Abstract
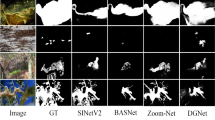
In camouflaged object detection (COD), wholly and accurately segmenting the foreground from the background is a major focus of research. However, the similarity in color and texture between foreground targets and the background makes it difficult to distinguish them. Despite numerous deep learning networks utilizing different approaches for camouflaged object detection, precisely identifying object contours and enhancing the model’s resistance to interference from similar backgrounds remains a challenging problem. To address this issue, this paper proposes a camouflaged object detection network named boundary refinement network (BRNet) that achieves a fine-grained description of object contours by utilizing boundary semantic information constraints. Firstly, the multi-level asymmetric convolution module (MACM) is designed to enhance feature representation within the backbone architecture via a sequence of asymmetric convolutions and cross-layer connections. Additionally, the Boundary Constraint Guided Module (BCGM) is proposed to impose constraints on foreground shape and refine constrained foreground contours. Lastly, we introduce the Boundary Fusion Extraction Module (BFEM), which enables interaction between boundaries and objects in an additional dimension, leading to the generation of prediction results. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments conducted on three datasets demonstrate that BRNet performs well on the camouflaged object detection task, achieving superior results compared to 21 state-of-the-art approaches.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original dataset and the results generated through our network can be requested from the corresponding authors via email within a reasonable range of requirements. No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Cuthill, I.C., Stevens, M., Sheppard, J., et al.: Disruptive coloration and background pattern matching. Nature 434, 72–74 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03312
Liu, L., Ouyang, W., Wang, X., et al.: Deep learning for generic object detection: a survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 128, 261–318 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-019-01247-4
Li G, Zhu C (2017) A Three-Pathway Psychobiological Framework of Salient Object Detection Using Stereoscopic Technology. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW). pp 3008–3014
Owens A, Barnes C, Flint A, et al (2014) Camouflaging an object from many viewpoints. In: 2014 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). pp 2782–2789
Troscianko, T., Benton, C.P., Lovell, P.G., et al.: Camouflage and visual perception. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 364, 449–461 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2008.0218
Fan DP, Ji GP, Sun G, et al (2020) Camouflaged object detection. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). pp 2774–2784
Lv Y, Zhang J, Dai Y, et al (2021) Simultaneously Localize, Segment and Rank the Camouflaged Objects. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
Mei H, Ji GP, Wei Z, et al (2021) Camouflaged Object Segmentation with Distraction Mining. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). pp 8768–8777
Ji, G.P., Fan, D.P., Chou, Y.C., et al.: Deep gradient learning for efficient camouflaged object detection. Mach Intell Res 20, 92–108 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-022-1365-9
Sun Y, Wang S, Chen C, et al (2022) Boundary-Guided Camouflaged Object Detection. In: 2022 International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence(IJCAI). pp 1335–1341
Bi, H., Tong, Y., Zhang, J., et al.: Depth alignment interaction network for camouflaged object detection. Multimed Syst 30, 51 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-023-01250-3
Fan, D.-P., Ji, G.-P., Xu, P., et al.: Advances in deep concealed scene understanding. Vis Intell 1, 16 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44267-023-00019-6
He, J., Zhang, Y., Chung, M., et al.: Whole-body tumor segmentation from PET/CT images using a two-stage cascaded neural network with camouflaged object detection mechanisms. Med. Phys. 50, 6151–6162 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.16438
Bhajantri NU, Nagabhushan P (2006) Camouflage defect identification: A novel approach. In: 2006 International Conference on Information Technology (ICIT). pp 145–148
Boot, W.R., Neider, M.B., Kramer, A.F.: Training and transfer of training in the search for camouflaged targets. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 71, 950–963 (2009). https://doi.org/10.3758/app.71.4.950
Fan, D.P., Ji, G.P., Cheng, M.M., et al.: Concealed object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44, 6024–6042 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3085766
Yin, B., Zhang, X., Hou, Q., et al.: CamoFormer: masked separable attention for camouflaged object detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3438565
He R, Dong Q, Lin J, et al (2023) Weakly-supervised Camouflaged object detection with scribble annotations. In: 2023 Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence(AAAI). pp 781–789
Pang Y, Zhao X, Xiang TZ, et al (2022) Zoom in and out: a mixed-scale triplet network for Camouflaged object detection. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). pp 2150–2160
Zhu C, Yan W, Liu S, et al (2019) Salient contour-aware based twice learning strategy for saliency detection. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW). pp 2541–2548
Yu, J., Chen, S., Lu, L., et al.: Alternate guidance network for boundary-aware camouflaged object detection. Mach. Vis. Appl. 34, 69 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-023-01424-z
Liu, K., Qiu, T., Yu, Y., et al.: Edge-guided camouflaged object detection via multi-level feature integration. Sensors 23, 5789 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/s23135789
Li, P., Yan, X., Zhu, H., et al.: FindNet: can you find me? Boundary-and-texture enhancement network for Camouflaged object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 6396–6411 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2022.3189828
Wang, W., Xie, E., Li, X., et al.: PVT v2: improved baselines with pyramid vision transformer. Comput Vis Media 8, 415–424 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41095-022-0274-8
DIng X, Guo Y, DIng G, et al (2019) ACNet: Strengthening the kernel skeletons for powerful CNN via asymmetric convolution blocks. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). pp 1911–1920
Xu, X., Zhu, M., Yu, J., et al.: Boundary guidance network for camouflage object detection. Image Vis. Comput. 114, 104283 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2021.104283
Xiao, J., Chen, T., Hu, X., et al.: Boundary-guided context-aware network for camouflaged object detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 35, 15075–15093 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-08502-3
Wei J, Wang S, Huang Q (2020) F3Net: fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. In: 2020 Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence(AAAI). pp 12321–12328
Kingma DP, Ba JL (2015) Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: 2015 International Conference on Learning Representations(ICLR). p 14
Le, T.N., Nguyen, T.V., Nie, Z., et al.: Anabranch network for camouflaged object segmentation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 184, 45–56 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2019.04.006
Sun Y, Chen G, Zhou T, et al (2021) Context-aware Cross-level Fusion Network for Camouflaged Object Detection. In: 2021 International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence(IJCAI). pp 1025–1031
Wang, K., Bi, H., Zhang, Y., et al.: DC-Net: a dual-branch, dual-guidance and cross-refine network for camouflaged object detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 69, 5364–5374 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2021.3078379
Zhang, C., Wang, K., Bi, H., et al.: Camouflaged object detection via neighbor connection and hierarchical information transfer. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 221, 103450 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2022.103450
Zhai Q, Li X, Yang F, et al (2021) Mutual graph learning for camouflaged object detection. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). pp 12992–13002
Ji, G.P., Zhu, L., Zhuge, M., et al.: Fast camouflaged object detection via edge-based reversible re-calibration network. Pattern Recognit 123, 108414 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108414
Zhang M, Xu S, Piao Y, et al (2022) PreyNet: Preying on Camouflaged Objects. In: 2022 ACM International Conference on Multimedia(ACM MM). pp 5323–5332
Wu Z, Paudel DP, Fan DP, et al (2023) Source-free Depth for Object Pop-out. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). pp 1032–1042
Mei, H., Yang, X., Zhou, Y., et al.: Distraction-aware camouflaged object segmentation. Sci Sin Inf 54, 653–673 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1360/SSI-2022-0138
Liu Z, Zhang Z, Tan Y, et al (2022) Boosting Camouflaged object detection with dual-task interactive transformer. In: 2022 International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). pp 140–146
Hu X, Wang S, Qin X, et al (2023) High-resolution iterative feedback network for camouflaged object detection. In: 2023 Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence(AAAI). pp 881–889
Pang, Y., Zhao, X., Xiang, T.Z., et al.: ZoomNeXt: a unified collaborative pyramid network for camouflaged object detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3417329
Jha D, Smedsrud PH, Riegler MA, et al (2020) Kvasir-SEG: a segmented polyp dataset. In: 2020 Multimedia Modeling(MMM). pp 451–462
Bernal, J., Sánchez, F.J., Fernández-Esparrach, G., et al.: WM-DOVA maps for accurate polyp highlighting in colonoscopy: validation vs. saliency maps from physicians. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 43, 99–111 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2015.02.007
Silva, J., Histace, A., Romain, O., et al.: Toward embedded detection of polyps in WCE images for early diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 9, 283–293 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0926-3
Mamonov, A.V., Figueiredo, I.N., Figueiredo, P.N., et al.: Automated polyp detection in colon capsule endoscopy. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33, 1488–1502 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2014.2314959
Vázquez, D., Bernal, J., Javier Sánchez, F., et al.: A benchmark for endoluminal scene segmentation of colonoscopy images. J Healthc Eng 2017, 4037190 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4037190
Fan D-P, Ji G-P, Zhou T, et al (2020) PraNet: parallel reverse attention network for polyp segmentation. In: 2020 Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention(MICCAI). pp 263–273
Trinh Q-H, Nguyen M-V, Thi P-T (2024) KDAS: knowledge distillation via attention supervision framework for polyp segmentation. arXiv-Preprint. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2312.08555
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: 2015 Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention(MICCAI). pp 234–241
Fang Y, Chen C, Yuan Y, et al (2019) Selective feature aggregation network with area-boundary constraints for polyp segmentation. In: 2019 Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention(MICCAI). pp 302–310
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62002100, 62202142).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China, 62002100, 62202142.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Miaohui Zhang: supervision, work coordination. Chenxing Shen: methodology, software. Yangyang Deng: data support, resources. LI Wang: editing, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Junyu Gao.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Shen, C., Deng, Y. et al. Camouflaged object detection via boundary refinement. Multimedia Systems 31, 56 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-024-01662-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-024-01662-9