian, Y., Lin, K., Gao, X., Lan, T., Luo, J., Song, F.: Cloud model combined with multiple weighting methods to evaluate hydrological alteration and its contributing factors. J Hydrol (Amst) 610, 127794 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127794
Zhao, Y., Kou, G., Peng, Y., Chen, Y.: Understanding influence power of opinion leaders in e-commerce networks: an opinion dynamics theory perspective. Inf Sci (N Y) 426, 131–147 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.10.031
Soleymani, M., Garcia, D., Jou, B., Schuller, B., Chang, S.F., Pantic, M.: A survey of multimodal sentiment analysis. Image Vis. Comput. 65, 3–14 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2017.08.003
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 71672004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QC wrote the main manuscript text. ZT contributed the conceptualization and funding acquisition. DH performed the paper revisions. DZ contributed Supervision. JW performed the investigation. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Qianqian Xu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Tang, Z., He, D. et al. A three-stage quality evaluation method for experience products: taking animation as an example. Multimedia Systems 30, 203 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-024-01401-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-024-01401-0